ModBase, a database of annotated comparative protein structure models and associated resources - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2014 Jan;42(Database issue):D336-46.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1144. Epub 2013 Nov 23.
Benjamin M Webb, Guang Qiang Dong, Dina Schneidman-Duhovny, Hao Fan, Seung Joong Kim, Natalia Khuri, Yannick G Spill, Patrick Weinkam, Michal Hammel, John A Tainer, Michael Nilges, Andrej Sali
Affiliations
- PMID: 24271400
- PMCID: PMC3965011
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt1144
ModBase, a database of annotated comparative protein structure models and associated resources
Ursula Pieper et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan.
Abstract
ModBase (http://salilab.org/modbase) is a database of annotated comparative protein structure models. The models are calculated by ModPipe, an automated modeling pipeline that relies primarily on Modeller for fold assignment, sequence-structure alignment, model building and model assessment (http://salilab.org/modeller/). ModBase currently contains almost 30 million reliable models for domains in 4.7 million unique protein sequences. ModBase allows users to compute or update comparative models on demand, through an interface to the ModWeb modeling server (http://salilab.org/modweb). ModBase models are also available through the Protein Model Portal (http://www.proteinmodelportal.org/). Recently developed associated resources include the AllosMod server for modeling ligand-induced protein dynamics (http://salilab.org/allosmod), the AllosMod-FoXS server for predicting a structural ensemble that fits an SAXS profile (http://salilab.org/allosmod-foxs), the FoXSDock server for protein-protein docking filtered by an SAXS profile (http://salilab.org/foxsdock), the SAXS Merge server for automatic merging of SAXS profiles (http://salilab.org/saxsmerge) and the Pose & Rank server for scoring protein-ligand complexes (http://salilab.org/poseandrank). In this update, we also highlight two applications of ModBase: a PSI:Biology initiative to maximize the structural coverage of the human alpha-helical transmembrane proteome and a determination of structural determinants of human immunodeficiency virus-1 protease specificity.
Figures
Figure 1.
The computed profiles for filament models of the XLF–XRCC4 complex (63) are fitted to the experimental SAXS profile with FoXS. The interactive user interface displays the profiles in the left and the models in the right using the same color for each model/profile pair. The table below the panels displays the fit parameters and includes buttons to simultaneously show or hide each model/profile pair. Clicking on Minimal Ensemble Search (MES) results (above the display panel) takes the user to the MES output page.
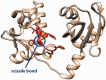
Figure 2.
Cleavage of human proteins by the HIV-1 protease: crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of human Lupus La protein (92) (left). Residues of the cleavage site (Ile-Asp-Tyr-Tyr-Phe-Gly-Glu-Phe) are shown in orange. Scissile bond between Tyr and Phe in the alpha-helix is cleaved by the HIV-1 protease in vitro.
Figure 3.
ModBase interface elements. Search Form: search options are available through the pull-down menu. A quick overview of the available representations is displayed below the search form. Model Details Sketch: the Model details page provides information for all models of a given sequences. The sketch comprises two parts: the model coverage sketch that indicates the sequence coverage by all models (top line) and the sequence coverage by the current model (second line), and a ribbon diagram of the current model. Other models are available via thumbprints. Update and Remodel: this box shows the date of the last modeling calculation for the current sequence, and allows the user to request an update. Chimera Visualization: the visualization includes the model and template structures and the alignment. Cross-references: links to the PMP, UniProtKB, Genbank, UCSC Genome Browser and other databases. Model Details Options: the pull-down menu switches between representations and allows downloads of coordinate and alignment files. Quality Criteria: red indicates unreliable, green reliable. Model Overview: a different representation for several sequences gives a quick overview on modeling coverage and quality. Chimera Cavity View: visualizes cavities predicted by ConCavity.
Similar articles
- ModBase, a database of annotated comparative protein structure models, and associated resources.
Pieper U, Webb BM, Barkan DT, Schneidman-Duhovny D, Schlessinger A, Braberg H, Yang Z, Meng EC, Pettersen EF, Huang CC, Datta RS, Sampathkumar P, Madhusudhan MS, Sjölander K, Ferrin TE, Burley SK, Sali A. Pieper U, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(Database issue):D465-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1091. Epub 2010 Nov 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21097780 Free PMC article. - MODBASE: a database of annotated comparative protein structure models and associated resources.
Pieper U, Eswar N, Davis FP, Braberg H, Madhusudhan MS, Rossi A, Marti-Renom M, Karchin R, Webb BM, Eramian D, Shen MY, Kelly L, Melo F, Sali A. Pieper U, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jan 1;34(Database issue):D291-5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj059. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16381869 Free PMC article. - MODBASE, a database of annotated comparative protein structure models and associated resources.
Pieper U, Eswar N, Webb BM, Eramian D, Kelly L, Barkan DT, Carter H, Mankoo P, Karchin R, Marti-Renom MA, Davis FP, Sali A. Pieper U, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jan;37(Database issue):D347-54. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn791. Epub 2008 Oct 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 18948282 Free PMC article. - Integrative structural modeling with small angle X-ray scattering profiles.
Schneidman-Duhovny D, Kim SJ, Sali A. Schneidman-Duhovny D, et al. BMC Struct Biol. 2012 Jul 16;12:17. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-12-17. BMC Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22800408 Free PMC article. Review. - Hybrid Methods for Modeling Protein Structures Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering Data.
Ekimoto T, Ikeguchi M. Ekimoto T, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1105:237-258. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-2200-6_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30617833 Review.
Cited by
- Genome-wide mitochondrial DNA sequence variations and lower expression of OXPHOS genes predict mitochondrial dysfunction in oral cancer tissue.
Chattopadhyay E, De Sarkar N, Singh R, Ray A, Roy R, Paul RR, Pal M, Ghose S, Ghosh S, Kabiraj D, Banerjee R, Roy B. Chattopadhyay E, et al. Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):11861-11871. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5026-x. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27055661 - Genome-Wide Inference of Protein-Protein Interaction Networks Identifies Crosstalk in Abscisic Acid Signaling.
Zhang F, Liu S, Li L, Zuo K, Zhao L, Zhang L. Zhang F, et al. Plant Physiol. 2016 Jun;171(2):1511-22. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00057. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27208273 Free PMC article. - Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER.
Webb B, Sali A. Webb B, et al. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2016 Jun 20;54:5.6.1-5.6.37. doi: 10.1002/cpbi.3. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27322406 Free PMC article. - AraPPINet: An Updated Interactome for the Analysis of Hormone Signaling Crosstalk in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Zhao J, Lei Y, Hong J, Zheng C, Zhang L. Zhao J, et al. Front Plant Sci. 2019 Jul 5;10:870. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00870. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31333706 Free PMC article. - Mabellini: a genome-wide database for understanding the structural proteome and evaluating prospective antimicrobial targets of the emerging pathogen Mycobacterium abscessus.
Skwark MJ, Torres PHM, Copoiu L, Bannerman B, Floto RA, Blundell TL. Skwark MJ, et al. Database (Oxford). 2019 Jan 1;2019(1):baz113. doi: 10.1093/database/baz113. Database (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 31681953 Free PMC article.
References
- Baker D, Sali A. Protein structure prediction and structural genomics. Science. 2001;294:93–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P41 GM103311/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM094625/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA092584/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM105404/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM093342/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM094662/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM105404/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases