Metabolomic analyses for atherosclerosis, diabetes, and obesity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Metabolomic analyses for atherosclerosis, diabetes, and obesity
Fuyong Du et al. Biomark Res. 2013.
Abstract
Insulin resistance associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), obesity, and atherosclerosis is a global health problem. A portfolio of abnormalities of metabolic and vascular homeostasis accompanies T2DM and obesity, which are believed to conspire to lead to accelerated atherosclerosis and premature death. The complexity of metabolic changes in the diseases presents challenges for a full understanding of the molecular pathways contributing to the development of these diseases. The recent advent of new technologies in this area termed "Metabolomics" may aid in comprehensive metabolic analysis of these diseases. Therefore, metabolomics has been extensively applied to the metabolites of T2DM, obesity, and atherosclerosis not only for the assessment of disease development and prognosis, but also for the biomarker discovery of disease diagnosis. Herein, we summarize the recent applications of metabolomics technology and the generated datasets in the metabolic profiling of these diseases, in particular, the applications of these technologies to these diseases at the cellular, animal models, and human disease levels. In addition, we also extensively discuss the mechanisms linking the metabolic profiling in insulin resistance, T2DM, obesity, and atherosclerosis, with a particular emphasis on potential roles of increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitochondria dysfunctions.
Figures
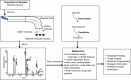
Figure 1
The work flow of Mass Spectrometry Schematic (MS-S) for metabolome analysis. The left panel depicts a triple-collector system arranged to analyze molecules and an example of total mass spectrum for the compounds A, B, C, D, E, F, and G in a reaction. The right panel outlines the relationship between the genome, proteome, and metabolome, as well as the significances of metabolomics.
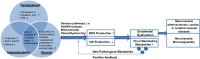
Figure 2
Metabolome analysis related to hyperglycemia/insulin resistance, obesity, and hyperlipidemia which contribute to the development of endothelial dysfunction. The reciprocal effects of hyperglycemia/insulin resistance, obesity, and dyslipidemia result in mitochondria stress/dysfunction via a complex of factors including oxidative stress, inflammation, incomplete fat oxidation, etc. As a result, mitochondria dysfunction increases the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and decreases nitric oxide (NO), which ultimately produces endothelial dysfunction and progressively causes atherosclerosis in macrovessels and microangiopathy in microvessels.
Similar articles
- Translational Metabolomics of Head Injury: Exploring Dysfunctional Cerebral Metabolism with Ex Vivo NMR Spectroscopy-Based Metabolite Quantification.
Wolahan SM, Hirt D, Glenn TC. Wolahan SM, et al. In: Kobeissy FH, editor. Brain Neurotrauma: Molecular, Neuropsychological, and Rehabilitation Aspects. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2015. Chapter 25. In: Kobeissy FH, editor. Brain Neurotrauma: Molecular, Neuropsychological, and Rehabilitation Aspects. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2015. Chapter 25. PMID: 26269925 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Small intestine proteomics coupled with serum metabolomics reveal disruption of amino acid metabolism in Chinese hamsters with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Wang C, Yu J, Zhang R, Wang W, Shi Z, Liu Y, Song G, Wang H, Han N, Huang L, An Y, Tian S, Chen Z. Wang C, et al. J Proteomics. 2020 Jul 15;223:103823. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2020.103823. Epub 2020 May 16. J Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 32428569 - Distinctive Metabolomics Patterns Associated With Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
Gu X, Al Dubayee M, Alshahrani A, Masood A, Benabdelkamel H, Zahra M, Li L, Abdel Rahman AM, Aljada A. Gu X, et al. Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Dec 14;7:609806. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.609806. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33381523 Free PMC article. - Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.
Valero T. Valero T. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795 - Increased oxidative stress in obesity: implications for metabolic syndrome, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, and cancer.
Matsuda M, Shimomura I. Matsuda M, et al. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2013 Sep-Oct;7(5):e330-41. doi: 10.1016/j.orcp.2013.05.004. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2013. PMID: 24455761 Review.
Cited by
- Metabolomics in diabetic nephropathy: Unveiling novel biomarkers for diagnosis (Review).
Luo Y, Zhang W, Qin G. Luo Y, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2024 Sep;30(3):156. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13280. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38963028 Free PMC article. Review. - Old and New Biomarkers Associated with Endothelial Dysfunction in Chronic Hyperglycemia.
Baldassarre MPA, Pipino C, Pandolfi A, Consoli A, Di Pietro N, Formoso G. Baldassarre MPA, et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Dec 27;2021:7887426. doi: 10.1155/2021/7887426. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34987703 Free PMC article. Review. - Editorial: Debates in cardiovascular pharmacology and drug discovery: 2022.
Xu K, Saaoud F, Shao Y, Lu Y, Jiang X, Wu S, Sun J, Fernades Conti F, Martinez L, Vazquez-Padron R, Wang H, Yang X. Xu K, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Oct 18;10:1304680. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1304680. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37920177 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Metabolomics in asthma: A platform for discovery.
Xu S, Panettieri RA Jr, Jude J. Xu S, et al. Mol Aspects Med. 2022 Jun;85:100990. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2021.100990. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Mol Aspects Med. 2022. PMID: 34281719 Free PMC article. Review. - Mechanism of Action of Acupuncture in Obesity: A Perspective From the Hypothalamus.
Wang L, Yu CC, Li J, Tian Q, Du YJ. Wang L, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Apr 2;12:632324. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.632324. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33868169 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Scarfe GB, Wright B, Clayton E, Taylor S, Wilson ID, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK. 19 F-NMR and directly coupled HPLC-NMR-MS investigations into the metabolism of 2-bromo-4-trifluoromethylaniline in rat: a urinary excretion balance study without the use of radiolabelling. Xenobiotica. 1998;28:373–388. doi: 10.1080/004982598239489. - DOI - PubMed
- Lindon JC, Holmes E, Nicholson JK. So what’s the deal with metabonomics? Anal Chem. 2003;75:384A–391A. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- R01 HL094451/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL108910/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL116917/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117654/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources