Beyond Darwin: evolvability and the generation of novelty - PubMed (original) (raw)
Beyond Darwin: evolvability and the generation of novelty
Marc Kirschner. BMC Biol. 2013.
No abstract available
Figures
Marc Kirschner
Figure 1.
Darwin’s or Galapagos finches. Drawing from Darwin’s account of his observations on the voyage of HMS Beagle [2], showing the distinct adaptations of the beaks of the finches on Galapagos to different diets.
Figure 2.
The four-winged fruit fly. In the homeotic mutant bithorax, the halteres, which are a balancing organ, are transformed into a second pair of wings. The same transformation can be achieved by treating fruit fly pupae with ether, and selection of fruit flies by this treatment over several generations for expression of the phenotype in the absence of ether led Waddington to his theory of genetic assimilation [4]. (Figure credit: FlyBase)
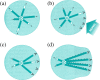
Figure 3.
Plasticity of microtubule arrays. Microtubules are composed of tubulin subunits that can rapidly polymerize and depolymerize, and are thus said to show dynamic instability. They are here shown (a) growing rapidly from the cell center (centrosome), and shrinking more rapidly, producing a random organization. (b) A signal from the cell surface leads to (c) the selective stabilization of the growing and shrinking microtubule ends locally, and in (d) the microtubules are further stabilized by modifications that accumulate along their length. In this way, spatially random polymerization and local stabilization can lead to organized arrays of microtubules (here polarizing the cell), and allow the evolution of stable structures such as flagella and dynamic ones such as the mitotic spindle. Figure modified with permission from Figure 4-5 of Gerhart and Kirschner, Cells, Embryos, and Evolution, Oxford: Blackwell Science; © 1997.
Similar articles
- Evolution and evolvability: celebrating Darwin 200.
Brookfield JF. Brookfield JF. Biol Lett. 2009 Feb 23;5(1):44-6. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2008.0639. Biol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19049953 Free PMC article. Review. - Is evolvability involved in the origin of modular variation?
Gardner A, Zuidema W. Gardner A, et al. Evolution. 2003 Jun;57(6):1448-50. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2003.tb00352.x. Evolution. 2003. PMID: 12894952 - Cooperation and conflict in the evolution of individuality. IV. Conflict mediation and evolvability in Volvox carteri.
Michod RE, Nedelcu AM, Roze D. Michod RE, et al. Biosystems. 2003 May;69(2-3):95-114. doi: 10.1016/s0303-2647(02)00133-8. Biosystems. 2003. PMID: 12689724 - The mutation matrix and the evolution of evolvability.
Jones AG, Arnold SJ, Bürger R. Jones AG, et al. Evolution. 2007 Apr;61(4):727-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00071.x. Evolution. 2007. PMID: 17439608 - From genes to phenotype: dynamical systems and evolvability.
Alberch P. Alberch P. Genetica. 1991;84(1):5-11. doi: 10.1007/BF00123979. Genetica. 1991. PMID: 1874440 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- The Role of Information in Evolutionary Biology.
Dickins TE. Dickins TE. Acta Biotheor. 2023 May 15;71(3):17. doi: 10.1007/s10441-023-09468-4. Acta Biotheor. 2023. PMID: 37184719 Free PMC article. - Compound Dynamics and Combinatorial Patterns of Amino Acid Repeats Encode a System of Evolutionary and Developmental Markers.
Pelassa I, Cibelli M, Villeri V, Lilliu E, Vaglietti S, Olocco F, Ghirardi M, Montarolo PG, Corà D, Fiumara F. Pelassa I, et al. Genome Biol Evol. 2019 Nov 1;11(11):3159-3178. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evz216. Genome Biol Evol. 2019. PMID: 31589292 Free PMC article. - Evolvability Is an Evolved Ability: The Coding Concept as the Arch-Unit of Natural Selection.
Janković S, Ćirković MM. Janković S, et al. Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2016 Mar;46(1):67-79. doi: 10.1007/s11084-015-9464-z. Epub 2015 Sep 29. Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2016. PMID: 26419865 - Multilevel Selection Theory and the Evolutionary Functions of Transposable Elements.
Brunet TD, Doolittle WF. Brunet TD, et al. Genome Biol Evol. 2015 Aug 6;7(8):2445-57. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv152. Genome Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 26253318 Free PMC article. - Mitochondria--metabolism and beyond.
Robertson M. Robertson M. BMC Biol. 2014 May 27;12:37. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-12-37. BMC Biol. 2014. PMID: 24885067 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
- Darwin CR. On the Origin of Species. London: John Murray; 1859.
- Darwin CR. Journal of Researches into the Natural History and Geology of the Countries Visited During the Voyage of H.M.S. Beagle Round the World, Under the Command of Capt. Fitz Roy RN. 2. London: John Murray; 1845.
- Waddington CH. Genetic assimilation of an acquired character. Evolution. 1953;7:118–126. doi: 10.2307/2405747. - DOI
- West Eberhard MJ. Developmental Plasticity and Evolution. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources