Circulating tumor cells as a surrogate marker for determining clinical outcome to mFOLFOX chemotherapy in patients with stage III colon cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Circulating tumor cells as a surrogate marker for determining clinical outcome to mFOLFOX chemotherapy in patients with stage III colon cancer
C-Y Lu et al. Br J Cancer. 2013.
Abstract
Background: This study was aimed to detect post-chemotherapeutic circulating tumour cells (CTCs) in stage III colon cancer patients and identify those who were at high risk of relapse.
Methods: We used human telomerase reverse transcriptase, cytokeratin-19, cytokeratin-20, and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) as the biomarkers to detect CTCs in 90 stage III colon cancer patients undergoing curative resection followed by mFOLFOX chemotherapy.
Results: Post-chemotherapeutic relapse occurred in 30 (33.3%) patients. By univariate analysis and multivariate proportional hazards regression analysis, perineural invasion (hazard ratio (HR): 2.752; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.026-7.381), high post-chemotherapeutic serum CEA levels (HR: 2.895; 95% CI: 1.143-7.333) and persistent presence of post-chemotherapeutic CTCs (HR: 6.273; 95% CI: 2.442-16.117) were independent predictors of post-chemotherapeutic relapse. In addition, the persistent presence of post-chemotherapeutic CTCs strongly correlated with reduced disease-free survival and overall survival. Accuracy of detecting relapse in post-chemotherapeutic stage III colon cancer patients by analysing the persistent presence of post-chemotherapeutic CTCs was higher than that by post-chemotherapeutic CEA levels (odds ratio: 50.091 vs 5.211).
Conclusion: The persistent presence of post-chemotherapeutic CTCs is a potential powerful surrogate marker for determining clinical outcome in stage III colon cancer patients receiving adjuvant mFOLFOX chemotherapy.
Figures
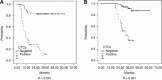
Figure 1
(A) Cumulative disease-free survival (DFS) of 90 stage III colon cancer patients undergoing mFOLFOX chemotherapy according to the post-chemotherapeutic presence of circulating tumour cells (CTCs). Colon cancer patients with positive CTCs in peripheral blood showed a significantly reduced DFS than those without CTCs in the peripheral blood (P<0.001); (B) Cumulative OS of 90 stage III colon cancer patients undergoing mFOLFOX chemotherapy according to the post-chemotherapeutic presence of CTCs. Colon cancer patients with persistent post-chemotherapeutic CTCs in peripheral blood showed a significantly reduced OS than those without CTCs in the peripheral blood (P<0.001).
Similar articles
- Molecular detection of persistent postoperative circulating tumour cells in stages II and III colon cancer patients via multiple blood sampling: prognostic significance of detection for early relapse.
Lu CY, Uen YH, Tsai HL, Chuang SC, Hou MF, Wu DC, Juo SH, Lin SR, Wang JY. Lu CY, et al. Br J Cancer. 2011 Mar 29;104(7):1178-84. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.40. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Br J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21343933 Free PMC article. - Preoperative Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen Level as a Prognostic Factor for Recurrence and Survival After Curative Resection Followed by Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Stage III Colon Cancer.
Kim CG, Ahn JB, Jung M, Beom SH, Heo SJ, Kim JH, Kim YJ, Kim NK, Min BS, Koom WS, Kim H, Roh YH, Ma BG, Shin SJ. Kim CG, et al. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017 Jan;24(1):227-235. doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5613-5. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27699609 - Effect of adjuvant capecitabine or fluorouracil, with or without oxaliplatin, on survival outcomes in stage III colon cancer and the effect of oxaliplatin on post-relapse survival: a pooled analysis of individual patient data from four randomised controlled trials.
Schmoll HJ, Twelves C, Sun W, O'Connell MJ, Cartwright T, McKenna E, Saif M, Lee S, Yothers G, Haller D. Schmoll HJ, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2014 Dec;15(13):1481-1492. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70486-3. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25456367 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Improvement in the Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio after Combined Fluorouracil, Leucovorina and Oxaliplatino based (FOLFOX) Chemotherapy for Stage III Colon Cancer is Associated with Improved Minimal Residual Disease and Outcome.
Murray NP, Villalon R, Hartmann D, Rodriguez PM, Aedo S. Murray NP, et al. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022 Feb 1;23(2):591-599. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.2.591. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022. PMID: 35225472 Free PMC article. - [Adjuvant and palliative anticancer treatment of colon carcinoma in 2004].
Medinger M, Steinbild S, Mross K. Medinger M, et al. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2004 Sep 29;93(40):1633-44. doi: 10.1024/0369-8394.93.40.1633. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2004. PMID: 15495753 Review. German.
Cited by
- KRAS mutations by digital PCR in circulating tumor cells isolated from the mesenteric vein are associated with residual disease and overall survival in resected colorectal cancer patients.
Li Y, Monzo M, Moreno I, Martinez-Rodenas F, Hernandez R, Castellano JJ, Canals J, Han B, Muñoz C, Navarro A. Li Y, et al. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2020 May;35(5):805-813. doi: 10.1007/s00384-020-03538-6. Epub 2020 Feb 22. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2020. PMID: 32088737 - A randomized trial of aerobic exercise in colorectal cancer: Rationale, design, recruitment, and exercise adherence results.
Compton SLE, Yang S, Maniscalco LS, Muhsen RA, Shrestha P, Wu X, Woodard KT, Zunica ERM, Cho E, Wall RL, Brown J, Jayaraman A, Kirby BJ, Gilmore LA, Greenway FL, Spielmann G, Brown JC. Compton SLE, et al. Contemp Clin Trials. 2024 Nov;146:107702. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2024.107702. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Contemp Clin Trials. 2024. PMID: 39362405 Clinical Trial. - Silver Nanoscale Hexagonal Column Chips for Detecting Cell-free DNA and Circulating Nucleosomes in Cancer Patients.
Ito H, Hasegawa K, Hasegawa Y, Nishimaki T, Hosomichi K, Kimura S, Ohba M, Yao H, Onimaru M, Inoue I, Inoue H. Ito H, et al. Sci Rep. 2015 May 21;5:10455. doi: 10.1038/srep10455. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25994878 Free PMC article. - Circulating Tumor Cells Versus Circulating Tumor DNA in Colorectal Cancer: Pros and Cons.
Tan CR, Zhou L, El-Deiry WS. Tan CR, et al. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep. 2016 Jun;12(3):151-161. doi: 10.1007/s11888-016-0320-y. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep. 2016. PMID: 27516729 Free PMC article. - Detection of KRAS Exon 2 Mutations in Circulating Tumor Cells Isolated by the ISET System from Patients with RAS Wild Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer.
Matikas A, Voutsina A, Lagoudaki E, Hatzidaki D, Trypaki M, Stoupis G, Tzardi M, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V. Matikas A, et al. Transl Oncol. 2017 Aug;10(4):693-698. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2017.06.005. Epub 2017 Jul 7. Transl Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28692881 Free PMC article.
References
- Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, Zaninelli M, Clingan P, Bridgewater J, Tabah-Fisch I, de Gramont A. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2343–2351. - PubMed
- Andre T, Boni C, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, Bonetti A, Clingan P, Bridgewater J, Rivera F, de Gramont A. Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or III colon cancer in the MOSAIC trial. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3109–3116. - PubMed
- Ashworth TR. A case of cancer in which cells similar to those in the tumours were seen in the blood after death. Aus Med J. 1869;14:146–149.
- De Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J, Boni C, Cortes-Funes H, Cervantes A, Freyer G, Papamichael D, Le Bail N, Louvet C, Hendler D, de Braud F, Wilson C, Morvan F, Bonetti A. Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2938–2947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources