Adrenergic signaling and oxidative stress: a role for sirtuins? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Adrenergic signaling and oxidative stress: a role for sirtuins?
Graziamaria Corbi et al. Front Physiol. 2013.
Abstract
The adrenergic system plays a central role in stress signaling and stress is often associated with increased production of ROS. However, ROS overproduction generates oxidative stress, that occurs in response to several stressors. β-adrenergic signaling is markedly attenuated in conditions such as heart failure, with downregulation and desensitization of the receptors and their uncoupling from adenylyl cyclase. Transgenic activation of β2-adrenoceptor leads to elevation of NADPH oxidase activity, with greater ROS production and p38MAPK phosphorylation. Inhibition of NADPH oxidase or ROS significantly reduced the p38MAPK signaling cascade. Chronic β2-adrenoceptor activation is associated with greater cardiac dilatation and dysfunction, augmented pro-inflammatory and profibrotic signaling, while antioxidant treatment protected hearts against these abnormalities, indicating ROS production to be central to the detrimental signaling of β2-adrenoceptors. It has been demonstrated that sirtuins are involved in modulating the cellular stress response directly by deacetylation of some factors. Sirt1 increases cellular stress resistance, by an increased insulin sensitivity, a decreased circulating free fatty acids and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1), an increased activity of AMPK, increased activity of PGC-1a, and increased mitochondrial number. Sirt1 acts by involving signaling molecules such P-I-3-kinase-Akt, MAPK and p38-MAPK-β. βAR stimulation antagonizes the protective effect of the AKT pathway through inhibiting induction of Hif-1α and Sirt1 genes, key elements in cell survival. More studies are needed to better clarify the involvement of sirtuins in the β-adrenergic response and, overall, to better define the mechanisms by which tools such as exercise training are able to counteract the oxidative stress, by both activation of sirtuins and inhibition of GRK2 in many cardiovascular conditions and can be used to prevent or treat diseases such as heart failure.
Keywords: GRK2; exercise training; heart failure; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species; sirtuins; β-adrenergic system.
Figures
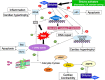
Figure 1
Cellular response to oxidative stress mediating by β-adrenergic response and sirtuins involvement. The ROS induce GRK2 hyperactivity that determines desensitization and internalization of β ARs with induction of cardiac hypertrophy (via AKT/NFkB pathway), apoptosis and senescence (by inhibition of FOXOs). Sirtuins (and their activators) are able to counteract these actions by direct effects on different molecules. ROS, reactive oxygen species; CR, caloric restriction; Ac, acetyl; P, phosphoryl. ↓ activation; ⊥ inhibition.
Similar articles
- Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.
Valero T. Valero T. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795 - Role of Beta-adrenergic Receptors and Sirtuin Signaling in the Heart During Aging, Heart Failure, and Adaptation to Stress.
Spadari RC, Cavadas C, de Carvalho AETS, Ortolani D, de Moura AL, Vassalo PF. Spadari RC, et al. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Jan;38(1):109-120. doi: 10.1007/s10571-017-0557-2. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29063982 Free PMC article. Review. - Regulation of cellular oxidative stress and apoptosis by G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2; The role of NADPH oxidase 4.
Theccanat T, Philip JL, Razzaque AM, Ludmer N, Li J, Xu X, Akhter SA. Theccanat T, et al. Cell Signal. 2016 Mar;28(3):190-203. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.11.013. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Cell Signal. 2016. PMID: 26631573 Free PMC article. - Myocardial oxidative stress contributes to transgenic β₂-adrenoceptor activation-induced cardiomyopathy and heart failure.
Xu Q, Dalic A, Fang L, Kiriazis H, Ritchie RH, Sim K, Gao XM, Drummond G, Sarwar M, Zhang YY, Dart AM, Du XJ. Xu Q, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Mar;162(5):1012-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01043.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20955367 Free PMC article. - Distinct beta-adrenergic receptor subtype signaling in the heart and their pathophysiological relevance.
Zheng M, Han QD, Xiao RP. Zheng M, et al. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2004 Feb 25;56(1):1-15. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2004. PMID: 14985822 Review.
Cited by
- Metabolic Changes in Cardiac Aging.
Hao Y, Liu W. Hao Y, et al. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Mar 6;24(3):82. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2403082. eCollection 2023 Mar. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39077479 Free PMC article. Review. - β-adrenergic receptor responsiveness in aging heart and clinical implications.
Ferrara N, Komici K, Corbi G, Pagano G, Furgi G, Rengo C, Femminella GD, Leosco D, Bonaduce D. Ferrara N, et al. Front Physiol. 2014 Jan 9;4:396. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00396. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24409150 Free PMC article. Review. - Exercise training enhanced SIRT1 longevity signaling replaces the IGF1 survival pathway to attenuate aging-induced rat heart apoptosis.
Lai CH, Ho TJ, Kuo WW, Day CH, Pai PY, Chung LC, Liao PH, Lin FH, Wu ET, Huang CY. Lai CH, et al. Age (Dordr). 2014;36(5):9706. doi: 10.1007/s11357-014-9706-4. Epub 2014 Aug 23. Age (Dordr). 2014. PMID: 25148910 Free PMC article. - Notoginsenoside R1 Protects Against High Glucose-Induced Cell Injury Through AMPK/Nrf2 and Downstream HO-1 Signaling.
Du F, Huang H, Cao Y, Ran Y, Wu Q, Chen B. Du F, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Dec 1;9:791643. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.791643. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34926469 Free PMC article. - Recent Advances on the Role of G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Hypoxia-Mediated Signaling.
Lappano R, Rigiracciolo D, De Marco P, Avino S, Cappello AR, Rosano C, Maggiolini M, De Francesco EM. Lappano R, et al. AAPS J. 2016 Mar;18(2):305-10. doi: 10.1208/s12248-016-9881-6. Epub 2016 Feb 10. AAPS J. 2016. PMID: 26865461 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Alcendor R. R., Kirshenbaum L. A., Imai S., Vatner S. F., Sadoshima J. (2004). Silent information regulator 2alpha, a longevity factor and class III histone deacetylase, is an essential endogenous apoptosis inhibitor in cardiac myocytes. Circ. Res. 95, 971–980 10.1161/01.RES.0000147557.75257.ff - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous