Effects of stabilization exercise using a ball on mutifidus cross-sectional area in patients with chronic low back pain - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2013 Sep 1;12(3):533-41.
eCollection 2013.
Affiliations
- PMID: 24149162
- PMCID: PMC3772599
Effects of stabilization exercise using a ball on mutifidus cross-sectional area in patients with chronic low back pain
Sinho Chung et al. J Sports Sci Med. 2013.
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to compare the effects of lumbar stabilization exercises using balls to the effects of general lumbar stabilization exercises with respect to changes in the cross section of the multifidus (MF), weight bearing, pain, and functional disorders in patients with non-specific chronic low back pain. Twelve patients participated in either a 8 week (3 days per week) stabilization exercise program using balls and control group (n = 12). The computer tomography (CT) was used to analyze MF cross-sectional areas (CSA) and Tetrax balancing scale was used to analyze left and right weight bearing differences. Both groups had significant changes in the CSA of the MF by segment after training (p < 0.05) and the experimental group showed greater increases at the L4 (F = 9.854, p = 0.005) and L5 (F = 39. 266, p = 0.000). Both groups showed significant decreases in weight bearing, from 9.25% to 5.83% in the experimental group and from 9.33% to 4.25% in the control group (p < 0.05), but did not differ significantly between the two groups. These results suggests that stabilization exercises using ball can increases in the CSA of the MF segments, improvement in weight bearing, pain relief, and recovery from functional disorders, and the increases in the CSA of the MF of the L4 and L5 segments for patients with low back pain. Key PointsCompared with the stabilization exercise using a ball and general stabilization exercise increased the CSA of the MF, weight bearing, pain, and functional ability in patients with low back pain.We verified that increases in the CSA of the MF of the L4 and L5 segments and functional ability during the stabilization exercise using a ball.The stabilization exercise using a ball was shown to be an effective exercise method for patients with low back pain in a rehabilitation program by increasing functional ability and the CSA of the MF.
Keywords: Stabilization exercise; ball; cross-sectional area; low back pain; multifidus.
Figures
Figure 1.
CONSORT flowchart of this study
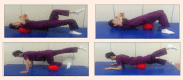
Figure 2.
The stabilization exercise using a ball
Figure 3.
The balance measurement
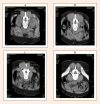
Figure 4.
Cross-sectional images of the multifidus muscle. (A) L2 region. (B) L3 region. (C) L4 region. (D) L5 region
Similar articles
- The effects of exposure to microgravity and reconditioning of the lumbar multifidus and anterolateral abdominal muscles: implications for people with LBP.
Hides JA, Lambrecht G, Sexton CT, Pruett C, Petersen N, Jaekel P, Rosenberger A, Weerts G. Hides JA, et al. Spine J. 2021 Mar;21(3):477-491. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2020.09.006. Epub 2020 Sep 20. Spine J. 2021. PMID: 32966906 - The association between back muscle characteristics and pressure pain sensitivity in low back pain patients.
Goubert D, Meeus M, Willems T, De Pauw R, Coppieters I, Crombez G, Danneels L. Goubert D, et al. Scand J Pain. 2018 Apr 25;18(2):281-293. doi: 10.1515/sjpain-2017-0142. Scand J Pain. 2018. PMID: 29794309 - Effect of stabilization training on multifidus muscle cross-sectional area among young elite cricketers with low back pain.
Hides JA, Stanton WR, McMahon S, Sims K, Richardson CA. Hides JA, et al. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2008 Mar;38(3):101-8. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2008.2658. Epub 2007 Dec 7. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2008. PMID: 18349481 - Effects of McKenzie and stabilization exercises in reducing pain intensity and functional disability in individuals with nonspecific chronic low back pain: a systematic review.
Alhakami AM, Davis S, Qasheesh M, Shaphe A, Chahal A. Alhakami AM, et al. J Phys Ther Sci. 2019 Jul;31(7):590-597. doi: 10.1589/jpts.31.590. Epub 2019 Jul 9. J Phys Ther Sci. 2019. PMID: 31417227 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Randomized Trial of General Strength and Conditioning Versus Motor Control and Manual Therapy for Chronic Low Back Pain on Physical and Self-Report Outcomes.
Tagliaferri SD, Miller CT, Ford JJ, Hahne AJ, Main LC, Rantalainen T, Connell DA, Simson KJ, Owen PJ, Belavy DL. Tagliaferri SD, et al. J Clin Med. 2020 Jun 3;9(6):1726. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061726. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32503243 Free PMC article. - Criterion Validity of Ultrasound Imaging: Assessment of Multifidi Cross-Sectional Area in Older Adults With and Without Chronic Low Back Pain.
Sions JM, Teyhen DS, Hicks GE. Sions JM, et al. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2017 Apr/Jun;40(2):74-79. doi: 10.1519/JPT.0000000000000073. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2017. PMID: 26703525 Free PMC article. - Comparing the Effects of Different Types of Aquatic Walking on Endurance and Electrical Activities of Spine Extensor Muscles in Men with Nonspecific Chronic Back Pain.
Rezai V, Mahdavi-Nejad R, Zolaktaf V. Rezai V, et al. Int J Prev Med. 2020 Oct 5;11:168. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_403_19. eCollection 2020. Int J Prev Med. 2020. PMID: 33312477 Free PMC article. - Optimising conservative management of chronic low back pain: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.
Simson KJ, Miller CT, Ford J, Hahne A, Main L, Rantalainen T, Teo WP, Teychenne M, Connell D, Trudel G, Zheng G, Thickbroom G, Belavy DL. Simson KJ, et al. Trials. 2017 Apr 20;18(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-1913-8. Trials. 2017. PMID: 28427472 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - An Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel Restores Disc Volume and Alleviates Axial Hypersensitivity in a Rat Model of Disc-Associated Pain.
Lillyman DJ, Reddick EC, Ney KE, Caparaso SM, Wachs RA. Lillyman DJ, et al. JOR Spine. 2025 May 15;8(2):e70073. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.70073. eCollection 2025 Jun. JOR Spine. 2025. PMID: 40386495 Free PMC article.
References
- Alexander K.M., LaPier T.L. (1998) Differences in static balance and weight distribution between normal subjects and subjects with chronic unilateral low back pain. Physical Therapy Journal of Orthopedic & Sports Physical Therapy 28(6), 378-383 - PubMed
- Anderson K., Behm D.G. (2005) Trunk muscle activity increases with unstable squat movements. Canadian Journal of Applied Physiology 30(1), 33-45 - PubMed
- Beneck G.J., Kulig K. (2012) Multifidus atrophy is localized and bilateral in active persons with chronic unilateral low back pain. Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 93(2), 300-306 - PubMed
- Bennell K.L., Goldie P.A. (1994) The differential effects of external ankle support on postural control. Physical Therapy Journal of Orthopedic & Sports Physical Therapy 20(6), 287-295 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources