Application and interpretation of current autophagy inhibitors and activators - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Application and interpretation of current autophagy inhibitors and activators
Ya-ping Yang et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013 May.
Abstract
Autophagy is the major intracellular degradation system, by which cytoplasmic materials are delivered to and degraded in the lysosome. As a quality control mechanism for cytoplasmic proteins and organelles, autophagy plays important roles in a variety of human diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes and infectious and inflammatory diseases. The discovery of ATG genes and the dissection of the signaling pathways involved in regulating autophagy have greatly enriched our knowledge on the occurrence and development of this lysosomal degradation pathway. In addition to its role in degradation, autophagy may also promote a type of programmed cell death that is different from apoptosis, termed type II programmed cell death. Owing to the dual roles of autophagy in cell death and the specificity of diseases, the exact mechanisms of autophagy in various diseases require more investigation. The application of autophagy inhibitors and activators will help us understand the regulation of autophagy in human diseases, and provide insight into the use of autophagy-targeted drugs. In this review, we summarize the latest research on autophagy inhibitors and activators and discuss the possibility of their application in human disease therapy.
Figures
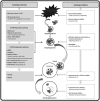
Figure 1
Pharmacological targeting of control points in the autophagic pathway. EBSS, Earle's Balanced Salt Solution; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; SMER, small molecule enhancers of rapamycin; IMPase, inositol monophosphatase; IP3R, inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate receptor; HDAC6, histone deacetylase 6; 3-MA, 3-methyladenine; ATG, autophagy-specific gene.
Similar articles
- Autophagy: A Druggable Process.
Morel E, Mehrpour M, Botti J, Dupont N, Hamaï A, Nascimbeni AC, Codogno P. Morel E, et al. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017 Jan 6;57:375-398. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010716-104936. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28061686 Review. - Therapeutic Targeting of Autophagy.
Towers CG, Thorburn A. Towers CG, et al. EBioMedicine. 2016 Dec;14:15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.10.034. Epub 2016 Oct 23. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 28029600 Free PMC article. Review. - Autophagy in ageing and ageing-associated diseases.
He LQ, Lu JH, Yue ZY. He LQ, et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013 May;34(5):605-11. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.188. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013. PMID: 23416930 Free PMC article. Review. - Targeting autophagy using saponins as a therapeutic and preventive strategy against human diseases.
Han B, He C. Han B, et al. Pharmacol Res. 2021 Apr;166:105428. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105428. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33540047 Review. - Targeting selective autophagy and beyond: From underlying mechanisms to potential therapies.
Ma W, Lu Y, Jin X, Lin N, Zhang L, Song Y. Ma W, et al. J Adv Res. 2024 Nov;65:297-327. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.05.009. Epub 2024 May 14. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 38750694 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Understanding the autophagic functions in cancer stem cell maintenance and therapy resistance.
Niharika, Garg M. Niharika, et al. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024 Oct 8;26:e23. doi: 10.1017/erm.2024.23. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39375840 Free PMC article. Review. - Autophagy Alters the Susceptibility of Candida albicans Biofilms to Antifungal Agents.
Shen J, Ma M, Duan W, Huang Y, Shi B, Wu Q, Wei X. Shen J, et al. Microorganisms. 2023 Aug 5;11(8):2015. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11082015. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37630575 Free PMC article. - FGF2 Is Protective Towards Cisplatin-Induced KGN Cell Toxicity by Promoting FTO Expression and Autophagy.
Wang R, Wang L, Wang L, Cui Z, Cheng F, Wang W, Yang X. Wang R, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 16;13:890623. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.890623. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35784556 Free PMC article. - Autophagy Modulation in Cancer: Current Knowledge on Action and Therapy.
Marinković M, Šprung M, Buljubašić M, Novak I. Marinković M, et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Jan 31;2018:8023821. doi: 10.1155/2018/8023821. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29643976 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Yang YP, Liang ZQ, Gu ZL, Qin ZH. Molecular mechanism and regulation of autophagy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005;26:1421–34. - PubMed
- Meijer AJ, Codogno P. Autophagy: regulation and role in disease. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2009;46:210–40. - PubMed
- Klionsky DJ, Cregg JM, Dunn WA, Jr, Emr SD, Sakai Y, Sandoval IV, et al. A unified nomenclature for yeast autophagy-related genes. Dev Cell. 2003;5:539–45. - PubMed
- Ohsumi Y. Molecular dissection of autophagy: two ubiquitin-like systems. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:211–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials