Does HPV type affect outcome in oropharyngeal cancer? - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1186/1916-0216-42-9.
Sandeep S Dhaliwal, David A Palma, John Basmaji, Corina Chapeskie, Samuel Dowthwaite, Jason H Franklin, Kevin Fung, Keith Kwan, Brett Wehrli, Chris Howlett, Iram Siddiqui, Marina I Salvadori, Eric Winquist, Scott Ernst, Sara Kuruvilla, Nancy Read, Varagur Venkatesan, Biljana Todorovic, J Alex Hammond, James Koropatnick, Joe S Mymryk, John Yoo, John W Barrett
Affiliations
- PMID: 23663293
- PMCID: PMC3650940
- DOI: 10.1186/1916-0216-42-9
Does HPV type affect outcome in oropharyngeal cancer?
Anthony C Nichols et al. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013.
Abstract
Background: An epidemic of human papillomavirus (HPV)-related oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer (OPSCC) has been reported worldwide largely due to oral infection with HPV type-16, which is responsible for approximately 90% of HPV-positive cases. The purpose of this study was to determine the rate of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer in Southwestern Ontario, Canada.
Methods: A retrospective search identified ninety-five patients diagnosed with OPSCC. Pre-treatment biopsy specimens were tested for p16 expression using immunohistochemistry and for HPV-16, HPV-18 and other high-risk subtypes, including 31,33,35,39,45,51,52,56,58,59,67,68, by real-time qPCR.
Results: Fifty-nine tumours (62%) were positive for p16 expression and fifty (53%) were positive for known high-risk HPV types. Of the latter, 45 tumors (90%) were identified as HPV-16 positive, and five tumors (10%) were positive for other high-risk HPV types (HPV-18 (2), HPV-67 (2), HPV-33 (1)). HPV status by qPCR and p16 expression were extremely tightly correlated (p < 0.001, Fishers exact test). Patients with HPV-positive tumors had improved 3-year overall (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) compared to patients with HPV-negative tumors (90% vs 65%, p = 0.001; and 85% vs 49%, p = 0.005; respectively). HPV-16 related OPSCC presented with cervical metastases more frequently than other high-risk HPV types (p = 0.005) and poorer disease-free survival was observed, although this was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: HPV-16 infection is responsible for a significant proportion of OPSCC in Southwestern Ontario. Other high-risk subtypes are responsible for a smaller subset of OPSCC that present less frequently with cervical metastases and may have a different prognosis.
Figures
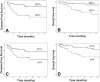
Figure 1
Disease-free and overall survival by HPV status (A and B) and p16 status (C and D).
Figure 2
Disease-free (A) and overall survival (B) for HPV-positive patients stratified by HPV type.
References
- SEER Cancder Statistics Review, 1975–2008. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2011. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2008/
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical