Exosomes as intercellular signaling organelles involved in health and disease: basic science and clinical applications - PubMed (original) (raw)
Exosomes as intercellular signaling organelles involved in health and disease: basic science and clinical applications
Chiara Corrado et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2013.
Abstract
Cell to cell communication is essential for the coordination and proper organization of different cell types in multicellular systems. Cells exchange information through a multitude of mechanisms such as secreted growth factors and chemokines, small molecules (peptides, ions, bioactive lipids and nucleotides), cell-cell contact and the secretion of extracellular matrix components. Over the last few years, however, a considerable amount of experimental evidence has demonstrated the occurrence of a sophisticated method of cell communication based on the release of specialized membranous nano-sized vesicles termed exosomes. Exosome biogenesis involves the endosomal compartment, the multivesicular bodies (MVB), which contain internal vesicles packed with an extraordinary set of molecules including enzymes, cytokines, nucleic acids and different bioactive compounds. In response to stimuli, MVB fuse with the plasma membrane and vesicles are released in the extracellular space where they can interact with neighboring cells and directly induce a signaling pathway or affect the cellular phenotype through the transfer of new receptors or even genetic material. This review will focus on exosomes as intercellular signaling organelles involved in a number of physiological as well as pathological processes and their potential use in clinical diagnostics and therapeutics.
Figures
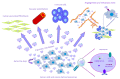
Figure 1
Schematic representation of exosome-mediated crosstalk. Tumor and normal stroma cells communicate through exosomes to establish a favourable tumor microenvironment and promote cancer growth, invasion and metastasis. Exosomes contain soluble factors, mRNA and miRNAs that may affect the phenotypes of different cytotypes such as fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and immune cells.
Similar articles
- Do plant cells secrete exosomes derived from multivesicular bodies?
An Q, van Bel AJ, Hückelhoven R. An Q, et al. Plant Signal Behav. 2007 Jan;2(1):4-7. doi: 10.4161/psb.2.1.3596. Plant Signal Behav. 2007. PMID: 19704795 Free PMC article. - To be or not to be... secreted as exosomes, a balance finely tuned by the mechanisms of biogenesis.
Palmulli R, van Niel G. Palmulli R, et al. Essays Biochem. 2018 May 15;62(2):177-191. doi: 10.1042/EBC20170076. Print 2018 May 15. Essays Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29717057 Review. - The Small GTPase Ral orchestrates MVB biogenesis and exosome secretion.
Hyenne V, Labouesse M, Goetz JG. Hyenne V, et al. Small GTPases. 2018 Nov 2;9(6):445-451. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1251378. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Small GTPases. 2018. PMID: 27875100 Free PMC article. - The biogenesis and functions of exosomes.
Stoorvogel W, Kleijmeer MJ, Geuze HJ, Raposo G. Stoorvogel W, et al. Traffic. 2002 May;3(5):321-30. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2002.30502.x. Traffic. 2002. PMID: 11967126 Review. - Exosomes--vesicular carriers for intercellular communication.
Simons M, Raposo G. Simons M, et al. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009 Aug;21(4):575-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.007. Epub 2009 May 11. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19442504 Review.
Cited by
- Complement in Tumourigenesis and the Response to Cancer Therapy.
O'Brien RM, Cannon A, Reynolds JV, Lysaght J, Lynam-Lennon N. O'Brien RM, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 10;13(6):1209. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061209. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33802004 Free PMC article. Review. - Research trends and hotspots in prostate cancer associated exosome: a bibliometric analysis.
Zhu Z, Zhou Y, Li H, Xu W, Wang T, Liu J, Jiang H. Zhu Z, et al. Front Oncol. 2023 Nov 21;13:1270104. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1270104. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38090502 Free PMC article. - Drug Value of Drynariae Rhizoma Root-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Neurodegenerative Diseases Based on Proteomics and Bioinformatics.
Cao Y, Zhao Q, Liu F, Zheng L, Lin X, Pan M, Tan X, Sun G, Zhao K. Cao Y, et al. Plant Signal Behav. 2022 Dec 31;17(1):2129290. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2022.2129290. Plant Signal Behav. 2022. PMID: 36196516 Free PMC article. - Towards Microfluidic-Based Exosome Isolation and Detection for Tumor Therapy.
Wang J, Ma P, Kim DH, Liu BF, Demirci U. Wang J, et al. Nano Today. 2021 Apr;37:101066. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2020.101066. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Nano Today. 2021. PMID: 33777166 Free PMC article. - Viscosity of Plasma as a Key Factor in Assessment of Extracellular Vesicles by Light Scattering.
Božič D, Sitar S, Junkar I, Štukelj R, Pajnič M, Žagar E, Kralj-Iglič V, Kogej K. Božič D, et al. Cells. 2019 Sep 6;8(9):1046. doi: 10.3390/cells8091046. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31500151 Free PMC article.
References
- Alessandro R., Kohn E.C. Signal transduction targets in invasion. Clin. Exp. Metastasis. 2002;19:265–273. - PubMed
- Simons M., Raposo G. Exosomes—Vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009;21:575–581. - PubMed
- Mathivanan S., Ji H., Simpson R.J. Exosomes: Extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J. Proteomics. 2010;73:1907–1920. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources