Low-level laser therapy and vibration therapy for the treatment of localized adiposity and fibrous cellulite - PubMed (original) (raw)
Low-level laser therapy and vibration therapy for the treatment of localized adiposity and fibrous cellulite
Antonella Savoia et al. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2013.
Abstract
Introduction: In recent years, there has been an upsurge in the application of low-level laser therapy in various medical diseases. Additionally, vibration therapy is a new and effective measure to prevent muscular atrophy and osteoporosis, along with some general health-related beneficial effects of exercise on skeletal muscles such as improvement of endothelial function and an increased enzyme capacity of energy metabolism. The aim of this study was to evaluate the application of a 635 nm and 0.040 W exit power per multiple diode laser in combination with vibration therapy for the application of non-invasive reduction of circumference in patients with localized adiposity and cellulite.
Methods: The study enrolled men and women (N = 33) aged 18-64 years with localized adiposity or fibrous cellulite. The evaluation parameters were: photographic evaluation, perimetric evaluation, blood tests, ecographic evaluation, histological evaluation, and subjective and objective tests.
Results: The results produced were statistically analyzed and resulted in a significant reduction of fat thickness when compared to the measurement prior to the treatment (P < 0.0001). Moreover, subjective and objective tests, as well as ecographic and histological evaluations, confirmed the reduction of fat thickness.
Conclusion: In this study we have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of the combination between low-level laser therapy and vibration therapy for the resolution of localized adiposity and fibrous cellulite.
Keywords: Body contouring; Fibrous cellulite; Localized adiposity; Low-level laser therapy; Ultrasound; Vibration therapy.
Figures
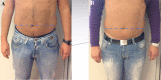
Fig. 1
Abdomen of a patient before treatment (a) and after treatment (b)
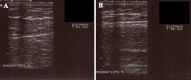
Fig. 2
Fat thickness assessment by ultrasound before treatment (a) and after treatment (b), shows thinning of the subcutaneous fat layer from 12.0 to 8.0 mm (reduction of 4 mm). This patient was treated on the abdomen
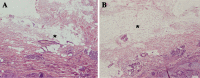
Fig. 3
Histopathology of skin and of subcutaneous fat tissue. One characteristic and representative slide taken from the central part of the skin-sample (a) and a corresponding slide (control) of the not treated skin-sample (b) are depicted. The reduction on fat thickness in the treated skin samples (indicated by asterisks) is observed (haematoxylin and eosin staining, original magnification ×20)
Similar articles
- Review of the Mechanisms and Effects of Noninvasive Body Contouring Devices on Cellulite and Subcutaneous Fat.
Alizadeh Z, Halabchi F, Mazaheri R, Abolhasani M, Tabesh M. Alizadeh Z, et al. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jul 3;14(4):e36727. doi: 10.5812/ijem.36727. eCollection 2016 Oct. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 28123436 Free PMC article. Review. - Synergistic effects of cryolipolysis and shock waves for noninvasive body contouring.
Ferraro GA, De Francesco F, Cataldo C, Rossano F, Nicoletti G, D'Andrea F. Ferraro GA, et al. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2012 Jun;36(3):666-79. doi: 10.1007/s00266-011-9832-7. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2012. PMID: 22042359 - Use of a microwave device for the treatment of cellulite and localized fat adiposity: a 1-year follow-up study.
Salsi B, Coli F, Ronconi L, Fusco I, Zingoni T, Bonan P. Salsi B, et al. Skin Res Technol. 2023 Jul;29(7):e13408. doi: 10.1111/srt.13408. Skin Res Technol. 2023. PMID: 37522509 Free PMC article. - Treatment of cellulite using a 1440-nm pulsed laser with one-year follow-up.
DiBernardo BE. DiBernardo BE. Aesthet Surg J. 2011 Mar;31(3):328-41. doi: 10.1177/1090820X11398353. Aesthet Surg J. 2011. PMID: 21385743 Clinical Trial. - A Review of the Use of Ultrasound for Skin Tightening, Body Contouring, and Cellulite Reduction in Dermatology.
Juhász M, Korta D, Mesinkovska NA. Juhász M, et al. Dermatol Surg. 2018 Jul;44(7):949-963. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001551. Dermatol Surg. 2018. PMID: 29846343 Review.
Cited by
- Combination of monopolar 2 MHz radiofrequency and electrical multidirectional stimulation for reducing abdominal circumference and enhancing the muscle definition in subjects with overweight range body mass index.
Manuskiatti W, Nanchaipruek Y, Gervasio MK, Lektrakul N, Apinuntham C. Manuskiatti W, et al. Lasers Surg Med. 2022 Nov;54(9):1198-1206. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23606. Epub 2022 Oct 2. Lasers Surg Med. 2022. PMID: 36183371 Free PMC article. - Review of the Mechanisms and Effects of Noninvasive Body Contouring Devices on Cellulite and Subcutaneous Fat.
Alizadeh Z, Halabchi F, Mazaheri R, Abolhasani M, Tabesh M. Alizadeh Z, et al. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jul 3;14(4):e36727. doi: 10.5812/ijem.36727. eCollection 2016 Oct. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 28123436 Free PMC article. Review. - Changes in Skin Microcirculation Resulting from Vibration Therapy in Women with Cellulite.
Piotrowska A, Czerwińska-Ledwig O, Stefańska M, Pałka T, Maciejczyk M, Bujas P, Bawelski M, Ridan T, Żychowska M, Sadowska-Krępa E, Dębiec-Bąk A. Piotrowska A, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 13;19(6):3385. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19063385. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35329074 Free PMC article. - The Effect of Combination of Red, Infrared and Blue Wavelengths of Low-Level Laser on Reduction of Abdominal Girth: A Before-After Case Series.
Montazeri K, Mokmeli S, Barat M. Montazeri K, et al. J Lasers Med Sci. 2017 Summer;8(Suppl 1):S22-S26. doi: 10.15171/jlms.2017.s5. Epub 2017 Aug 29. J Lasers Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29071031 Free PMC article. - A German Prospective Study of the Safety and Efficacy of a Non-Invasive, High-intensity, Electromagnetic Abdomen and Buttock Contouring Device.
Giesse S. Giesse S. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021 Jan;14(1):30-33. Epub 2021 Jan 1. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33584965 Free PMC article.
References
- Stonecipher KG, Kezirian GM. Wavefront-optimized versus wavefront guided LASIK for myopic astigmatism with the ALLEGRETTO WAVE: three-month result of a prospective FDA trial. J Refract Surg. 2008;24:S424–S430. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources