Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence:significant findings in African- and European-Americans including novel risk loci - PubMed (original) (raw)
Multicenter Study
doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.145. Epub 2013 Oct 29.
H R Kranzler 2, R Sherva 3, L Almasy 4, R Koesterer 3, A H Smith 5, R Anton 6, U W Preuss 7, M Ridinger 8, D Rujescu 7, N Wodarz 8, P Zill 9, H Zhao 10, L A Farrer 11
Affiliations
- PMID: 24166409
- PMCID: PMC4165335
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2013.145
Multicenter Study
Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence:significant findings in African- and European-Americans including novel risk loci
J Gelernter et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2014 Jan.
Abstract
We report a GWAS of alcohol dependence (AD) in European-American (EA) and African-American (AA) populations, with replication in independent samples of EAs, AAs and Germans. Our sample for discovery and replication was 16 087 subjects, the largest sample for AD GWAS to date. Numerous genome-wide significant (GWS) associations were identified, many novel. Most associations were population specific, but in several cases were GWS in EAs and AAs for different SNPs at the same locus,showing biological convergence across populations. We confirmed well-known risk loci mapped to alcohol-metabolizing enzyme genes, notably ADH1B (EAs: Arg48His, P=1.17 × 10(-31); AAs: Arg369Cys, P=6.33 × 10(-17)) and ADH1C in AAs (Thr151Thr, P=4.94 × 10(-10)), and identified novel risk loci mapping to the ADH gene cluster on chromosome 4 and extending centromerically beyond it to include GWS associations at LOC100507053 in AAs (P=2.63 × 10(-11)), PDLIM5 in EAs (P=2.01 × 10(-8)), and METAP in AAs (P=3.35 × 10(-8)). We also identified a novel GWS association (1.17 × 10(-10)) mapped to chromosome 2 at rs1437396, between MTIF2 and CCDC88A, across all of the EA and AA cohorts, with supportive gene expression evidence, and population-specific GWS for markers on chromosomes 5, 9 and 19. Several of the novel associations implicate direct involvement of, or interaction with, genes previously identified as schizophrenia risk loci. Confirmation of known AD risk loci supports the overall validity of the study; the novel loci are worthy of genetic and biological follow-up. The findings support a convergence of risk genes (but not necessarily risk alleles) between populations, and, to a lesser extent, between psychiatric traits.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Although unrelated to the current study, Dr Kranzler has been a consultant or advisory board member for Alkermes, Lilly, Lundbeck, Pfizer and Roche. He is also a member of the American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology’s Alcohol Clinical Trials Initiative, which is supported by Lilly, Lundbeck, AbbVie and Pfizer.
Figures
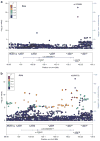
Figure 1
Chromosome 4 regional Manhattan plots. (a) European-Americans: regional Manhattan plot for the ADH gene cluster and adjacent regions on chromosome 4 showing the adjusted symptom count meta-analysis _P_-values from the discovery sample EAs, as well as points for the meta-analysis results after including our replication sample (diamonds). The points are colored based on degree of LD with rs1229984. Square points indicate genotyped SNPs and round points indicate imputed SNPs. All SNPs in the replication sample were genotyped. Data include the GCD sample plus SAGE, and GCD and German replication samples (diamonds). (b) African-Americans: regional Manhattan plot for the ADH gene cluster and adjacent regions on chromosome 4 showing the adjusted symptom count meta-analysis _P_-values from AAs in the discovery sample, as well as points for the meta-analysis result after inclusion of our replication sample (diamonds). The points are colored based on degree of LD with rs2066702. Square points indicate genotyped SNPs and round points indicate imputed SNPs. All SNPs in the replication sample were genotyped. Data include the GCD sample plus SAGE and the GCD replication sample (diamonds). AA, African-American; EA, European-American; LD, linkage disequilibrium; SAGE, study of addiction: genetics and environment.
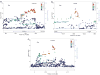
Figure 2
(a) Chromosome 2 regional Manhattan plot in European-Americans: regional Manhattan plot for the 136.70–136.90 MB region on chromosome 2 showing the adjusted symptom count meta-analysis _P_-values from EAs in the discovery sample. The points are colored based on the LD with rs925966. Square points indicate genotyped SNPs and round points indicate imputed SNPs. Data include the GCD sample plus SAGE. (b) Chromosome 4 PDLIM5 region in EAs: regional Manhattan plot for the 95.27–95.69 MB region containing PDLIM5 on chromosome 4 showing the adjusted symptom count meta-analysis _P_-values from EAs in the discovery sample. The points are colored based on the LD with rs10031423. Square points indicate genotyped SNPs and round points indicate imputed SNPs. Data include the GCD sample plus SAGE. (c) Chromosome 5 regional Manhattan plot in African-Americans: regional Manhattan plot for the 3.98–4.18 MB region on chromosome 5 showing the adjusted symptom count meta-analysis _P_-values from AAs in the discovery sample. The points are colored based on degree of LD with rs1493464. Square points indicate genotyped SNPs and round points indicate imputed SNPs. Data include the GCD sample plus SAGE. AA, African-American; EA, European-American; LD, linkage disequilibrium; SAGE, study of addiction: genetics and environment.
Similar articles
- Ancestry-specific and sex-specific risk alleles identified in a genome-wide gene-by-alcohol dependence interaction study of risky sexual behaviors.
Polimanti R, Zhao H, Farrer LA, Kranzler HR, Gelernter J. Polimanti R, et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017 Dec;174(8):846-853. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32604. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017. PMID: 28990359 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide association study of nicotine dependence in American populations: identification of novel risk loci in both African-Americans and European-Americans.
Gelernter J, Kranzler HR, Sherva R, Almasy L, Herman AI, Koesterer R, Zhao H, Farrer LA. Gelernter J, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Mar 1;77(5):493-503. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.08.025. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25555482 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence implicates KIAA0040 on chromosome 1q.
Zuo L, Gelernter J, Zhang CK, Zhao H, Lu L, Kranzler HR, Malison RT, Li CS, Wang F, Zhang XY, Deng HW, Krystal JH, Zhang F, Luo X. Zuo L, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012 Jan;37(2):557-66. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.229. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012. PMID: 21956439 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide association study of body mass index in subjects with alcohol dependence.
Polimanti R, Zhang H, Smith AH, Zhao H, Farrer LA, Kranzler HR, Gelernter J. Polimanti R, et al. Addict Biol. 2017 Mar;22(2):535-549. doi: 10.1111/adb.12317. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Addict Biol. 2017. PMID: 26458734 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide association discoveries of alcohol dependence.
Zuo L, Lu L, Tan Y, Pan X, Cai Y, Wang X, Hong J, Zhong C, Wang F, Zhang XY, Vanderlinden LA, Tabakoff B, Luo X. Zuo L, et al. Am J Addict. 2014 Nov-Dec;23(6):526-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1521-0391.2014.12147.x. Am J Addict. 2014. PMID: 25278008 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Depressive symptoms, avoidant coping, and alcohol use: differences based on gender and posttraumatic stress disorder in emerging adults.
Danielson CK, Hahn AM, Bountress KE, Gilmore AK, Roos L, Adams ZW, Kirby CM, Amstadter AB. Danielson CK, et al. Curr Psychol. 2024 Aug;43(29):24518-24526. doi: 10.1007/s12144-024-06150-x. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Curr Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39359620 Free PMC article. - Association patterns of antisocial personality disorder across substance use disorders.
Low A, Stiltner B, Nunez YZ, Adhikari K, Deak JD, Pietrzak RH, Kranzler HR, Gelernter J, Polimanti R. Low A, et al. Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Aug 28;14(1):346. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-03054-z. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39198385 Free PMC article. - Human genetics and epigenetics of alcohol use disorder.
Zhou H, Gelernter J. Zhou H, et al. J Clin Invest. 2024 Aug 15;134(16):e172885. doi: 10.1172/JCI172885. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39145449 Free PMC article. Review. - A genome-wide investigation into the underlying genetic architecture of personality traits and overlap with psychopathology.
Gupta P, Galimberti M, Liu Y, Beck S, Wingo A, Wingo T, Adhikari K, Kranzler HR; VA Million Veteran Program; Stein MB, Gelernter J, Levey DF. Gupta P, et al. Nat Hum Behav. 2024 Aug 12. doi: 10.1038/s41562-024-01951-3. Online ahead of print. Nat Hum Behav. 2024. PMID: 39134740 - Shared and unique 3D genomic features of substance use disorders across multiple cell types.
Trang KB, Chesi A, Toikumo S, Pippin JA, Pahl MC, O'Brien JM, Amundadottir LT, Brown KM, Yang W, Welles J, Santoleri D, Titchenell PM, Seale P, Zemel BS, Wagley Y, Hankenson KD, Kaestner KH, Anderson SA, Kayser MS, Wells AD, Kranzler HR, Kember RL, Grant SFA. Trang KB, et al. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 19:2024.07.18.24310649. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.18.24310649. medRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39072016 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
- Gelernter J, Sherva R, Koesterer R, Almasy L, Zhao H, Kranzler HR, et al. Genomewide association study of cocaine dependence and related traits: FAM53B identified as a risk gene. Mol Psychiatry. 2013 Aug 20; doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.99. advance online publication, (e-pub ahead of print) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RC2 DA028909/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA11330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 AA017435/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA089392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA12849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA018432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AA013736/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004422/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA013423/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007205/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA017535/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA12690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U10 AA008401/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA18432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HG65403/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases