Signalling C-type lectin receptors, microbial recognition and immunity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Signalling C-type lectin receptors, microbial recognition and immunity
J Claire Hoving et al. Cell Microbiol. 2014 Feb.
Abstract
Signalling C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) are crucial in shaping the immune response to fungal pathogens, but comparably little is known about the role of these receptors in bacterial, viral and parasitic infections. CLRs have many diverse functions depending on the signalling motifs in their cytoplasmic domains, and can induce endocytic, phagocytic, antimicrobial, pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory responses which are either protective or not during an infection. Understanding the role of CLRs in shaping anti-microbial immunity offers great potential for the future development of therapeutics for disease intervention. In this review we will focus on the recognition of bacterial, viral and parasitic pathogens by CLRs, and how these receptors influence the outcome of infection. We will also provide a brief update on the role of CLRs in antifungal immunity.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
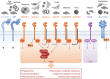
Figure 1
Recognition of microorganisms by signalling
CLR
s. Cartoon representation of the
C
‐type lectin receptors discussed in the text. Also shown is the microbes they recognize, the major intracellular signalling pathways utilized by these receptors, and the responses they induce.
ITAM
indicates receptors utilizing immunoreceptor tyrosine‐based activation motifs;
ITIM
indicates receptors utilizing immunoreceptor tyrosine‐based inhibitory motifs.
CR
(cysteine‐rich domain),
FNII
(fibronectin domain).
Similar articles
- The role of platelets in defence against pathogens.
Clemetson KJ. Clemetson KJ. Hamostaseologie. 2011 Nov;31(4):264-8. doi: 10.5482/ha-1152. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Hamostaseologie. 2011. PMID: 21709931 - C-type lectin receptors in anti-fungal immunity.
Shiokawa M, Yamasaki S, Saijo S. Shiokawa M, et al. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2017 Dec;40:123-130. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2017.11.004. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29169147 Review. - Parasitic infections: a role for C-type lectins receptors.
Vázquez-Mendoza A, Carrero JC, Rodriguez-Sosa M. Vázquez-Mendoza A, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:456352. doi: 10.1155/2013/456352. Epub 2013 Jan 27. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23509724 Free PMC article. Review. - T Cell Antifungal Immunity and the Role of C-Type Lectin Receptors.
Speakman EA, Dambuza IM, Salazar F, Brown GD. Speakman EA, et al. Trends Immunol. 2020 Jan;41(1):61-76. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2019.11.007. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Trends Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31813764 Free PMC article. Review. - Eating the enemy within: autophagy in infectious diseases.
Orvedahl A, Levine B. Orvedahl A, et al. Cell Death Differ. 2009 Jan;16(1):57-69. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2008.130. Epub 2008 Sep 5. Cell Death Differ. 2009. PMID: 18772897 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Innate immune pattern recognition: a cell biological perspective.
Brubaker SW, Bonham KS, Zanoni I, Kagan JC. Brubaker SW, et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 2015;33:257-90. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112240. Epub 2015 Jan 2. Annu Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25581309 Free PMC article. Review. - Resolution of neuroinflammation: mechanisms and potential therapeutic option.
Dokalis N, Prinz M. Dokalis N, et al. Semin Immunopathol. 2019 Nov;41(6):699-709. doi: 10.1007/s00281-019-00764-1. Epub 2019 Nov 8. Semin Immunopathol. 2019. PMID: 31705317 Review. - Inflammatory cell death: how macrophages sense neighbouring cell infection and damage.
Wang X, Labzin LI. Wang X, et al. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Feb 27;51(1):303-313. doi: 10.1042/BST20220807. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 36695550 Free PMC article. Review. - CARD9 Is Required for Classical Macrophage Activation and the Induction of Protective Immunity against Pulmonary Cryptococcosis.
Campuzano A, Castro-Lopez N, Martinez AJ, Olszewski MA, Ganguly A, Leopold Wager C, Hung CY, Wormley FL Jr. Campuzano A, et al. mBio. 2020 Jan 7;11(1):e03005-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03005-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 31911495 Free PMC article. - Crosstalk Between Autophagy and the cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway in Type I Interferon Production.
Zhang K, Wang S, Gou H, Zhang J, Li C. Zhang K, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 29;9:748485. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.748485. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34926445 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Akira, S. , Uematsu, S. , and Takeuchi, O. (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124: 783–801. - PubMed
- Avota, E. , Koethe, S. , and Schneider‐Schaulies, S. (2013) Membrane dynamics and interactions in measles virus dendritic cell infections. Cell Microbiol 15: 161–169. - PubMed
- Broz, P. , and Monack, D.M. (2013) Newly described pattern recognition receptors team up against intracellular pathogens. Nat Rev Immunol 13: 551–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 102705/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 097377/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 102705/Z/13/Z/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical