RNA-guided gene activation by CRISPR-Cas9-based transcription factors - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2600. Epub 2013 Jul 25.
D Dewran Kocak, Christopher M Vockley, Andrew F Adler, Ami M Kabadi, Lauren R Polstein, Pratiksha I Thakore, Katherine A Glass, David G Ousterout, Kam W Leong, Farshid Guilak, Gregory E Crawford, Timothy E Reddy, Charles A Gersbach
Affiliations
- PMID: 23892895
- PMCID: PMC3911785
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.2600
RNA-guided gene activation by CRISPR-Cas9-based transcription factors
Pablo Perez-Pinera et al. Nat Methods. 2013 Oct.
Abstract
Technologies for engineering synthetic transcription factors have enabled many advances in medical and scientific research. In contrast to existing methods based on engineering of DNA-binding proteins, we created a Cas9-based transactivator that is targeted to DNA sequences by guide RNA molecules. Coexpression of this transactivator and combinations of guide RNAs in human cells induced specific expression of endogenous target genes, demonstrating a simple and versatile approach for RNA-guided gene activation.
Figures
Figure 1
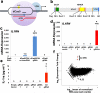
RNA-guided activation of the human IL1RN gene by dCas9-VP64. (a) An RNA-guided transcriptional activator was created by fusing dCas9 (D10A/H840A) to the VP64 transactivation domain. dCas9-VP64 recognizes genomic target sites through the hybridization of a guide RNA (gRNA) to a 20 bp target sequence. (b) The structure of dCas9-VP64 is shown, including Flag and HA epitope tags, two nuclear localization signals (NLS), and the positions of the RuvC- and HNH-like endonuclease domains that target the noncomplementary and complementary DNA strands, respectively, if not inactivated by the mutations D10A and H840A.(c) Expression plasmids for four gRNAs or crRNA/tracrRNAs targeted to sequences in the IL1RN promoter were co-transfected with the dCas9-VP64 expression plasmid into HEK293T cells. Activation of IL1RN expression was assessed by qRT-PCR. (d) The four gRNA expression plasmids were co-transfected with dCas9-VP64 individually or in combination. Robust gene activation was observed by qRT-PCR only in response to the combination of gRNAs. (e) Activation of IL1RN expression was confirmed by assessing secretion of the IL-1ra gene product into the media by ELISA. IL-1ra was only detectable above background in three of the six samples treated with the combination of gRNAs. For (c-e), data are shown as the mean ± s.e.m (n = 3 independent experiments). Treatment with the combination of gRNAs was statistically different than all other treatments (*P ≤ 0.05) by Tukey’s test. (f) RNA-seq was performed on samples treated with empty expression vector (n = 2) or co-transfected with the expression plasmids for dCas9-VP64 and the four gRNAs targeting IL1RN (n = 2). The only statistically significant changes in gene expression between these treatments were an increase in the four IL1RN isoforms (false discovery rate ≤ 3 × 10−4) and a decrease in IL32 (false discovery rate = 0.03).
Figure 2
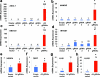
RNA-guided activation of human genes relevant to cell and gene therapy, genetic reprogramming, and regenerative medicine. HEK293T cells were transfected with the dCas9-VP64 expression plasmid and four gRNAs individually or in combination. Target gene expression was measured by qRT-PCR and normalized to GAPDH mRNA levels. Data are shown as the mean ± s.e.m (n = 3 independent experiments). Treatment with the combination of gRNAs was statistically different than all other treatments (*P < 0.05) by Tukey’s test.
Similar articles
- CRISPR RNA-guided activation of endogenous human genes.
Maeder ML, Linder SJ, Cascio VM, Fu Y, Ho QH, Joung JK. Maeder ML, et al. Nat Methods. 2013 Oct;10(10):977-9. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2598. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 23892898 Free PMC article. - Cas9 as a versatile tool for engineering biology.
Mali P, Esvelt KM, Church GM. Mali P, et al. Nat Methods. 2013 Oct;10(10):957-63. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2649. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 24076990 Free PMC article. Review. - Multiplexed activation of endogenous genes by CRISPR-on, an RNA-guided transcriptional activator system.
Cheng AW, Wang H, Yang H, Shi L, Katz Y, Theunissen TW, Rangarajan S, Shivalila CS, Dadon DB, Jaenisch R. Cheng AW, et al. Cell Res. 2013 Oct;23(10):1163-71. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.122. Epub 2013 Aug 27. Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23979020 Free PMC article. - Engineering synthetic TALE and CRISPR/Cas9 transcription factors for regulating gene expression.
Kabadi AM, Gersbach CA. Kabadi AM, et al. Methods. 2014 Sep;69(2):188-97. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.06.014. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Methods. 2014. PMID: 25010559 Free PMC article. - Gene Editing With CRISPR/Cas9 RNA-Directed Nuclease.
Doetschman T, Georgieva T. Doetschman T, et al. Circ Res. 2017 Mar 3;120(5):876-894. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.309727. Circ Res. 2017. PMID: 28254804 Review.
Cited by
- In vivo genome editing in single mammalian brain neurons through CRISPR-Cas9 and cytosine base editors.
Song B, Kang CY, Han JH, Kano M, Konnerth A, Bae S. Song B, et al. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Apr 25;19:2477-2485. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.04.051. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34025938 Free PMC article. - Choosing the Right Tool for the Job: RNAi, TALEN, or CRISPR.
Boettcher M, McManus MT. Boettcher M, et al. Mol Cell. 2015 May 21;58(4):575-85. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.04.028. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26000843 Free PMC article. Review. - Highly efficient Cas9-mediated transcriptional programming.
Chavez A, Scheiman J, Vora S, Pruitt BW, Tuttle M, P R Iyer E, Lin S, Kiani S, Guzman CD, Wiegand DJ, Ter-Ovanesyan D, Braff JL, Davidsohn N, Housden BE, Perrimon N, Weiss R, Aach J, Collins JJ, Church GM. Chavez A, et al. Nat Methods. 2015 Apr;12(4):326-8. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3312. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Nat Methods. 2015. PMID: 25730490 Free PMC article. - Reprogramming the anti-tumor immune response via CRISPR genetic and epigenetic editing.
Alves E, Taifour S, Dolcetti R, Chee J, Nowak AK, Gaudieri S, Blancafort P. Alves E, et al. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021 Apr 24;21:592-606. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2021.04.009. eCollection 2021 Jun 11. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021. PMID: 34095343 Free PMC article. Review. - Androgen receptor mitigates postoperative disease progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing CD90+ populations and cell migration and by promoting anoikis in circulating tumor cells.
Lai HC, Yeh CC, Jeng LB, Huang SF, Liao PY, Lei FJ, Cheng WC, Hsu CL, Cai X, Chang C, Ma WL. Lai HC, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 19;7(29):46448-46465. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10186. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27340775 Free PMC article.
References
- Rebar EJ, et al. Induction of angiogenesis in a mouse model using engineered transcription factors. Nat Med. 2002;8:1427–1432. - PubMed
- Graslund T, Li X, Magnenat L, Popkov M, Barbas CF., 3rd Exploring strategies for the design of artificial transcription factors: targeting sites proximal to known regulatory regions for the induction of gamma-globin expression and the treatment of sickle cell disease. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:3707–3714. - PubMed
- Beltran A, et al. Re-activation of a dormant tumor suppressor gene maspin by designed transcription factors. Oncogene. 2007;26:2791–2798. - PubMed
- Bartsevich VV, Miller JC, Case CC, Pabo CO. Engineered zinc finger proteins for controlling stem cell fate. Stem Cells. 2003;21:632–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM008555/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP2OD008586/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR048852/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG004563/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM008555/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR48852/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL109442/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB015300/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AR061042/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL109442/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R03AR061042/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 OD008586/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- (U54HG004563/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- EB015300/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials