Neurokinin-1 receptor signalling impacts bone marrow repopulation efficiency - PubMed (original) (raw)
Neurokinin-1 receptor signalling impacts bone marrow repopulation efficiency
Alexandra Berger et al. PLoS One. 2013.
Abstract
Tachykinins are a large group of neuropeptides with both central and peripheral activity. Despite the increasing number of studies reporting a growth supportive effect of tachykinin peptides in various in vitro stem cell systems, it remains unclear whether these findings are applicable in vivo. To determine how neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) deficient hematopoietic stem cells would behave in a normal in vivo environment, we tested their reconstitution efficiency using competitive bone marrow repopulation assays. We show here that bone marrow taken from NK-1R deficient mice (Tacr1(-/-)) showed lineage specific B and T cell engraftment deficits compared to wild-type competitor bone marrow cells, providing evidence for an involvement of NK-1R signalling in adult hematopoiesis. Tachykinin knockout mice lacking the peptides SP and/or HK-1 (Tac1 (-/-), Tac4 (-/-) and Tac1 (-/-)/Tac4 (-/-) mice) repopulated a lethally irradiated wild-type host with similar efficiency as competing wild-type bone marrow. The difference between peptide and receptor deficient mice indicates a paracrine and/or endocrine mechanism of action rather than autocrine signalling, as tachykinin peptides are supplied by the host environment.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
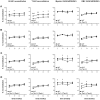
Figure 1. Analysis of the in vivo reconstitution efficiency of tachykinin knockout and wild-type mice.
In vivo reconstitution efficiency for (A) Tacr1 −/− (NK-1R ko mice, n = 10), (B) Tac4 −/− (HK-1 ko mice, n = 8), (C) Tac1 −/− (SP/NKA ko mice, n = 7) and (D) Tac1 −/−/Tac4 −/− (SP/NKA/HK-1 double ko mice, n = 8) versus C57BL/6 mice (n = 10). Each graph shows four time points (8, 16, 24 and 32 weeks) when blood was drawn to assess the donor/host reconstitution efficiency by flow cytometry. Four independent in vivo reconstitution experiments were performed and three to five individual recipient mice per strain were injected in each experiment. The results of the four experiments were pooled. Knockout mouse strains versus wild-type were analyzed at each time point separately using Student's t-test. Time points where knockouts differ significantly from wild-type are indicated and defined as follows: *p = 0.01–0.05, **p = 0.01–0.001 and ***p<0.001.
Similar articles
- Role of tachykinin 1 and 4 gene-derived neuropeptides and the neurokinin 1 receptor in adjuvant-induced chronic arthritis of the mouse.
Borbély E, Hajna Z, Sándor K, Kereskai L, Tóth I, Pintér E, Nagy P, Szolcsányi J, Quinn J, Zimmer A, Stewart J, Paige C, Berger A, Helyes Z. Borbély E, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Apr 23;8(4):e61684. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061684. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23626716 Free PMC article. - Diminished pheromone-induced sexual behavior in neurokinin-1 receptor deficient (TACR1(-/-)) mice.
Berger A, Tran AH, Dida J, Minkin S, Gerard NP, Yeomans J, Paige CJ. Berger A, et al. Genes Brain Behav. 2012 Jul;11(5):568-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2012.00787.x. Epub 2012 Apr 26. Genes Brain Behav. 2012. PMID: 22471406 - Targeted deletion of the tachykinin 4 gene (TAC4-/-) influences the early stages of B lymphocyte development.
Berger A, Benveniste P, Corfe SA, Tran AH, Barbara M, Wakeham A, Mak TW, Iscove NN, Paige CJ. Berger A, et al. Blood. 2010 Nov 11;116(19):3792-801. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-291062. Epub 2010 Jul 26. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20660792 - Tachykinin-mediated modulation of the immune response.
Bost KL. Bost KL. Front Biosci. 2004 Sep 1;9:3331-2. doi: 10.2741/1484. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 15358592 Review. - Hematopoietic modulation by the tachykinins.
Rameshwar P, Gascón P. Rameshwar P, et al. Acta Haematol. 1997;98(2):59-64. doi: 10.1159/000203593. Acta Haematol. 1997. PMID: 9286300 Review.
Cited by
- Neuroimmune/Hematopoietic Axis with Distinct Regulation by the High-Mobility Group Box 1 in Association with Tachykinin Peptides.
Gergues M, Nagula V, Bliss SA, Eljarrah A, Ayer S, Gnanavel N, Sinha G, Wu Q, Yehia G, Greco SJ, Qian J, Rameshwar P. Gergues M, et al. J Immunol. 2020 Feb 15;204(4):879-891. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900582. Epub 2020 Jan 10. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31924647 Free PMC article. - The Regulation of Immunological Processes by Peripheral Neurons in Homeostasis and Disease.
Ordovas-Montanes J, Rakoff-Nahoum S, Huang S, Riol-Blanco L, Barreiro O, von Andrian UH. Ordovas-Montanes J, et al. Trends Immunol. 2015 Oct;36(10):578-604. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2015.08.007. Trends Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26431937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Berger A, Paige CJ (2005) Hemokinin-1 has Substance P-like function in U-251 MG astrocytoma cells: a pharmacological and functional study. J Neuroimmunol 164: 48–56. - PubMed
- Morteau O, Lu B, Gerard C, Gerard NP (2001) Hemokinin 1 is a full agonist at the substance P receptor. Nature Immunology 2: 1088. - PubMed
- Patacchini R, Maggi CA (2001) Peripheral tachykinin receptors as targets for new drugs. European Journal of Pharmacology 429: 13–21. - PubMed
- Benveniste P, Cantin C, Hyam D, Iscove NN (2003) Hematopoietic stem cells engraft in mice with absolute efficiency. Nat Immunol 4: 708–713. - PubMed
- Benveniste P, Frelin C, Janmohamed S, Barbara M, Herrington R, et al. (2010) Intermediate-term hematopoietic stem cells with extended but time-limited reconstitution potential. Cell Stem Cell 6: 48–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous