Species differences and molecular determinant of TRPA1 cold sensitivity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Species differences and molecular determinant of TRPA1 cold sensitivity
Jun Chen et al. Nat Commun. 2013.
Free PMC article
Abstract
TRPA1 is an ion channel and has been proposed as a thermosensor across species. In invertebrate and ancestral vertebrates such as fly, mosquito, frog, lizard and snakes, TRPA1 serves as a heat receptor, a sensory input utilized for heat avoidance or infrared detection. However, in mammals, whether TRPA1 is a receptor for noxious cold is highly controversial, as channel activation by cold was observed by some groups but disputed by others. Here we attribute the discrepancy to species differences. We show that cold activates rat and mouse TRPA1 but not human or rhesus monkey TRPA1. At the molecular level, a single residue within the S5 transmembrane domain (G878 in rodent but V875 in primate) accounts for the observed difference in cold sensitivity. This residue difference also underlies the species-specific effects of menthol. Together, our findings identify the species-specific cold activation of TRPA1 and reveal a molecular determinant of cold-sensitive gating.
Conflict of interest statement
J.C., J.X., M.L., C.S., K.W. and B.Y. are AbbVie employees. All other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
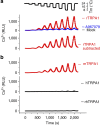
Figure 1. Cold responses of TRPA1 species variants in Ca2+ assay.
(a) In rTRPA1-expressing cells, lowering temperature in steps (from 24 to 20, 18, 16, 14, 12, 10 and 8 °C) evoked progressively larger Ca2+ influx, as reflected by increases in relative light unit (RLU). Signals in A967079 (5 μM)-treated rTRPA1 cells and mock-transfected cells were small and overlapped. A967079-specific signals (rTRPA1 subtracted) were obtained to represent TRPA1 activities. (b) Cold increased (Ca2+) in cells expressing mTRPA1 but not hTRPA1 or rhTRPA1. Fluorescence traces are shown as mean±s.d. from 12 wells. More than five transfections were performed.
Figure 2. Cold sensitivity of rTRPA1 and hTRPA1 in whole-cell and single-channel recordings.
(a) Time course and current traces of rTRPA1 whole-cell currents. Numbers indicate time points and dotted line indicates zero current level. Scale bars are 1 nA and 50 s. (b) hTRPA1 whole-cell currents in response to cold and AITC (100 μM). Scale bars are 2 nA and 50 s. (c,d) Cell-attached single-channel recordings of r- and hTRPA1 at 24 and 8 °C (−60 mV). Expanded current tracings are shown as indicated. Scale bars are 5 pA and 100 ms. (e) Current–voltage relationships of rTRPA1 and hTRPA1 at 24 and 8 °C (−60 mV). AITC (100 μM)-evoked currents were used for hTRPA1 due to lack of cold activation. _n_=4–5. (f) Relative channel activity as function of temperature. _n_=4–5. Channel activity in response to cold was determined by normalizing _NP_o of cold response to NP_o of AITC response. rTRPA1 activities were fitted with an exponential regression. n_=5. *P<0.05 (Student’s _t-_test). All error bars are s.d.
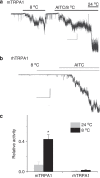
Figure 3. Cold activates mTRPA1 but not rhTRPA1.
(a,b) Representative m- and rhTRPA1 current traces. Scale bars are 5 pA and 20 s for mTRPA1, and 5 pA and 30 s for rhTRPA1. (c) Relative activity of m- and rhTRPA1 at 24 and 8 °C. Relative activity was determined by normalizing _NP_o of cold response to _NP_o of AITC response. _n_=6 for mTRPA1 and _n_=5 for rhTRPA1. *P<0.05 from Student’s _t_-test. Error bars are s.d.
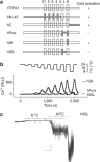
Figure 4. S5 and S5-S6 linker domains are required for cold activation of rTRPA1.
(a) Schematic representation of chimeras. The amino-acid compositions of chimeras are described in Methods. (b) Cold-activated hS6 but not hPore or hS5L in the Ca2+ assays_. n_=12. Five independent transfections were tested. (c) Representative traces of cell-attached single-channel recording of hS5L at 24 and 8 °C and then with AITC (100 μM). Note the changing temperature from 8 to 24 °C increased amplitudes of AITC currents, indicating that the conductance sensitivity to cold remains intact. Scale bars are 5 pA and 20 s.
Figure 5. A single residue determines cold sensitivity of r- and mTRPA1.
(a) Sequence alignment of S5 and S5-S6 linker domains of r-and hTRPA1. The critical residues G878 (rTRPA1) is marked by *. (b,c) rTRPA1-V893I/F897L/A900P/T903S/L908I but not rTRPA1-G878V retained cold sensitivity in Ca2+ assay (_n_=12) and single-channel recordings (_n_=4). Scale bars are 10 pA and 25 s (left) and 10 pA and 50 s (right). (d) Representative single-channel recordings of mTRPA1/G878V in responses to cold and AITC (100 μM). Scale bars are 4 pA and 50 s. (e) Relative activity of wild type and mTRPA1/G878V, as determined by normalizing _NP_o against AITC response. _n_=5. *P<0.05 from Student’s _t_-test. Error bars are s.d.
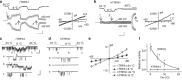
Figure 6. G878 determines species-specific menthol responses.
(a) In Ca2+ assay, 1 mM menthol activated hTRPA1, rTRPA1-G878V but blocked rTRPA1 activation by AITC (30 μM). Solid line: addition of menthol followed by AITC; dotted line: addition of buffer followed by AITC. (b) Activation dose–response of menthol as normalized against responses of 30 μM AITC. EC50 was 95±4 μM for hTRPA1, and 103±7 μM for rTRPA1-G878V, respectively. Note the bell-shaped activation dose–response of rTRPA1. (c) Inhibition dose–responses of menthol. Inhibition of AITC (30 μM)-evoked responses were plotted. IC50 of menthol was 245±11 μM on rTRPA1. Menthol did not inhibit hTRPA1 or rTRPA1-G878V. _n_=12, values above are ±s.d.
Similar articles
- Structural modeling and patch-clamp analysis of pain-related mutation TRPA1-N855S reveal inter-subunit salt bridges stabilizing the channel open state.
Zíma V, Witschas K, Hynkova A, Zímová L, Barvík I, Vlachova V. Zíma V, et al. Neuropharmacology. 2015 Jun;93:294-307. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.02.018. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25724085 - The molecular basis for species-specific activation of human TRPA1 protein by protons involves poorly conserved residues within transmembrane domains 5 and 6.
de la Roche J, Eberhardt MJ, Klinger AB, Stanslowsky N, Wegner F, Koppert W, Reeh PW, Lampert A, Fischer MJ, Leffler A. de la Roche J, et al. J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 12;288(28):20280-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.479337. Epub 2013 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23709225 Free PMC article. - Molecular determinants of species-specific activation or blockade of TRPA1 channels.
Chen J, Zhang XF, Kort ME, Huth JR, Sun C, Miesbauer LJ, Cassar SC, Neelands T, Scott VE, Moreland RB, Reilly RM, Hajduk PJ, Kym PR, Hutchins CW, Faltynek CR. Chen J, et al. J Neurosci. 2008 May 7;28(19):5063-71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0047-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18463259 Free PMC article. - Irritating channels: the case of TRPA1.
Nilius B, Prenen J, Owsianik G. Nilius B, et al. J Physiol. 2011 Apr 1;589(Pt 7):1543-9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.200717. Epub 2010 Nov 15. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21078588 Free PMC article. Review. - TRPA1 and cold transduction: an unresolved issue?
Caspani O, Heppenstall PA. Caspani O, et al. J Gen Physiol. 2009 Mar;133(3):245-9. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200810136. J Gen Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19237589 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Isoform-specific modulation of the chemical sensitivity of conserved TRPA1 channel in the major honeybee ectoparasitic mite, Tropilaelaps mercedesae.
Dong X, Kashio M, Peng G, Wang X, Tominaga M, Kadowaki T. Dong X, et al. Open Biol. 2016 Jun;6(6):160042. doi: 10.1098/rsob.160042. Open Biol. 2016. PMID: 27307515 Free PMC article. - Neuronal transient receptor potential (TRP) channels and noxious sensory detection in sickle cell disease.
Sadler KE, Stucky CL. Sadler KE, et al. Neurosci Lett. 2019 Feb 16;694:184-191. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.11.056. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 30508569 Free PMC article. Review. - Thermo-Sensitive TRP Channels: Novel Targets for Treating Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Pain.
Nazıroğlu M, Braidy N. Nazıroğlu M, et al. Front Physiol. 2017 Dec 13;8:1040. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.01040. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29326595 Free PMC article. Review. - Regulation of ThermoTRP Channels by PIP2 and Cholesterol.
Rosenbaum T, Morales-Lázaro SL. Rosenbaum T, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1422:245-277. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-21547-6_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 36988884
References
- Bandell M. et al.. Noxious cold ion channel TRPA1 is activated by pungent compounds and bradykinin. Neuron 41, 849–857 (2004). - PubMed
- Bautista D. M. et al.. TRPA1 mediates the inflammatory actions of environmental irritants and proalgesic agents. Cell 124, 1269–1282 (2006). - PubMed
- Jordt S. E. et al.. Mustard oils and cannabinoids excite sensory nerve fibres through the TRP channel ANKTM1. Nature 427, 260–265 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources