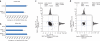Integrated proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications by serial enrichment - PubMed (original) (raw)
Integrated proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications by serial enrichment
Philipp Mertins et al. Nat Methods. 2013 Jul.
Abstract
We report a mass spectrometry-based method for the integrated analysis of protein expression, phosphorylation, ubiquitination and acetylation by serial enrichments of different post-translational modifications (SEPTM) from the same biological sample. This technology enabled quantitative analysis of nearly 8,000 proteins and more than 20,000 phosphorylation, 15,000 ubiquitination and 3,000 acetylation sites per experiment, generating a holistic view of cellular signal transduction pathways as exemplified by analysis of bortezomib-treated human leukemia cells.
Figures
Figure 1
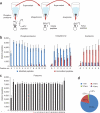
SEPTM enables deep, quantitative analysis of the PTM-ome of a biological sample. (a) Integrated proteome and PTM-ome profiling by sequential enrichment for phosphorylated peptides with IMAC, for ubiquitinated peptides with K(GG)-specific antibodies and for lysine-acetylated peptides with K(Ac)-specific antibodies. (b) Ideal and even partitioning of phosphorylated, ubiquitinated and acetylated peptides by basic RP fractionation. The specificity of each enrichment step (distinct modified peptides out of total peptides) was >93% for phosphopeptides, >71% for ubiquitinated peptides and >18% for acetylated peptides. (c) We used 5% of the starting samples for whole-proteome analysis; basic RP separation yielded even partitioning of unmodified peptides. Average numbers of PTM sites (b) and proteins (c) per replicate are shown with s.d. error bars. (d) Uniqueness and occurrence of unmodified peptides per fraction (fxn).
Figure 2
Comparison of nonserial to serial enrichments for K(GG) and K(Ac) enrichments. (a,b) Comparison of the number of identified K(GG) (a) and K(Ac) (b) sites. Label-free, tryptic HeLa peptides (2.5 mg) were either singly or doubly enriched for the indicated PTM enrichments. Each identified modification-site value is that of the last PTM enriched in the sample. s.d. error bars were calculated for three process replicates. (c,d) SILAC ratio comparisons of doubly versus singly K(GG)-enriched (c) or K(Ac)-enriched (d) samples. SILAC heavy (H)- and light (L)-labeled HeLa peptides (2.5 mg) were subjected to either one or two rounds of differential PTM enrichment (as indicated). log2 SILAC ratios of replicates 1 and 2 are visualized as scatter plots and associated histograms. We used a moderated _t_-test (P < 0.05) to detect any statistically significant up- or downregulated sites among 2,131 K(GG) sites (c) and 193 K(Ac)-sites (d). Only one data point had a P <0.05; this is colored red in the scatter plot. The second replicates were performed with an inverted SILAC labeling strategy.
Comment in
- Eavesdropping on PTM cross-talk through serial enrichment.
Webb K, Bennett EJ. Webb K, et al. Nat Methods. 2013 Jul;10(7):620-1. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2526. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 23807195 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Eavesdropping on PTM cross-talk through serial enrichment.
Webb K, Bennett EJ. Webb K, et al. Nat Methods. 2013 Jul;10(7):620-1. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2526. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 23807195 No abstract available. - Identification, Quantification, and Site Localization of Protein Posttranslational Modifications via Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics.
Ke M, Shen H, Wang L, Luo S, Lin L, Yang J, Tian R. Ke M, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;919:345-382. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-41448-5_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27975226 Review. - Quantitative mass spectrometry of posttranslational modifications: keys to confidence.
Hennrich ML, Gavin AC. Hennrich ML, et al. Sci Signal. 2015 Apr 7;8(371):re5. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa6466. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 25852188 Review. - Application of targeted mass spectrometry in bottom-up proteomics for systems biology research.
Manes NP, Nita-Lazar A. Manes NP, et al. J Proteomics. 2018 Oct 30;189:75-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2018.02.008. Epub 2018 Feb 13. J Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29452276 Free PMC article. Review. - Recent findings and technological advances in phosphoproteomics for cells and tissues.
von Stechow L, Francavilla C, Olsen JV. von Stechow L, et al. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2015;12(5):469-87. doi: 10.1586/14789450.2015.1078730. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 26400465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Immunogenetics. Dynamic profiling of the protein life cycle in response to pathogens.
Jovanovic M, Rooney MS, Mertins P, Przybylski D, Chevrier N, Satija R, Rodriguez EH, Fields AP, Schwartz S, Raychowdhury R, Mumbach MR, Eisenhaure T, Rabani M, Gennert D, Lu D, Delorey T, Weissman JS, Carr SA, Hacohen N, Regev A. Jovanovic M, et al. Science. 2015 Mar 6;347(6226):1259038. doi: 10.1126/science.1259038. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Science. 2015. PMID: 25745177 Free PMC article. - pCysMod: Prediction of Multiple Cysteine Modifications Based on Deep Learning Framework.
Li S, Yu K, Wu G, Zhang Q, Wang P, Zheng J, Liu ZX, Wang J, Gao X, Cheng H. Li S, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 23;9:617366. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.617366. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33732693 Free PMC article. - A conserved, N-terminal tyrosine signal directs Ras for inhibition by Rabex-5.
Washington C, Chernet R, Gokhale RH, Martino-Cortez Y, Liu HY, Rosenberg AM, Shahar S, Pfleger CM. Washington C, et al. PLoS Genet. 2020 Jun 19;16(6):e1008715. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008715. eCollection 2020 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32559233 Free PMC article. - Multimodality assessment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction skeletal muscle reveals differences in the machinery of energy fuel metabolism.
Zamani P, Proto EA, Wilson N, Fazelinia H, Ding H, Spruce LA, Davila A Jr, Hanff TC, Mazurek JA, Prenner SB, Desjardins B, Margulies KB, Kelly DP, Arany Z, Doulias PT, Elrod JW, Allen ME, McCormack SE, Schur GM, D'Aquilla K, Kumar D, Thakuri D, Prabhakaran K, Langham MC, Poole DC, Seeholzer SH, Reddy R, Ischiropoulos H, Chirinos JA. Zamani P, et al. ESC Heart Fail. 2021 Aug;8(4):2698-2712. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13329. Epub 2021 May 15. ESC Heart Fail. 2021. PMID: 33991175 Free PMC article. - Dynamic Protein Acetylation in Plant-Pathogen Interactions.
Song G, Walley JW. Song G, et al. Front Plant Sci. 2016 Mar 30;7:421. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00421. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27066055 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Olsen JV, et al. Sci. Signal. 2010;3:ra3. - PubMed
- Choudhary C, et al. Science. 2009;325:834–840. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U24 CA160034/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL096738/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL096738/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201000033C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24CA160034/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases