Crawling of effector T cells on extracellular matrix: role of integrins in interstitial migration in inflamed tissues - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comment
Crawling of effector T cells on extracellular matrix: role of integrins in interstitial migration in inflamed tissues
Chang H Kim. Cell Mol Immunol. 2014 Jan.
No abstract available
Figures
Figure 1
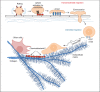
Integrins regulate interstitial migration of effector T cells. Circulating memory and effector T cells in the blood circulation enter into tissues through the endothelial cell layer. Adhesion molecules and chemokines cooperatively induce the endothelial cell migration process. Constitutively expressed tissue-specific or inflammation-induced chemokines and adhesion molecules regulate the migration. Integrins play critical roles in transendothelial cell migration by mediating the rolling and firm adhesion process. After transendothelial migration, T cells still need to migrate to specialized microenvironments for their effector functions. This migration is called interstitial migration and involves crawling and squeezing movement on ECM fibers (e.g., collagen and fibronectin), which undergo dramatic alteration to support T-cell migration in inflamed tissues. In inflamed skin, integrins, particularly αV-containing integrins (e.g., αVβ1 and αVβ3), are required for normal interstitial migration of effector T cells. Chemoattractants are likely to be involved in regulating the migration of effector T cells on ECM fibers. Considerable diversity is expected in terms of chemokines and integrins that regulate T-cell migration in different tissues and conditions. ECM, extracellular matrix.
Comment on
- Inflammation-induced interstitial migration of effector CD4⁺ T cells is dependent on integrin αV.
Overstreet MG, Gaylo A, Angermann BR, Hughson A, Hyun YM, Lambert K, Acharya M, Billroth-Maclurg AC, Rosenberg AF, Topham DJ, Yagita H, Kim M, Lacy-Hulbert A, Meier-Schellersheim M, Fowell DJ. Overstreet MG, et al. Nat Immunol. 2013 Sep;14(9):949-58. doi: 10.1038/ni.2682. Epub 2013 Aug 11. Nat Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23933892 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- Inflammation-induced interstitial migration of effector CD4⁺ T cells is dependent on integrin αV.
Overstreet MG, Gaylo A, Angermann BR, Hughson A, Hyun YM, Lambert K, Acharya M, Billroth-Maclurg AC, Rosenberg AF, Topham DJ, Yagita H, Kim M, Lacy-Hulbert A, Meier-Schellersheim M, Fowell DJ. Overstreet MG, et al. Nat Immunol. 2013 Sep;14(9):949-58. doi: 10.1038/ni.2682. Epub 2013 Aug 11. Nat Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23933892 Free PMC article. - IL-4 attenuates Th1-associated chemokine expression and Th1 trafficking to inflamed tissues and limits pathogen clearance.
Lazarski CA, Ford J, Katzman SD, Rosenberg AF, Fowell DJ. Lazarski CA, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Aug 26;8(8):e71949. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071949. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23991011 Free PMC article. - L-selectin, alpha 4 beta 1, and alpha 4 beta 7 integrins participate in CD4+ T cell recruitment to chronically inflamed small intestine.
Rivera-Nieves J, Olson T, Bamias G, Bruce A, Solga M, Knight RF, Hoang S, Cominelli F, Ley K. Rivera-Nieves J, et al. J Immunol. 2005 Feb 15;174(4):2343-52. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.4.2343. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15699171 - Lymphocyte migration into tissue: the paradigm derived from CD4 subsets.
Bradley LM, Watson SR. Bradley LM, et al. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996 Jun;8(3):312-20. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(96)80118-x. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8793991 Review. - The spatio-temporal control of effector T cell migration.
Fowell DJ, Kim M. Fowell DJ, et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021 Sep;21(9):582-596. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00507-0. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33627851 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Fibronectin-targeted FUD and PEGylated FUD peptides for fibrotic diseases.
Lee HJ, Tomasini-Johansson BR, Gupta N, Kwon GS. Lee HJ, et al. J Control Release. 2023 Aug;360:69-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.06.008. Epub 2023 Jun 22. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 37315694 Free PMC article. - Investigating Cancerous Exosomes' Effects on CD8+ T-Cell IL-2 Production in a 3D Unidirectional Flow Bioreactor Using 3D Printed, RGD-Functionalized PLLA Scaffolds.
Karami D, Srivastava A, Ramesh R, Sikavitsas VI. Karami D, et al. J Funct Biomater. 2022 Mar 11;13(1):30. doi: 10.3390/jfb13010030. J Funct Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35323230 Free PMC article. - The Potential Role of FREM1 and Its Isoform TILRR in HIV-1 Acquisition through Mediating Inflammation.
Kashem MA, Li H, Liu LR, Liang B, Omange RW, Plummer FA, Luo M. Kashem MA, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 22;22(15):7825. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157825. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360591 Free PMC article. Review. - Leukocyte arrest: Biomechanics and molecular mechanisms of β2 integrin activation.
Fan Z, Ley K. Fan Z, et al. Biorheology. 2015;52(5-6):353-77. doi: 10.3233/BIR-15085. Biorheology. 2015. PMID: 26684674 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Woolf E, Grigorova I, Sagiv A, Grabovsky V, Feigelson SW, Shulman Z, et al. Lymph node chemokines promote sustained T lymphocyte motility without triggering stable integrin adhesiveness in the absence of shear forces. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:1076–1085. - PubMed
- Lammermann T, Bader BL, Monkley SJ, Worbs T, Wedlich-Soldner R, Hirsch K, et al. Rapid leukocyte migration by integrin-independent flowing and squeezing. Nature. 2008;453:51–55. - PubMed
- Lu TT, Cyster JG. Integrin-mediated long-term B cell retention in the splenic marginal zone. Science. 2002;297:409–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01DK076616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI074745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI080769/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI080769/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI074745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources