Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in children and adolescents: a single center experience - PubMed (original) (raw)
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in children and adolescents: a single center experience
Ilknur Erol et al. Pediatr Neurol. 2013 Oct.
Abstract
Background: Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis is an immune-mediated disease that produces multiple inflammatory lesions in the brain and spinal cord.
Methods: This study retrospectively evaluated 15 children with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in children and adolescents from a single institution in Adana, Turkey.
Results: The patients presented in a seasonal distribution, with 73.3%: (11/15) presenting in winter or spring. The majority of patients (13/15, 86.7%) had a history of acute febrile illness 2 to 40 days before presentation, and five children had serologic evidence of specific triggers: mycoplasma (2 children), influenza-A (H1N1) (1 child), or Epstein-Barr virus. All children were treated with a standard protocol of 3 to 5 days of intravenous administration of methylprednisolone and intravenous immunoglobulin for patients who continued to deteriorate. Oseltamivir and clarithromycin were administered in patients with influenza-A (H1N1) and mycoplasma according to the serology. In 13 patients, all neurologic signs and symptoms resolved after treatment. Only one patient was left with severe neurologic sequelae and another child had recurrent attacks and was ultimately diagnosed with possible multiple sclerosis.
Conclusions: The present series demonstrates that acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in children occurs predominantly in winter or spring and often follows an upper respiratory tract illness for those along the southern coast of Anatolia (Mediterranean region). Early treatment with immunomodulative agents is recommended and is likely to result in a favorable outcome or full recovery. This study also suggests benefit from antiviral and antibiotic treatment initiated as soon as possible after the onset of illness.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Turkey; acute disseminated encephalomyelitis; adolescents; children; multiple sclerosis.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
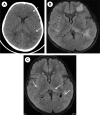
Figure 1
(A) Computed tomography shows hypodensity in the left periventricular white matter (arrows), and (B) fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MRI sequence shows multiple hyperintense lesions in the periventricular white matter and left thalamic. (C) Follow-up brain MRI obtained 1 month later shows size decrease and no appearance of new lesions (arrows).
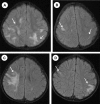
Figure 2
(A) The first MRI scan shows multiple hyperintense lesions in the subcortical and deep white matter. (B) One year later, a follow-up MRI shows partial resolution of the lesions. (C) One month after the scan shown in part B, brain MRI shows new lesions in the right frontoparietal subcortical and deep white matter. (D) Follow-up brain MRI image obtained 6 months later shows partial resolution of the these lesions and new lesion in the left parietal subcortical white matter.
Similar articles
- Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in children.
Murthy SN, Faden HS, Cohen ME, Bakshi R. Murthy SN, et al. Pediatrics. 2002 Aug;110(2 Pt 1):e21. doi: 10.1542/peds.110.2.e21. Pediatrics. 2002. PMID: 12165620 - Improvement of atypical acute disseminated encephalomyelitis with steroids and intravenous immunoglobulins.
Straussberg R, Schonfeld T, Weitz R, Karmazyn B, Harel L. Straussberg R, et al. Pediatr Neurol. 2001 Feb;24(2):139-43. doi: 10.1016/s0887-8994(00)00229-0. Pediatr Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11275464 Review. - Outcome of severe encephalomyelitis in children: effect of high-dose methylprednisolone and immunoglobulins.
Shahar E, Andraus J, Savitzki D, Pilar G, Zelnik N. Shahar E, et al. J Child Neurol. 2002 Nov;17(11):810-4. doi: 10.1177/08830738020170111001. J Child Neurol. 2002. PMID: 12585719 Clinical Trial. - Evaluation of the cases with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis.
Tosun A, Serdaroglu G, Polat M, Tekgul H, Gokben S. Tosun A, et al. Indian J Pediatr. 2009 May;76(5):547-50. doi: 10.1007/s12098-009-0069-2. Epub 2009 Apr 23. Indian J Pediatr. 2009. PMID: 19390813 - Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis After Influenza Vaccination: A Case Report.
Chen WT, Huang YC, Peng MC, Wang MC, Lin KP. Chen WT, et al. Crit Care Nurse. 2016 Jun;36(3):e1-6. doi: 10.4037/ccn2016808. Crit Care Nurse. 2016. PMID: 27252106 Review.
Cited by
- Juvenile multiple sclerosis: addressing epidemiology, diagnosis, therapeutic, and prognostic updates along with cognitive dysfunction and quality of life.
Prajjwal P, M D M M, Natarajan B, Inban P, Gadam S, Sowndarya D, John J, Abbas R, Vaja H, A D M M, Amir Hussin O. Prajjwal P, et al. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 May 25;85(9):4433-4441. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000930. eCollection 2023 Sep. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37663711 Free PMC article. Review. - A spectrum of inflammation and demyelination in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) of children.
Esposito S, Di Pietro GM, Madini B, Mastrolia MV, Rigante D. Esposito S, et al. Autoimmun Rev. 2015 Oct;14(10):923-9. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.06.002. Epub 2015 Jun 14. Autoimmun Rev. 2015. PMID: 26079482 Free PMC article. Review. - Promising candidate cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of seizure disorder, infection, inflammation, tumor, and traumatic brain injury in pediatric patients.
Kim SH, Chae SA. Kim SH, et al. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022 Feb;65(2):56-64. doi: 10.3345/cep.2021.00241. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 34425669 Free PMC article. - Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: current controversies in diagnosis and outcome.
Koelman DL, Mateen FJ. Koelman DL, et al. J Neurol. 2015 Sep;262(9):2013-24. doi: 10.1007/s00415-015-7694-7. Epub 2015 Mar 13. J Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25761377 Review. - Clinical pattern, neuroimaging findings and outcome of Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis in children: A retrospective study.
Mukhtiar K, Raza M, Ishaque S, Maha Q, Noor A. Mukhtiar K, et al. Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Aug;40(7):1479-1484. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.7.8015. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39092058 Free PMC article.
References
- Krupp L.B., Banwell B., Tenembaum S., International Pediatric MS Study Group Consensus definitions proposed for pediatric multiple sclerosis and related disorders. Neurology. 2007;68(16 Suppl 2):S7–S12. - PubMed
- Schwarz S., Mohr A., Knauth M., Wildemann B., Storch-Hagenlocher B. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: A follow-up study of 40 adult patients. Neurology. 2001;56:1313–1318. - PubMed
- Murtthy S.N., Faden H.S., Cohen M.E., Bakshi R. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in children. Pediatrics. 2002;110(2 Pt 1):e21. - PubMed
- Tenembaum S., Chitnis T., Ness J., Hahn J.S., International Pediatric MS Study Group Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Neurology. 2007;68(16 Suppl 2):23–36. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources