The new sequencer on the block: comparison of Life Technology's Proton sequencer to an Illumina HiSeq for whole-exome sequencing - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
The new sequencer on the block: comparison of Life Technology's Proton sequencer to an Illumina HiSeq for whole-exome sequencing
Joseph F Boland et al. Hum Genet. 2013 Oct.
Abstract
We assessed the performance of the new Life Technologies Proton sequencer by comparing whole-exome sequence data in a Centre d'Etude du Polymorphisme Humain trio (family 1463) to the Illumina HiSeq instrument. To simulate a typical user's results, we utilized the standard capture, alignment and variant calling methods specific to each platform. We restricted data analysis to include the capture region common to both methods. The Proton produced high quality data at a comparable average depth and read length, and the Ion Reporter variant caller identified 96 % of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) detected by the HiSeq and GATK pipeline. However, only 40 % of small insertion and deletion variants (indels) were identified by both methods. Usage of the trio structure and segregation of platform-specific alleles supported this result. Further comparison of the trio data with Complete Genomics sequence data and Illumina SNP microarray genotypes documented high concordance and accurate SNP genotyping of both Proton and Illumina platforms. However, our study underscored the problem of accurate detection of indels for both the Proton and HiSeq platforms.
Figures
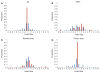
Fig. 1
Distribution of sizes of insertion/deletion polymorphisms (indels) by a all indels detected by Proton and Illumina overall, b indels detected in common by both Illumina and Proton, c indels detected by Illumina only and d indels detected by Proton only. Blue bars represent indels previously reported in dbSNP build 137, while red bars represent novel indels
Fig. 2
Venn diagrams of the overlap in numbers of variant calls by sequencing platform for a SNPs and b indels
Similar articles
- Comparison and evaluation of two exome capture kits and sequencing platforms for variant calling.
Zhang G, Wang J, Yang J, Li W, Deng Y, Li J, Huang J, Hu S, Zhang B. Zhang G, et al. BMC Genomics. 2015 Aug 5;16(1):581. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1796-6. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26242175 Free PMC article. - OTG-snpcaller: an optimized pipeline based on TMAP and GATK for SNP calling from ion torrent data.
Zhu P, He L, Li Y, Huang W, Xi F, Lin L, Zhi Q, Zhang W, Tang YT, Geng C, Lu Z, Xu X. Zhu P, et al. PLoS One. 2014 May 13;9(5):e97507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097507. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24824529 Free PMC article. - Validation of multiple single nucleotide variation calls by additional exome analysis with a semiconductor sequencer to supplement data of whole-genome sequencing of a human population.
Motoike IN, Matsumoto M, Danjoh I, Katsuoka F, Kojima K, Nariai N, Sato Y, Yamaguchi-Kabata Y, Ito S, Kudo H, Nishijima I, Nishikawa S, Pan X, Saito R, Saito S, Saito T, Shirota M, Tsuda K, Yokozawa J, Igarashi K, Minegishi N, Tanabe O, Fuse N, Nagasaki M, Kinoshita K, Yasuda J, Yamamoto M. Motoike IN, et al. BMC Genomics. 2014 Aug 10;15(1):673. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-673. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25109789 Free PMC article. - Comparison of solution-based exome capture methods for next generation sequencing.
Sulonen AM, Ellonen P, Almusa H, Lepistö M, Eldfors S, Hannula S, Miettinen T, Tyynismaa H, Salo P, Heckman C, Joensuu H, Raivio T, Suomalainen A, Saarela J. Sulonen AM, et al. Genome Biol. 2011 Sep 28;12(9):R94. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-9-r94. Genome Biol. 2011. PMID: 21955854 Free PMC article. - Impact of post-alignment processing in variant discovery from whole exome data.
Tian S, Yan H, Kalmbach M, Slager SL. Tian S, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Oct 3;17(1):403. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1279-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27716037 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Next Generation Semiconductor Based Sequencing of the Donkey (Equus asinus) Genome Provided Comparative Sequence Data against the Horse Genome and a Few Millions of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms.
Bertolini F, Scimone C, Geraci C, Schiavo G, Utzeri VJ, Chiofalo V, Fontanesi L. Bertolini F, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Jul 7;10(7):e0131925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131925. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26151450 Free PMC article. - Recent advances in the methods and clinical applications of next-generation sequencing in genomic profiling and precision cancer therapy.
Alsaiari AA. Alsaiari AA. EXCLI J. 2025 Jan 3;24:15-33. doi: 10.17179/excli2024-7594. eCollection 2025. EXCLI J. 2025. PMID: 39967910 Free PMC article. Review. - Application of Next Generation Sequencing in Laboratory Medicine.
Zhong Y, Xu F, Wu J, Schubert J, Li MM. Zhong Y, et al. Ann Lab Med. 2021 Jan;41(1):25-43. doi: 10.3343/alm.2021.41.1.25. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Ann Lab Med. 2021. PMID: 32829577 Free PMC article. Review. - Mutation spectrum of six genes in Chinese phenylketonuria patients obtained through next-generation sequencing.
Gu Y, Lu K, Yang G, Cen Z, Yu L, Lin L, Hao J, Yang Z, Peng J, Cui S, Huang J. Gu Y, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Apr 4;9(4):e94100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094100. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24705691 Free PMC article. - Toward better understanding of artifacts in variant calling from high-coverage samples.
Li H. Li H. Bioinformatics. 2014 Oct 15;30(20):2843-51. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu356. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24974202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bras J, Guerreiro R, Hardy J. Use of next-generation sequencing and other whole-genome strategies to dissect neurological disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13:453–464. - PubMed
- Dausset J, Cann H, Cohen D, Lathrop M, Lalouel JM, White R. Centre d’etude du polymorphisme humain (CEPH): collaborative genetic mapping of the human genome. Genomics. 1990;6:575–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources