Sarcopenia and body mass index predict sunitinib-induced early dose-limiting toxicities in renal cancer patients - PubMed (original) (raw)
Sarcopenia and body mass index predict sunitinib-induced early dose-limiting toxicities in renal cancer patients
O Huillard et al. Br J Cancer. 2013.
Abstract
Background: Little is known on factors predicting sunitinib toxicity. Recently, the condition of low muscle mass, named sarcopenia, was identified as a significant predictor of toxicity in metastatic renal cell cancer (mRCC) patients treated with sorafenib. We investigated whether sarcopenia could predict early dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) occurrence in mRCC patients treated with sunitinib.
Methods: Consecutive mRCC patients treated with sunitinib were retrospectively reviewed. A DLT was defined as any toxicity leading to dose reduction or treatment discontinuation. Body composition was evaluated using CT scan obtained within 1 month before treatment initiation.
Results: Among 61 patients eligible for analysis, 52.5% were sarcopenic and 32.8% had both sarcopenia and a body mass index (BMI)<25 kg m(-2). Eighteen patients (29.5%) experienced a DLT during the first cycle. Sarcopenic patients with a BMI<25 kg m(-2) experienced more DLTs (P=0.01; odds ratio=4.1; 95% CI: (1.3-13.3)), more cumulative grade 2 or 3 toxicities (P=0.008), more grade 3 toxicities (P=0.04) and more acute vascular toxicities (P=0.009).
Conclusion: Patients with sarcopenia and a BMI<25 kg m(-2) experienced significantly more DLTs during the first cycle of treatment.
Figures
Figure 1
Patients selection for analysis.
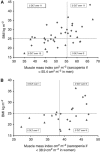
Figure 2
Distribution of BMI, muscle index and early DLT. (A) Distribution of BMI, muscle index and early DLT for men. Symbols represent individual patients, filled triangles represent patients with early DLT. (B) Distribution of BMI, muscle index and early DLT for women. Symbols represent individual patients, filled triangles represent patients with early DLT.
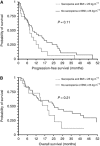
Figure 3
Progression-free survival and overall survival. (A) Progression-free survival in sarcopenic patients with low BMI compared with remaining patients. (B) Overall survival in sarcopenic patients with low BMI compared with remaining patients.
References
- Antoun S, Baracos VE, Birdsell L, Escudier B, Sawyer MB. Low body mass index and sarcopenia associated with dose-limiting toxicity of sorafenib in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2010a;21 (8:1594–1598. - PubMed
- Antoun S, Birdsell L, Sawyer MB, Venner P, Escudier B, Baracos VE. Association of skeletal muscle wasting with treatment with sorafenib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: results from a placebo-controlled study. J Clin Oncol. 2010b;28 (6:1054–1060. - PubMed
- Barrios CH, Hernandez-Barajas D, Brown MP, Lee SH, Fein L, Liu JH, Hariharan S, Martell BA, Yuan J, Bello A, Wang Z, Mundayat R, Rha SY. Phase II trial of continuous once-daily dosing of sunitinib as first-line treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2012;118 (5:1252–1259. - PubMed
- Chow LQ, Eckhardt SG. Sunitinib: from rational design to clinical efficacy. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25 (7:884–896. - PubMed
- Cosqueric G, Sebag A, Ducolombier C, Thomas C, Piette F, Weill-Engerer S. Sarcopenia is predictive of nosocomial infection in care of the elderly. Br J Nutr. 2006;96 (5:895–901. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical