Why do hip arthroscopy procedures fail? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Why do hip arthroscopy procedures fail?
Ljiljana Bogunovic et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013 Aug.
Abstract
Background: Despite the successes of hip arthroscopy, clinical failures do occur, and identifying risk factors for failure may facilitate refinement of surgical indications and treatment. Knowledge regarding the reasons for treatment failures may also improve surgical decision making.
Questions/purposes: We (1) characterized patients whose symptoms recurred after hip arthroscopy necessitating a revision hip preservation procedure or hip arthroplasty, (2) determined the etiologies of failure, (3) and reported the profile of revision surgical procedures.
Methods: In a prospective database of 1724 consecutive hip surgeries, we identified 58 patients (60 hips) with a history of failed hip arthroscopy. Thirty-seven patients (38 hips) underwent revision hip preservation and 21 (22) hip arthroplasty. Thirty-nine (67%) were female. Demographics, etiology of failure, and type of revision surgery were analyzed.
Results: Patients treated with revision hip preservation were younger, had a lower BMI, and lower Tönnis osteoarthritis grade at the time of revision surgery compared to patients treated with hip arthroplasty. Common etiologies of failure were residual femoroacetabular impingement (68%) and acetabular dysplasia (24%) in patients treated with revision hip preservation and advanced osteoarthritis in patients treated with hip arthroplasty. The revision preservation procedures included arthroscopy in 16 (42%), arthroscopy with limited open capsulorraphy in two (5.3%), periacetabular osteotomy in nine (24%), and surgical dislocation in 12 (32%).
Conclusions: Residual or unaddressed structural deformity of the hip and underlying osteoarthritis are commonly associated with failure after hip arthroscopy. Thorough patient evaluation with detailed characterization of structural hip anatomy and articular cartilage integrity are critical to the selection of proper surgical intervention and successful patient outcome.
Figures
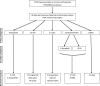
Fig. 1
A flowchart shows preoperative diagnoses and revision procedures after failed hip arthroscopy.
Similar articles
- What Are the Risk Factors for Revision Surgery After Hip Arthroscopy for Femoroacetabular Impingement at 7-year Followup?
Haefeli PC, Albers CE, Steppacher SD, Tannast M, Büchler L. Haefeli PC, et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017 Apr;475(4):1169-1177. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-5115-6. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 27718121 Free PMC article. - One-third of Hips After Periacetabular Osteotomy Survive 30 Years With Good Clinical Results, No Progression of Arthritis, or Conversion to THA.
Lerch TD, Steppacher SD, Liechti EF, Tannast M, Siebenrock KA. Lerch TD, et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017 Apr;475(4):1154-1168. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-5169-5. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 27905061 Free PMC article. - Predictors of Poor Clinical Outcome After Arthroscopic Labral Preservation, Capsular Plication, and Cam Osteoplasty in the Setting of Borderline Hip Dysplasia.
Hatakeyama A, Utsunomiya H, Nishikino S, Kanezaki S, Matsuda DK, Sakai A, Uchida S. Hatakeyama A, et al. Am J Sports Med. 2018 Jan;46(1):135-143. doi: 10.1177/0363546517730583. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Am J Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 28992426 - Why Does Hip Arthroscopy Fail? Indications and PEARLS for Revision Success.
Ross JR, Clohisy JC, Bedi A, Zaltz I. Ross JR, et al. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2021 Mar 1;29(1):44-51. doi: 10.1097/JSA.0000000000000300. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2021. PMID: 33395230 Review. - Revision Hip Arthroscopy Indications and Outcomes: A Systematic Review.
Sardana V, Philippon MJ, de Sa D, Bedi A, Ye L, Simunovic N, Ayeni OR. Sardana V, et al. Arthroscopy. 2015 Oct;31(10):2047-55. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2015.03.039. Epub 2015 May 29. Arthroscopy. 2015. PMID: 26033461 Review.
Cited by
- Functional Outcomes, Complications, and Failure Rates in Workers' Compensation Patients Following Hip Arthroscopic Repair: A Systematic Review.
Munim MA, Samuel LT, Rosneck JT, Kamath AF. Munim MA, et al. HSS J. 2024 Nov;20(4):577-588. doi: 10.1177/15563316231183093. Epub 2023 Jul 17. HSS J. 2024. PMID: 39494433 Review. - Diagnosis and Management of Borderline Hip Dysplasia and Acetabular Retroversion.
Willey M, Holland T, Thomas-Aitken H, Goetz JE. Willey M, et al. J Hip Surg. 2018 Dec;2(4):156-166. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1676307. Epub 2019 Jan 10. J Hip Surg. 2018. PMID: 38544698 Free PMC article. - Can intra-articular hip injections predict arthroscopy outcomes for femoroacetabular impingement syndrome? A systematic review.
Takla A, Gunatilake K, Ma N, Moaveni A. Takla A, et al. J Orthop. 2023 Dec 19;50:122-129. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2023.12.004. eCollection 2024 Apr. J Orthop. 2023. PMID: 38214002 Review. - Comparable Injury to the Indirect Head of the Rectus Femoris During Interportal and Periportal Capsulotomy: A Cadaveric Study.
Patel UJ, Anderson DE, Yen YM, Giordano BD. Patel UJ, et al. Orthop J Sports Med. 2023 Oct 11;11(10):23259671231198246. doi: 10.1177/23259671231198246. eCollection 2023 Oct. Orthop J Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 37840898 Free PMC article. - Hip Capsular Closure in Distraction: A Technique to Allow Easier Closure of T and Interportal Capsulotomies.
Özbek EA, Miller L, James M, Mauro CS. Özbek EA, et al. Arthrosc Tech. 2023 Jul 10;12(8):e1305-e1309. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2023.03.023. eCollection 2023 Aug. Arthrosc Tech. 2023. PMID: 37654878 Free PMC article.
References
- Barnard GA. A new test for 2 × 2 tables. Nature. 1945;156:177. doi: 10.1038/156177a0. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical