Discordant patterns of bacterial translocation markers and implications for innate immune imbalances in schizophrenia - PubMed (original) (raw)
Multicenter Study
Discordant patterns of bacterial translocation markers and implications for innate immune imbalances in schizophrenia
Emily G Severance et al. Schizophr Res. 2013 Aug.
Abstract
The origin of inflammation in psychiatric disorders is not well understood. The translocation of commensal microbiota across the gastrointestinal barrier can result in a persistent state of low-grade immune activation and/or inflammation. We measured serological surrogate markers of bacterial translocation (soluble CD14 (sCD14) and lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP)) in two psychiatric cohorts and compared these levels to C-reactive protein (CRP), body mass index (BMI), and food-related and autoimmune antibodies. The two cohorts were composed of the following: (1) n=141 schizophrenia, n=75 bipolar disorder, n=78 controls; (2) n=78 antipsychotic-naïve first-episode schizophrenia, n=38 medicated first-episode schizophrenia. sCD14 seropositivity conferred a 3.1-fold increased odds of association with schizophrenia (multivariate regressions, OR=3.09, p<0.0001) compared to controls. Case-control differences in sCD14 were not matched by LBP. Quantitative levels of LBP, but not sCD14, correlated with BMI in schizophrenia (R(2)=0.21, p<0.0001). sCD14 and LBP also exhibited some congruency in schizophrenia with both significantly correlated with CRP (R(2)=0.26-0.27, p<0.0001) and elevated in females compared to males (p<0.01). Antipsychotic treatment generally did not impact sCD14 or LBP levels except for significant correlations, especially sCD14, with gluten antibodies in antipsychotic-naïve schizophrenia (R(2)=0.27, p<0.0001). In bipolar disorder, sCD14 levels were significantly correlated with anti-tissue transglutaminase IgG (R(2)=0.37, p<0.001). In conclusion, these bacterial translocation markers produced discordant and complex patterns of activity, a finding that may reflect an imbalanced, activated innate immune state. Whereas both markers may upregulate following systemic exposure to Gram-negative bacteria, non-lipopolysaccharide-based monocyte activation, autoimmunity and metabolic dysfunction may also contribute to the observed marker profiles.
Keywords: BMI; C-reactive protein; CRP; Diet; GI; Gut; LBP; LPS; Macrophage; Mental illness; Metabolic syndrome; Microbiome; Psychosis; body mass index; gastrointestinal; lipopolysaccharide; lipopolysaccharide binding protein; sCD14; soluble CD14; tTG; tissue transglutaminase.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
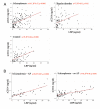
Figure 1
Markers of bacterial translocation, sCD14 and LBP, were inter-correlated. A. sCD14 and LBP marker correlations in cohort 1 based in Baltimore, MD, U.S.A. are shown. Multiple linear regressions included age, gender, race, smoking status, and assay plate designation. B. sCD14 and LBP marker correlations in cohort 2 based in Cologne, Germany, are shown. Multiple linear regressions included age, gender, and assay plate designation. AP refers to antipsychotic. [For color reproduction]
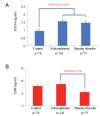
Figure 2
sCD14 and LBP levels in cohort 1 cases compared to controls. A. sCD14 levels were elevated in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder compared to controls. B. LBP levels were not different between cases and controls, but levels in schizophrenia were higher than levels in bipolar disorder. [For color reproduction]
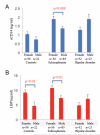
Figure 3
sCD14 and LBP exhibited sex-specific patterns. A. sCD14 levels were elevated in female individuals with schizophrenia compared to males. B. LBP levels were elevated in females compared to males in both the control and schizophrenia groups. [For color reproduction]
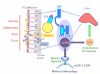
Figure 4
Overview of coordinated activation of sCD14 and LBP during bacterial translocation. Following episodes of increased GI permeability, enteric bacteria may be exposed to the immune cells of the lamina propria and to systemic circulation. LBP interacts directly with the LPS endotoxin of Gram-negative bacteria and transports LPS monomers to sCD14 and CD14 bound to macrophage membranes. sCD14 is manufactured by immune cells of the GI mucosa, whereas LBP is synthesized by GI epithelial cells. Both markers are also produced by the liver (Heumann and Roger, 2002; Kitchens and Thompson, 2005; Miyake, 2004; Sandler and Douek, 2012; Stehle et al., 2012). Dietary gluten may impact components of these pathways and based on our study results is included in a hypothetical role in this diagram. [For color reproduction]
Similar articles
- Monocyte activation detected prior to a diagnosis of schizophrenia in the US Military New Onset Psychosis Project (MNOPP).
Weber NS, Gressitt KL, Cowan DN, Niebuhr DW, Yolken RH, Severance EG. Weber NS, et al. Schizophr Res. 2018 Jul;197:465-469. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2017.12.016. Epub 2018 Jan 6. Schizophr Res. 2018. PMID: 29310912 Free PMC article. - Serum lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and soluble CD14 are markers of disease activity in patients with Crohn's disease.
Lakatos PL, Kiss LS, Palatka K, Altorjay I, Antal-Szalmas P, Palyu E, Udvardy M, Molnar T, Farkas K, Veres G, Harsfalvi J, Papp J, Papp M. Lakatos PL, et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011 Mar;17(3):767-77. doi: 10.1002/ibd.21402. Epub 2010 Sep 23. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011. PMID: 20865702 - Serum Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Protein is Associated with Chronic Inflammation and Metabolic Syndrome in Hemodialysis Patients.
Lim PS, Chang YK, Wu TK. Lim PS, et al. Blood Purif. 2019;47(1-3):28-36. doi: 10.1159/000492778. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Blood Purif. 2019. PMID: 30219816 Clinical Trial. - Biomarkers of intestinal permeability in major psychiatric disorders: Distinct biological roles call for a more nuanced application.
Ioannou M, Borkent J, Severance EG, Yolken RH, Fasano A, Sommer IEC, Haarman BCM. Ioannou M, et al. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2025 Jun 20;139:111405. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2025.111405. Epub 2025 May 26. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40436362 Review. - Modulatory effects of sCD14 and LBP on LPS-host cell interactions.
Kitchens RL, Thompson PA. Kitchens RL, et al. J Endotoxin Res. 2005;11(4):225-9. doi: 10.1179/096805105X46565. J Endotoxin Res. 2005. PMID: 16176659 Review.
Cited by
- Candida albicans exposures, sex specificity and cognitive deficits in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Severance EG, Gressitt KL, Stallings CR, Katsafanas E, Schweinfurth LA, Savage CL, Adamos MB, Sweeney KM, Origoni AE, Khushalani S, Leweke FM, Dickerson FB, Yolken RH. Severance EG, et al. NPJ Schizophr. 2016 May 4;2:16018. doi: 10.1038/npjschz.2016.18. eCollection 2016. NPJ Schizophr. 2016. PMID: 27336058 Free PMC article. - The Gut Microbiota and the Emergence of Autoimmunity: Relevance to Major Psychiatric Disorders.
Severance EG, Tveiten D, Lindström LH, Yolken RH, Reichelt KL. Severance EG, et al. Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(40):6076-6086. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666160914183804. Curr Pharm Des. 2016. PMID: 27634185 Free PMC article. Review. - Association between gut permeability, brain volume, and cognition in healthy participants and patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorder.
Scheurink TAW, Borkent J, Gangadin SS, El Aidy S, Mandl R, Sommer IEC. Scheurink TAW, et al. Brain Behav. 2023 Jun;13(6):e3011. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3011. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 37095714 Free PMC article. - Hidden Role of Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis in Schizophrenia: Antipsychotics or Psychobiotics as Therapeutics?
Munawar N, Ahsan K, Muhammad K, Ahmad A, Anwar MA, Shah I, Al Ameri AK, Al Mughairbi F. Munawar N, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 18;22(14):7671. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147671. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299291 Free PMC article. Review. - Cerebrospinal fluid microglia and neurodegenerative markers in twins concordant and discordant for psychotic disorders.
Johansson V, Jakobsson J, Fortgang RG, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Cannon TD, Hultman CM, Wetterberg L, Landén M. Johansson V, et al. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017 Aug;267(5):391-402. doi: 10.1007/s00406-016-0759-5. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28039552 Free PMC article.
References
- Berg AH, Scherer PE. Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2005;96(9):939–949. - PubMed
- Beumer W, Drexhage RC, De Wit H, Versnel MA, Drexhage HA, Cohen D. Increased level of serum cytokines, chemokines and adipokines in patients with schizophrenia is associated with disease and metabolic syndrome. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2012a;37(12):1901–1911. - PubMed
- Beumer W, Gibney SM, Drexhage RC, Pont-Lezica L, Doorduin J, Klein HC, Steiner J, Connor TJ, Harkin A, Versnel MA, Drexhage HA. The immune theory of psychiatric diseases: a key role for activated microglia and circulating monocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 2012b;92(5):959–975. - PubMed
- Brenchley JM, Price DA, Schacker TW, Asher TE, Silvestri G, Rao S, Kazzaz Z, Bornstein E, Lambotte O, Altmann D, Blazar BR, Rodriguez B, Teixeira-Johnson L, Landay A, Martin JN, Hecht FM, Picker LJ, Lederman MM, Deeks SG, Douek DC. Microbial translocation is a cause of systemic immune activation in chronic HIV infection. Nat Med. 2006;12(12):1365–1371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous