Assembly, remodelled - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comment
Assembly, remodelled
Karim Bouazoune et al. Elife. 2013.
Abstract
Biochemical assays reveal that nucleosome maturation and chromatin remodelling by the motor protein Chd1 are distinct, separable enzymatic activities.
Keywords: Chd1; D. melanogaster; S. cerevisiae; chromatin; chromatin assembly; chromatin remodelling; motor protein; nucleosome.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests:The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
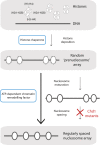
Figure 1.. Mature nucleosome arrays are formed in several stages.
Histone proteins are first loaded onto DNA to create non-canonical nucleosomal structures referred to as ‘prenucleosomes’ (top and second panels). The core histones, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4, associate with each other in heterodimers (H2A-H2B and H3-H4; top panel) and are deposited onto DNA in a specific order by proteins called histone chaperones (top blue box) to form an irregularly spaced prenucleosome array (dashed ovals, second panel). Mature nucleosomes are then formed, and also repositioned to ensure their even spacing on the DNA, by ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling factors (motor proteins; lower blue box). Maturation and repositioning were formerly thought to be achieved by a single enzymatic function (long arrow at left, bottom panel). Now, using mutant variants of a motor protein called Chd1, Torigoe et al. suggest that chromatin remodelling factors use not one but two distinct ATP-dependent activities to convert randomly deposited prenucleosomes into a mature array of evenly spaced nucleosomes (solid ovals; short arrows at right, third and bottom panels).
Comment on
- ATP-dependent chromatin assembly is functionally distinct from chromatin remodeling.
Torigoe SE, Patel A, Khuong MT, Bowman GD, Kadonaga JT. Torigoe SE, et al. Elife. 2013 Aug 20;2:e00863. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00863. Elife. 2013. PMID: 23986862 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- ATP-dependent chromatin assembly is functionally distinct from chromatin remodeling.
Torigoe SE, Patel A, Khuong MT, Bowman GD, Kadonaga JT. Torigoe SE, et al. Elife. 2013 Aug 20;2:e00863. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00863. Elife. 2013. PMID: 23986862 Free PMC article. - Distinct activities of CHD1 and ACF in ATP-dependent chromatin assembly.
Lusser A, Urwin DL, Kadonaga JT. Lusser A, et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005 Feb;12(2):160-6. doi: 10.1038/nsmb884. Epub 2005 Jan 9. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15643425 - Structure of the chromatin remodelling enzyme Chd1 bound to a ubiquitinylated nucleosome.
Sundaramoorthy R, Hughes AL, El-Mkami H, Norman DG, Ferreira H, Owen-Hughes T. Sundaramoorthy R, et al. Elife. 2018 Aug 6;7:e35720. doi: 10.7554/eLife.35720. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30079888 Free PMC article. - Mechanisms of action and regulation of ATP-dependent chromatin-remodelling complexes.
Clapier CR, Iwasa J, Cairns BR, Peterson CL. Clapier CR, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Jul;18(7):407-422. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.26. Epub 2017 May 17. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28512350 Free PMC article. Review. - The chromatin accessibility complex: chromatin dynamics through nucleosome sliding.
Becker PB. Becker PB. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2004;69:281-7. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2004.69.281. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2004. PMID: 16117660 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- PBRM1 bromodomains associate with RNA to facilitate chromatin association.
De Silva SM, Dhiman A, Sood S, Mercedes KF, Simmons WJ, Henen MA, Vögeli B, Dykhuizen EC, Musselman CA. De Silva SM, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 May 8;51(8):3631-3649. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad072. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36808431 Free PMC article. - The prenucleosome, a stable conformational isomer of the nucleosome.
Fei J, Torigoe SE, Brown CR, Khuong MT, Kassavetis GA, Boeger H, Kadonaga JT. Fei J, et al. Genes Dev. 2015 Dec 15;29(24):2563-75. doi: 10.1101/gad.272633.115. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 26680301 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases