Recent developments of protein kinase inhibitors as potential AD therapeutics - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Recent developments of protein kinase inhibitors as potential AD therapeutics
Volkmar Tell et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013.
Abstract
Present Alzheimer's disease (AD) therapies suffer from inefficient effects on AD symptoms like memory or cognition, especially in later states of the disease. Used acteylcholine esterase inhibitors or the NMDA receptor antagonist memantine address one target structure which is involved in a complex, multifactorial disease progression. So the benefit for patients is presently poor. A more close insight in the AD progression identified more suggested target structures for drug development. Strategies of AD drug development concentrate on novel target structures combined with the established ones dedicated for combined therapy regimes, preferably by the use of one drug which may address two target structures. Protein kinases have been identified as promising target structures because they are involved in AD progression pathways like pathophysiological tau protein phosphorylations and amyloid β toxicity. The review article will shortly view early inhibitors of single protein kinases like glycogen synthase kinase (gsk3) β and cyclin dependent kinase 5. Novel inhibitors will be discussed which address novel AD relevant protein kinases like dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A). Moreover, multitargeting inhibitors will be presented which target several protein kinases and those which are suspected in influencing other AD relevant processes. Such a multitargeting is the most promising strategy to effectively hamper the multifactorial disease progression and thus gives perspective hopes for a future better patient benefit.
Keywords: inhibitor; inhibitor binding; protein kinase; small molecules; structure–activity relationships; tau phosphorylation.
Figures
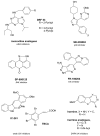
FIGURE 1
Single protein kinase-targeting inhibitors.
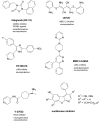
FIGURE 2
Multitargeting inhibitors.
Similar articles
- A novel DYRK1A (dual specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A) inhibitor for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: effect on Tau and amyloid pathologies in vitro.
Coutadeur S, Benyamine H, Delalonde L, de Oliveira C, Leblond B, Foucourt A, Besson T, Casagrande AS, Taverne T, Girard A, Pando MP, Désiré L. Coutadeur S, et al. J Neurochem. 2015 May;133(3):440-51. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13018. Epub 2015 Jan 26. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25556849 - Drug Development of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of AD-Relevant Kinases as Novel Perspective Multitargeted Approach.
Tell V, Hilbrich I, Holzer M, Totzke F, Schachtele C, Slynko I, Sippl W, Hilgeroth A. Tell V, et al. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(12):1330-1336. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666160615091821. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 27306698 Review. - Leucettine L41, a DYRK1A-preferential DYRKs/CLKs inhibitor, prevents memory impairments and neurotoxicity induced by oligomeric Aβ25-35 peptide administration in mice.
Naert G, Ferré V, Meunier J, Keller E, Malmström S, Givalois L, Carreaux F, Bazureau JP, Maurice T. Naert G, et al. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015 Nov;25(11):2170-82. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26381812 - [Therapy of Alzheimer disease].
Kovács T. Kovács T. Neuropsychopharmacol Hung. 2009 Mar;11(1):27-33. Neuropsychopharmacol Hung. 2009. PMID: 19731816 Review. Hungarian. - Kororamides, Convolutamines, and Indole Derivatives as Possible Tau and Dual-Specificity Kinase Inhibitors for Alzheimer's Disease: A Computational Study.
Llorach-Pares L, Nonell-Canals A, Avila C, Sanchez-Martinez M. Llorach-Pares L, et al. Mar Drugs. 2018 Oct 16;16(10):386. doi: 10.3390/md16100386. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30332805 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Advances in developing novel therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer's disease.
Cao J, Hou J, Ping J, Cai D. Cao J, et al. Mol Neurodegener. 2018 Dec 12;13(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0299-8. Mol Neurodegener. 2018. PMID: 30541602 Free PMC article. Review. - Kinase-Based Taming of Brain Microglia Toward Disease-Modifying Therapy.
Lee SH, Suk K. Lee SH, et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Dec 5;12:474. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00474. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30568577 Free PMC article. Review. - Profiling tyrosine kinase inhibitors as AD therapeutics in a mouse model of AD.
Lee HJ, Hwang JW, Park JH, Jeong YJ, Jang JY, Hoe HS. Lee HJ, et al. Mol Brain. 2023 Aug 14;16(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13041-023-01051-9. Mol Brain. 2023. PMID: 37580778 Free PMC article. - Hyperexpressed Netrin-1 Promoted Neural Stem Cells Migration in Mice after Focal Cerebral Ischemia.
Lu H, Song X, Wang F, Wang G, Wu Y, Wang Q, Wang Y, Yang GY, Zhang Z. Lu H, et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Sep 30;10:223. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00223. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27746720 Free PMC article. - l-Lactate Dehydrogenase Identified as a Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Substrate by Using K-BIPS.
Acharige NPN, Pflum MKH. Acharige NPN, et al. Chembiochem. 2021 Jan 5;22(1):186-192. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202000499. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Chembiochem. 2021. PMID: 33002308 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources