Twenty-first century mast cell stabilizers - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Twenty-first century mast cell stabilizers
D F Finn et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep.
Abstract
Mast cell stabilizing drugs inhibit the release of allergic mediators from mast cells and are used clinically to prevent allergic reactions to common allergens. Despite the relative success of the most commonly prescribed mast cell stabilizer, disodium cromoglycate, in use for the preventative treatment of bronchial asthma, allergic conjunctivitis and vernal keratoconjunctivitis, there still remains an urgent need to design new substances that are less expensive and require less frequent dosing schedules. In this regard, recent developments towards the discovery of the next generation of mast cell stabilizing drugs has included studies on substances isolated from natural sources, biological, newly synthesized compounds and drugs licensed for other indications. The diversity of natural products evaluated range from simple phenols, alkaloids, terpenes to simple amino acids. While in some cases their precise mode of action remains unknown it has nevertheless sparked interest in the development of synthetic derivatives with improved pharmacological properties. Within the purely synthetic class of inhibitors, particular attention has been devoted to the inhibition of important signalling molecules including spleen TK and JAK3. The statin class of cholesterol-lowering drugs as well as nilotinib, a TK inhibitor, are just some examples of clinically used drugs that have been evaluated for their anti-allergic properties. Here, we examine each approach under investigation, summarize the test data generated and offer suggestions for further preclinical evaluation before their therapeutic potential can be realized.
Keywords: allergy; anti-IgE; disodium cromoglycate; inhibitors; mast cell; mediator release; natural products; sensitization.
© 2013 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
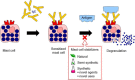
Figure 1
Sources of mast cell stabilizers. Significant data have been published on evaluating the mast cell stabilizing properties of natural products and their semi-synthetic derivatives, despite the fact that in many cases, their precise mechanism of action remains unknown. The data published on purely synthetic mast cell stabilizers have been more focussed on targeting specific events involved in the allergic cascade.
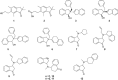
Figure 2
Benzocycloalkan-one (ol)-based mast cell stabilizers. Studies on semi-synthetic based mast cell stabilizers has primarily focussed on the preparation of ‘dimer-like’ compounds of the naturally occurring indanone, pterosin-Z.
Similar articles
- Curine inhibits mast cell-dependent responses in mice.
Ribeiro-Filho J, Leite FC, Costa HF, Calheiros AS, Torres RC, de Azevedo CT, Martins MA, Dias Cda S, Bozza PT, Piuvezam MR. Ribeiro-Filho J, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Sep 11;155(2):1118-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.06.041. Epub 2014 Jun 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24969825 - Mechanisms of antihistamines and mast cell stabilizers in ocular allergic inflammation.
Cook EB, Stahl JL, Barney NP, Graziano FM. Cook EB, et al. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2002 Jun;1(2):167-80. doi: 10.2174/1568010023344733. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2002. PMID: 14561198 Review. - Sensitization of skin mast cells with IgE antibodies to Culicoides allergens occurs frequently in clinically healthy horses.
Wagner B, Miller WH Jr, Erb HN, Lunn DP, Antczak DF. Wagner B, et al. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2009 Nov 15;132(1):53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2009.09.015. Epub 2009 Sep 23. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2009. PMID: 19836083 - Anti-allergic action of anti-malarial drug artesunate in experimental mast cell-mediated anaphylactic models.
Cheng C, Ng DS, Chan TK, Guan SP, Ho WE, Koh AH, Bian JS, Lau HY, Wong WS. Cheng C, et al. Allergy. 2013 Feb;68(2):195-203. doi: 10.1111/all.12077. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Allergy. 2013. PMID: 23253152 - Therapeutic management of allergic diseases.
Watelet JB, Gillard M, Benedetti MS, Lelièvre B, Diquet B. Watelet JB, et al. Drug Metab Rev. 2009;41(3):301-43. doi: 10.1080/10837450902891204. Drug Metab Rev. 2009. PMID: 19601717 Review.
Cited by
- Mast cell stabilizers: from pathogenic roles to targeting therapies.
Cao M, Gao Y. Cao M, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 1;15:1418897. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1418897. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39148726 Free PMC article. Review. - Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial measuring the effect of a dietetic food on dermatologic scoring and pruritus in dogs with atopic dermatitis.
de Santiago MS, Arribas JLG, Llamas YM, Becvarova I, Meyer H. de Santiago MS, et al. BMC Vet Res. 2021 Nov 19;17(1):354. doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-03063-w. BMC Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 34798876 Free PMC article. - Mast cell stabilizer ketotifen fumarate reverses inflammatory but not neuropathic-induced mechanical pain in mice.
Meloto CB, Ingelmo P, Perez EV, Pitt R, González Cárdenas VH, Mohamed N, Sotocinal SG, Bourassa V, Lima LV, Ribeiro-da-Silva A, Mogil JS, Diatchenko L. Meloto CB, et al. Pain Rep. 2021 Jun 3;6(2):e902. doi: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000000902. eCollection 2021 Jul-Aug. Pain Rep. 2021. PMID: 34104835 Free PMC article. - Amphiphilic Triazine Polymer Derivatives as Antibacterial And Anti-atopic Agents in Mice Model.
Gunasekaran P, Fan M, Kim EY, Shin JH, Lee JE, Son EJ, Kim J, Hwang E, Yim MS, Kim EH, Choi YJ, Lee YH, Chung YH, Kim HN, Ryu EK, Shin SY, Kim EK, Bang JK. Gunasekaran P, et al. Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 22;9(1):15161. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51561-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31641232 Free PMC article. - Flow Cytometry-Based Characterization of Mast Cells in Human Atherosclerosis.
Kritikou E, Depuydt MAC, de Vries MR, Mulder KE, Govaert AM, Smit MD, van Duijn J, Foks AC, Wezel A, Smeets HJ, Slütter B, Quax PHA, Kuiper J, Bot I. Kritikou E, et al. Cells. 2019 Apr 9;8(4):334. doi: 10.3390/cells8040334. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30970663 Free PMC article.
References
- Barlow JW, Walsh JJ. Synthesis and evaluation of 4-amino-3,4-dihydro-2H-naphthalen-1-one derivatives as mast cell stabilising and anti-inflammatory compounds. Eur J Med Chem. 2008;43:2891–2900. - PubMed
- Barlow JW, Walsh JJ. Synthesis and evaluation of dimeric 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-naphthalenylamine and indan-1-ylamine derivatives with mast cell-stabilising and anti-allergic activity. Eur J Med Chem. 2010;45:25–37. - PubMed
- Barlow JW, McHugh AP, Woods O, Walsh JJ. Synthesis of novel mast cell-stabilising and anti-allergic 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthalenols and related compounds. Eur J Med Chem. 2011a;46:1545–1554. - PubMed
- Barlow JW, Zhang T, Woods O, Byrne AJ, Walsh JJ. Novel Mast Cell-Stabilising Amine Derivatives of 3,4 Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one and 6,7,8,9-Tetrahydro-5H-benzo[7]annulen-5-one. Med Chem. 2011b;7:213–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical