Ligand for translocator protein reverses pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Ligand for translocator protein reverses pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Anna M Barron et al. J Neurosci. 2013.
Abstract
Ligands of the translocator protein (TSPO) elicit pleiotropic neuroprotective effects that represent emerging treatment strategies for several neurodegenerative conditions. To investigate the potential of TSPO as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease (AD), the current study assessed the effects of the TSPO ligand Ro5-4864 on the development of neuropathology in 3xTgAD mice. The effects of the TSPO ligand on neurosteroidogenesis and AD-related neuropathology, including β-amyloid accumulation, gliosis, and behavioral impairment, were examined under both early intervention (7-month-old young-adult male mice with low pathology) and treatment (24-month-old, aged male mice with advanced neuropathology) conditions. Ro5-4864 treatment not only effectively attenuated development of neuropathology and behavioral impairment in young-adult mice but also reversed these indices in aged 3xTgAD mice. Reduced levels of soluble β-amyloid were also observed by the combination of TSPO ligands Ro5-4864 and PK11195 in nontransgenic mice. These findings suggest that TSPO is a promising target for the development of pleiotropic treatment strategies for the management of AD.
Figures
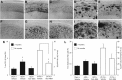
Figure 1.
Ro5-4864 reduces Aβ accumulation in the hippocampus of 3xTgAD mice. A–J, Representative photomicrographs show Aβ immunoreactivity in hippocampus CA1 (A–E) and subiculum (F–J) regions of 7-month-old 3xTgAD mice in the sham + vehicle (A, F), GDX + vehicle (B, G), and GDX + Ro5-4864 (C, H) conditions; and 24-month-old 3xTgAD mice administered vehicle (D, I) and Ro5-4864 (E, J). Data show mean Aβ immunoreactivity loads (±SEM) in 3xTgAD mice at ages 7 months (solid bars, left axis) and 24 months (open bars, right axis) in hippocampus CA1 (K) and subiculum (L). *p < 0.05, compared with all other groups.
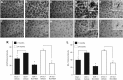
Figure 2.
Ro5-4864 reduces hippocampal gliosis in 3xTgAD mice. A–J, Representative photomicrographs show GFAP (A–E) and IBA-1 (F–J) immunoreactivities in the hippocampus CA1 region of 7-month-old 3xTgAD mice in the sham + vehicle (A, F), GDX + vehicle (B, G), and GDX + Ro5-4864 (C, H) conditions; and 24-month-old 3xTgAD mice administered vehicle (D, I) and Ro5-4864 (E, J). K, GFAP immunoreactivity volume density values (±SEM) in the hippocampus CA1 region. L, IBA-1 immunoreactivity volume density values (±SEM) in the hippocampus CA1 region. #p < 0.001, compared with GDX + vehicle. *p < 0.001, compared with all other groups.
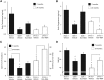
Figure 3.
Ro5-4864 regulates brain testosterone and progesterone levels and improves behavioral deficits in 3xTgAD mice. A, Brain testosterone levels were quantified in limbic structures. Ro5-4864 treatment attenuated GDX-induced testosterone depletion in young-adult 7-month-old mice. B, Brain progesterone levels were quantified in limbic structures. Ro5-4864 treatment increased PROG more than twofold in GDX 7-month-old mice. C, Percentage duration (±SEM) spent exploring the open arm of the EPM, with increased exploration of the open arm indicative of reduced anxiety. D, SAB, represented as percentage alternation (±SEM); both 7-month-old GDX and 24-month-old 3xTgAD mice administered Ro5-4864 exhibited significantly improved SAB performance. #p < 0.05, compared with sham + vehicle. *p < 0.05, compared with all other groups.
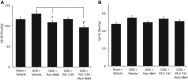
Figure 4.
Ro5-4864 alone or in combination with PK-11195 reduces brain Aβ levels in non-Tg mice. Brain levels of soluble AβX-40 (A) and AβX-42 (B) from hemibrain homogenates were assessed by ELISA in young-adult non-Tg mice treated for 4 weeks with vehicle, Ro5-4864, PK11195, or Ro5-4864 + PK11195. Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.02, compared with GDX + vehicle. ‡p < 0.001, compared with GDX + vehicle.
Similar articles
- TSPO ligand PK11195 improves Alzheimer-related outcomes in aged female 3xTg-AD mice.
Christensen A, Pike CJ. Christensen A, et al. Neurosci Lett. 2018 Sep 14;683:7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.06.029. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Neurosci Lett. 2018. PMID: 29925037 Free PMC article. - Chronic administration of XBD173 ameliorates cognitive deficits and neuropathology via 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO) in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
Pradhan AK, Neumüller T, Klug C, Fuchs S, Schlegel M, Ballmann M, Tartler KJ, Pianos A, Garcia MS, Liere P, Schumacher M, Kreuzer M, Rupprecht R, Rammes G. Pradhan AK, et al. Transl Psychiatry. 2023 Oct 27;13(1):332. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02630-z. Transl Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37891168 Free PMC article. - L-3-n-butylphthalide improves cognitive impairment and reduces amyloid-beta in a transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease.
Peng Y, Sun J, Hon S, Nylander AN, Xia W, Feng Y, Wang X, Lemere CA. Peng Y, et al. J Neurosci. 2010 Jun 16;30(24):8180-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0340-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20554868 Free PMC article. - Effects of CX3CR1 and Fractalkine Chemokines in Amyloid Beta Clearance and p-Tau Accumulation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Rodent Models: Is Fractalkine a Systemic Biomarker for AD?
Merino JJ, Muñetón-Gómez V, Alvárez MI, Toledano-Díaz A. Merino JJ, et al. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(4):403-12. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666151116125714. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26567742 Review. - The translocator protein as a drug target in Alzheimer's disease.
Chua SW, Kassiou M, Ittner LM. Chua SW, et al. Expert Rev Neurother. 2014 Apr;14(4):439-48. doi: 10.1586/14737175.2014.896201. Expert Rev Neurother. 2014. PMID: 24625007 Review.
Cited by
- Calcium regulation of neural rhythms, memory and Alzheimer's disease.
Berridge MJ. Berridge MJ. J Physiol. 2014 Jan 15;592(2):281-93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.257527. Epub 2013 Jun 10. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 23753528 Free PMC article. Review. - Translocator protein (18 kDa) (TSPO) is expressed in reactive retinal microglia and modulates microglial inflammation and phagocytosis.
Karlstetter M, Nothdurfter C, Aslanidis A, Moeller K, Horn F, Scholz R, Neumann H, Weber BH, Rupprecht R, Langmann T. Karlstetter M, et al. J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Jan 8;11:3. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 24397957 Free PMC article. - Microglial activation mediates chronic mild stress-induced depressive- and anxiety-like behavior in adult rats.
Wang YL, Han QQ, Gong WQ, Pan DH, Wang LZ, Hu W, Yang M, Li B, Yu J, Liu Q. Wang YL, et al. J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Jan 17;15(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1054-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29343269 Free PMC article. - Modulation of three key innate immune pathways for the most common retinal degenerative diseases.
Akhtar-Schäfer I, Wang L, Krohne TU, Xu H, Langmann T. Akhtar-Schäfer I, et al. EMBO Mol Med. 2018 Oct;10(10):e8259. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201708259. EMBO Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30224384 Free PMC article. Review. - Neuroinflammation in psychiatric disorders: PET imaging and promising new targets.
Meyer JH, Cervenka S, Kim MJ, Kreisl WC, Henter ID, Innis RB. Meyer JH, et al. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020 Dec;7(12):1064-1074. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30255-8. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 33098761 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Barreto G, Santos-Galindo M, Diz-Chaves Y, Pernía O, Carrero P, Azcoitia I, Garcia-Segura LM. Selective estrogen receptor modulators decrease reactive astrogliosis in the injured brain: effects of aging and prolonged depletion of ovarian hormones. Endocrinology. 2009;150:5010–5015. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0352. - DOI - PubMed
- Caruso D, Scurati S, Maschi O, De Angelis L, Roglio I, Giatti S, Garcia-Segura LM, Melcangi RC. Evaluation of neuroactive steroid levels by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in central and peripheral nervous system: effect of diabetes. Neurochem Int. 2008;52:560–568. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2007.06.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous