Intravaginal live attenuated Salmonella increase local antitumor vaccine-specific CD8+ T cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Intravaginal live attenuated Salmonella increase local antitumor vaccine-specific CD8+ T cells
Loane Decrausaz et al. Oncoimmunology. 2013.
Abstract
We have recently reported that the intravaginal instillation of synthetic Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) or TLR9 agonists after a subcutaneous vaccination against human papillomavirus E7 highly increases (~5-fold) the number of vaccine-specific CD8+ T cells in the genital mucosa of mice, without affecting E7-specific systemic responses. Here, we show that the instillation of live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium similarly, though more efficiently (~15- fold), increases both E7-specific and total CD8+ T cells in the genital mucosa. Cancer immunotherapeutic strategies combining vaccination with local immunostimulation with live bacteria deserve further investigations.
Keywords: CD8+ T cells; bacterial immunostimulant; genital mucosa; human papillomavirus; vaccination.
Figures
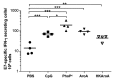
Figure 1. IVAG PhoPc or AroA bacteria administered after E7 immunization increased E7-specific effector CD8+ T cells in the cervix-vagina. Groups of mice were s.c. immunized with 50 μg E71–98 + 10 μg CpG + 0.4 μg Escherichia coli heat labile toxin (E7 vaccine) and 5 days later instilled in vagina with PBS, 100 μg CpG, ~5x 108 CFU of PhoPc, AroA or heat-killed (HK) AroA bacteria. Mice were sacrificed three days later and cells recovered from the cervix-vagina were analyzed by ex vivo IFNγ ELISPOT as previously described. The numbers of E749–57 specific IFNγ-secreting cells/105 cells are indicated. Horizontal bars represent mean responses. Significant differences are indicated by *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 following one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post test (GraphPad Prism 5).
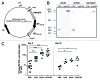
Figure 2. Bacterial expression of E7 modestly influenced the fold-increase of E7-specific CD8+ T cells in the cervix-vagina upon intravaginal instillation. (A) The plasmid pFSnsd-kan3-mtHsp70HPV16E7Δ21–26E6Δ118−122 contains within the _Nco_I and _Hind_III restrictions sites, instead of L1S, a sequence encompassing the full lenght Mycobacterium tuberculosis (mt) heat-shock protein 70 (Hsp70) open reading frame (ORF) fused to the E7 ORF deleted from residues 21 to 26 and the E6 ORF deleted from residues 118–122. (B). Expression of the fusion protein (~100 KDa) in PhoPc bacterial lysates (lane HspE7E6) is detected with polyclonal anti-E7 and anti-E6 antibodies (kindly provided by Dr. John Schiller, NCI, Bethesda, USA) as well as with a monoclonal anti-mtHsp70 antibody (HyTest Ltd, Turku, Finland). For comparison, E7 and E6 only are detected in bacterial lysates from PhoPc cells expressing an E7-E6 fusion without Hsp70 (~32 KDa). (C) Mice s.c. immunized with the adjuvanted E7 vaccine and receiving 5 d later intravaginal PBS, CpG, PhoPc or PhoPcE7 cells were sacrificed at day 9 (left) or at day 15 (right) and cells recovered from cervix-vagina were analyzed by ex vivo IFNγ ELISPOT. The numbers of E749–57- specific IFNγ-secreting cells/105 cells are indicated. Horizontal bars represent mean responses. Significant differences are indicated by *p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.001 following one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post test (GraphPad Prism 5).
Similar articles
- Carboplatin/paclitaxel, E7-vaccination and intravaginal CpG as tri-therapy towards efficient regression of genital HPV16 tumors.
Domingos-Pereira S, Galliverti G, Hanahan D, Nardelli-Haefliger D. Domingos-Pereira S, et al. J Immunother Cancer. 2019 May 6;7(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0593-1. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31060612 Free PMC article. - Local Salmonella immunostimulation recruits vaccine-specific CD8 T cells and increases regression of bladder tumor.
Domingos-Pereira S, Hojeij R, Reggi E, Derré L, Chevalier MF, Romero P, Jichlinski P, Nardelli-Haefliger D. Domingos-Pereira S, et al. Oncoimmunology. 2015 May 22;4(7):e1016697. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1016697. eCollection 2015 Jul. Oncoimmunology. 2015. PMID: 26140240 Free PMC article. - Local HPV Recombinant Vaccinia Boost Following Priming with an HPV DNA Vaccine Enhances Local HPV-Specific CD8+ T-cell-Mediated Tumor Control in the Genital Tract.
Sun YY, Peng S, Han L, Qiu J, Song L, Tsai Y, Yang B, Roden RB, Trimble CL, Hung CF, Wu TC. Sun YY, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Feb 1;22(3):657-69. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0234. Epub 2015 Sep 29. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26420854 Free PMC article. - Intravaginal immunization of mice with recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium expressing human papillomavirus type 16 antigens as a potential route of vaccination against cervical cancer.
Echchannaoui H, Bianchi M, Baud D, Bobst M, Stehle JC, Nardelli-Haefliger D. Echchannaoui H, et al. Infect Immun. 2008 May;76(5):1940-51. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01484-07. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18332214 Free PMC article. - Intravaginal and subcutaneous immunization induced vaccine specific CD8 T cells and tumor regression in the bladder.
Domingos-Pereira S, Derré L, Warpelin-Decrausaz L, Haefliger JA, Romero P, Jichlinski P, Nardelli-Haefliger D. Domingos-Pereira S, et al. J Urol. 2014 Mar;191(3):814-22. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.08.009. Epub 2013 Aug 13. J Urol. 2014. PMID: 23954582
Cited by
- Carboplatin/paclitaxel, E7-vaccination and intravaginal CpG as tri-therapy towards efficient regression of genital HPV16 tumors.
Domingos-Pereira S, Galliverti G, Hanahan D, Nardelli-Haefliger D. Domingos-Pereira S, et al. J Immunother Cancer. 2019 May 6;7(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0593-1. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31060612 Free PMC article. - Immunotherapeutic strategies for bladder cancer.
Chevalier MF, Nardelli-Haefliger D, Domingos-Pereira S, Jichlinski P, Derré L. Chevalier MF, et al. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(4):977-81. doi: 10.4161/hv.27621. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 24384699 Free PMC article. - Enhancing immunotherapy outcomes by targeted remodeling of the tumor microenvironment via combined cGAS-STING pathway strategies.
Huang M, Cha Z, Liu R, Lin M, Gafoor NA, Kong T, Ge F, Chen W. Huang M, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 May 16;15:1399926. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1399926. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38817608 Free PMC article. Review. - Tissue-resident memory T cells play a key role in the efficacy of cancer vaccines.
Granier C, Blanc C, Karaki S, Tran T, Roussel H, Tartour E. Granier C, et al. Oncoimmunology. 2017 Aug 8;6(11):e1358841. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1358841. eCollection 2017. Oncoimmunology. 2017. PMID: 29147623 Free PMC article. - Memory Inflation Drives Tissue-Resident Memory CD8+ T Cell Maintenance in the Lung After Intranasal Vaccination With Murine Cytomegalovirus.
Morabito KM, Ruckwardt TJ, Bar-Haim E, Nair D, Moin SM, Redwood AJ, Price DA, Graham BS. Morabito KM, et al. Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 14;9:1861. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01861. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30154789 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials