Prediction of S-glutathionylation sites based on protein sequences - PubMed (original) (raw)
Prediction of S-glutathionylation sites based on protein sequences
Chenglei Sun et al. PLoS One. 2013.
Abstract
S-glutathionylation, the reversible formation of mixed disulfides between glutathione(GSH) and cysteine residues in proteins, is a specific form of post-translational modification that plays important roles in various biological processes, including signal transduction, redox homeostasis, and metabolism inside cells. Experimentally identifying S-glutathionylation sites is labor-intensive and time consuming, whereas bioinformatics methods provide an alternative way to this problem by predicting S-glutathionylation sites in silico. The bioinformatics approaches give not only candidate sites for further experimental verification but also bio-chemical insights into the mechanism of S-glutathionylation. In this paper, we firstly collect experimentally determined S-glutathionylated proteins and their corresponding modification sites from the literature, and then propose a new method for predicting S-glutathionylation sites by employing machine learning methods based on protein sequence data. Promising results are obtained by our method with an AUC (area under ROC curve) score of 0.879 in 5-fold cross-validation, which demonstrates the predictive power of our proposed method. The datasets used in this work are available at http://csb.shu.edu.cn/SGDB.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
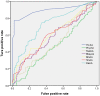
Figure 1. The ROC curves for different classifiers based on different feature extraction approaches.
ThrAA: triplet amino acid composition; Phyche:10 physicochemical properties; RedAA: reduced amino acid composition; Bbayes: Bi-profile Bayes; BinAA: binary encoding amino acid; SinAA: amino acid composition; PaiAA: pair amino acid composition.
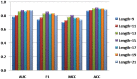
Figure 2. The effects of different window sizes on SVM performance.
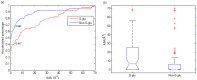
Figure 3. Distributions of thiol ASA values of _S_-glutathionylation cysteine and non-_S_-glutathionylation cysteine.
(a) The points on the curve mean the percentage of the samples that have an ASA  the corresponding ASA value. (b) Box plots of thiol ASA values.
the corresponding ASA value. (b) Box plots of thiol ASA values.
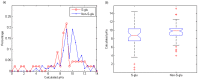
Figure 4. Distributions of thiol pKa values of _S_-glutathionylation cysteine and non-_S_-glutathionylation cysteine.
(a) Thiol pKa value distributions. (b) Box plots of thiol pKa values.
Figure 5. Graphical overview of the method for prediction of protein _S_-glutathionylation sites.
Similar articles
- GSHSite: exploiting an iteratively statistical method to identify s-glutathionylation sites with substrate specificity.
Chen YJ, Lu CT, Huang KY, Wu HY, Chen YJ, Lee TY. Chen YJ, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Apr 7;10(4):e0118752. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118752. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25849935 Free PMC article. - A novel approach for predicting protein S-glutathionylation.
Anashkina AA, Poluektov YM, Dmitriev VA, Kuznetsov EN, Mitkevich VA, Makarov AA, Petrushanko IY. Anashkina AA, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Sep 14;21(Suppl 11):282. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03571-w. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32921310 Free PMC article. - Identification of S-glutathionylation sites in species-specific proteins by incorporating five sequence-derived features into the general pseudo-amino acid composition.
Zhao X, Ning Q, Ai M, Chai H, Yang G. Zhao X, et al. J Theor Biol. 2016 Jun 7;398:96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2016.03.030. Epub 2016 Mar 26. J Theor Biol. 2016. PMID: 27025952 - Assessment of glutathione/glutathione disulphide ratio and S-glutathionylated proteins in human blood, solid tissues, and cultured cells.
Giustarini D, Colombo G, Garavaglia ML, Astori E, Portinaro NM, Reggiani F, Badalamenti S, Aloisi AM, Santucci A, Rossi R, Milzani A, Dalle-Donne I. Giustarini D, et al. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Nov;112:360-375. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.08.008. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28807817 Review. - Role of Glutathionylation in Infection and Inflammation.
Checconi P, Limongi D, Baldelli S, Ciriolo MR, Nencioni L, Palamara AT. Checconi P, et al. Nutrients. 2019 Aug 20;11(8):1952. doi: 10.3390/nu11081952. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31434242 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Dysregulation of the glutaredoxin/_S-_glutathionylation redox axis in lung diseases.
Chia SB, Elko EA, Aboushousha R, Manuel AM, van de Wetering C, Druso JE, van der Velden J, Seward DJ, Anathy V, Irvin CG, Lam YW, van der Vliet A, Janssen-Heininger YMW. Chia SB, et al. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Feb 1;318(2):C304-C327. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00410.2019. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31693398 Free PMC article. - Protein glutathionylation in cardiovascular diseases.
Pastore A, Piemonte F. Pastore A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Oct 17;14(10):20845-76. doi: 10.3390/ijms141020845. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24141185 Free PMC article. Review. - Structural and biochemical investigation into stable FGF2 mutants with novel mutation sites and hydrophobic replacements for surface-exposed cysteines.
An YJ, Jung YE, Lee KW, Kaushal P, Ko IY, Shin SM, Ji S, Yu W, Lee C, Lee WK, Cha K, Lee JH, Cha SS, Yim HS. An YJ, et al. PLoS One. 2024 Sep 5;19(9):e0307499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307499. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39236042 Free PMC article. - Profiling the Site of Protein CoAlation and Coenzyme A Stabilization Interactions.
Tossounian MA, Baczynska M, Dalton W, Newell C, Ma Y, Das S, Semelak JA, Estrin DA, Filonenko V, Trujillo M, Peak-Chew SY, Skehel M, Fraternali F, Orengo C, Gout I. Tossounian MA, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 14;11(7):1362. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071362. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883853 Free PMC article. - GSHSite: exploiting an iteratively statistical method to identify s-glutathionylation sites with substrate specificity.
Chen YJ, Lu CT, Huang KY, Wu HY, Chen YJ, Lee TY. Chen YJ, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Apr 7;10(4):e0118752. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118752. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25849935 Free PMC article.
References
- Dalle-Donne I, Milzani A, Gagliano N, Colombo R, Giustarini D, et al. (2008) Molecular mechanisms and potential clinical significance of S-glutathionylation. Antioxid Redox Signal 10(3): 445–473. - PubMed
- Dalle-Donne I, Rossi R, Colombo G, Milzani A (2009) Protein S-glutathionylation: a regulatory device from bacteria to humans. Trends Biochem Sci 34(2): 85–96. - PubMed
- Hamnell Y, Lind C, Palmberg C, Bergman T, Cotgreave IA (2005) Determination of site-specificity of S-glutathionylated cellular proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 332: 362–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA155069/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM010185/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM010185-02/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA155069-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources