Results of a follow-up study to the randomized Alzheimer's Disease Anti-inflammatory Prevention Trial (ADAPT) - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
Results of a follow-up study to the randomized Alzheimer's Disease Anti-inflammatory Prevention Trial (ADAPT)
Alzheimer's Disease Anti-inflammatory Prevention Trial Research Group. Alzheimers Dement. 2013 Nov.
Abstract
Objectives: The Alzheimer's Disease Anti-inflammatory Prevention Trial Follow-up Study (ADAPT-FS) was designed to evaluate the efficacy of naproxen and celecoxib for the primary prevention of Alzheimer's disease (AD) several years after cessation of treatment in ADAPT.
Methods: ADAPT was a randomized, double-masked, multicenter clinical trial of naproxen or celecoxib vs placebo (1:1:1.5 assignment ratio) at six U.S.-based clinics. The trial enrolled 2528 people between 2001 and 2004. Treatments were discontinued in December 2004 and participants were monitored regularly until 2007. In 2010 and 2011, ADAPT-FS screened 1537 participants by telephone and, if indicated, examined them in person using standardized clinical assessments. The primary outcome was time to diagnosis of AD. Death index searches were performed for participants not located.
Results: Eighty-nine additional AD events were identified (24 celecoxib, 25 naproxen, and 40 placebo) yielding a total of 161 events (48 [6.6% of randomized participants] celecoxib, 43 [6.0%] naproxen, and 70 [6.5%] placebo) across ADAPT and ADAPT-FS. Adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) comparing each treatment with placebo showed no overall reduction in risk of AD: HR celecoxib vs placebo, 1.03 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.72-1.50; P = .86); HR naproxen vs placebo, 0.92 (95% CI, 0.62-1.35; P = .66). There were 349 deaths (110 [15.2%] celecoxib, 96 [13.4%] naproxen, and 143 [13.2%] placebo). Risk of death was similar for the naproxen- and placebo-assigned groups (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.76-1.28; P = .93) and slightly higher for celecoxib compared with the placebo-assigned group (HR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.90-1.48; P = .27).
Conclusions: These results acquired during a follow-up of approximately 7 years (which included a median of less than 1.5 years of treatment) do not support the hypothesis that celecoxib or naproxen prevent AD in adults with a family history of dementia.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Celecoxib; Clinical trial; Naproxen; Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug; Prevention.
Copyright © 2013 The Alzheimer's Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
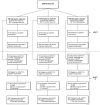
Fig. 1
Participant flow in the Alzheimer's Disease Anti-inflammatory Prevention Trial (ADAPT) and the Alzheimer's Disease Anti-inflammatory Prevention Trial Follow-up Study (ADAPT-FS). *Numbers available only for those randomized, not those screened for eligibility. †Participants considered to have terminated study drug if study drug had been started but was no longer issued prior to December 17, 2004. Does not include temporary interruptions. The number of participants who never took the study drug is updated from previous publications. ‡Participants were eligible but did not have an assessment. §Participants' status was considered unknown after final death sweep.
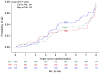
Fig. 2
Cumulative incidence of Alzheimer's disease (AD) over the Alzheimer's Disease Anti-inflammatory Prevention Trial and the Alzheimer's Disease Anti-inflammatory Prevention Trial Follow-up Study. Cel, celecoxib; Plb, placebo; Nap, naproxen.
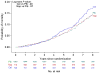
Fig. 3
Cumulative incidence of death the Alzheimer's Disease Anti-inflammatory Prevention Trial and the Alzheimer's Disease Anti-inflammatory PreventionTrial Follow-up Study. Cel, celecoxib; Plb, placebo; Nap, naproxen.
Similar articles
- Cognitive function over time in the Alzheimer's Disease Anti-inflammatory Prevention Trial (ADAPT): results of a randomized, controlled trial of naproxen and celecoxib.
ADAPT Research Group; Martin BK, Szekely C, Brandt J, Piantadosi S, Breitner JC, Craft S, Evans D, Green R, Mullan M. ADAPT Research Group, et al. Arch Neurol. 2008 Jul;65(7):896-905. doi: 10.1001/archneur.2008.65.7.nct70006. Epub 2008 May 12. Arch Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18474729 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Extended results of the Alzheimer's disease anti-inflammatory prevention trial.
Breitner JC, Baker LD, Montine TJ, Meinert CL, Lyketsos CG, Ashe KH, Brandt J, Craft S, Evans DE, Green RC, Ismail MS, Martin BK, Mullan MJ, Sabbagh M, Tariot PN; ADAPT Research Group. Breitner JC, et al. Alzheimers Dement. 2011 Jul;7(4):402-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2010.12.014. Alzheimers Dement. 2011. PMID: 21784351 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Celecoxib or naproxen treatment does not benefit depressive symptoms in persons age 70 and older: findings from a randomized controlled trial.
Fields C, Drye L, Vaidya V, Lyketsos C; ADAPT Research Group. Fields C, et al. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2012 Jun;20(6):505-13. doi: 10.1097/JGP.0b013e318227f4da. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 21775876 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Follow-up evaluation of cognitive function in the randomized Alzheimer's Disease Anti-inflammatory Prevention Trial and its Follow-up Study.
ADAPT-FS Research Group. ADAPT-FS Research Group. Alzheimers Dement. 2015 Feb;11(2):216-25.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2014.03.009. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Alzheimers Dement. 2015. PMID: 25022541 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - NSAIDs and Alzheimer's disease: how far to generalise from trials?
Breitner JC. Breitner JC. Lancet Neurol. 2003 Sep;2(9):527. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(03)00498-8. Lancet Neurol. 2003. PMID: 12941571 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Three midlife strategies to prevent cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease.
Henderson VW. Henderson VW. Climacteric. 2014 Dec;17 Suppl 2(0 2):38-46. doi: 10.3109/13697137.2014.929650. Epub 2014 Aug 17. Climacteric. 2014. PMID: 24893836 Free PMC article. - The role of the immune system in neurodegenerative disorders: Adaptive or maladaptive?
Doty KR, Guillot-Sestier MV, Town T. Doty KR, et al. Brain Res. 2015 Aug 18;1617:155-73. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.09.008. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25218556 Free PMC article. Review. - Prescription database analyses indicates that the asthma medicine montelukast might protect against dementia: a hypothesis to be verified.
Grinde B, Engdahl B. Grinde B, et al. Immun Ageing. 2017 Aug 31;14:20. doi: 10.1186/s12979-017-0102-7. eCollection 2017. Immun Ageing. 2017. PMID: 28874912 Free PMC article. - Hydrocortisone Mitigates Alzheimer's-Related Cognitive Decline through Modulating Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation.
Li J, Chen L, Liu S, Sun Y, Zhen L, Zhu Z, Wang G, Li X. Li J, et al. Cells. 2023 Sep 25;12(19):2348. doi: 10.3390/cells12192348. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37830561 Free PMC article. - Macrocyclic Immunoproteasome Inhibitors as a Potential Therapy for Alzheimer's Disease.
Lee MJ, Bhattarai D, Jang H, Baek A, Yeo IJ, Lee S, Miller Z, Lee S, Hong JT, Kim DE, Lee W, Kim KB. Lee MJ, et al. J Med Chem. 2021 Aug 12;64(15):10934-10950. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00291. Epub 2021 Jul 26. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34309393 Free PMC article.
References
- Szekely CA, Town T, Zandi PP. NSAIDs for the chemoprevention of Alzheimer's disease. Subcell Biochem. 2007;42:229–48. - PubMed
- Vane JR. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971;231:232–5. - PubMed
- Meade EA, Smith WL, DeWitt DL. Differential inhibition of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase (cyclooxygenase) isozymes by aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:6610–4. - PubMed
- McGeer EG, McGeer PL. Inflammatory processes in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003;27:741–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical