ZIP4 is a novel diagnostic and prognostic marker in human pancreatic cancer: a systemic comparison between EUS-FNA and surgical specimens - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.2174/1566524013666131217112921.
M B Wallace, J Yang, L Jiang, Q Zhai, Y Zhang, C Hong, Y Chen, T S Frank, J A Stauffer, H J Asbun, M Raimondo, T A Woodward, Z Li, S Guha, L Zheng, M Li 1
Affiliations
- PMID: 24345208
- PMCID: PMC6870177
- DOI: 10.2174/1566524013666131217112921
ZIP4 is a novel diagnostic and prognostic marker in human pancreatic cancer: a systemic comparison between EUS-FNA and surgical specimens
C Xu et al. Curr Mol Med. 2014 Mar.
Abstract
Aberrant expression of a zinc transporter ZIP4 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has been shown to contribute to tumor progression and is a potential target for individualized therapy. The overall objective of this study was to determine whether ZIP4 could serve as a novel diagnostic and prognostic marker in human PDAC, and if it can be assessed by minimally invasive sampling using endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA). Immunohistochemistry was performed to compare ZIP4 expression in the PDAC samples obtained from EUS-FNA and matched surgical tumors (parallel control). Samples were reported by sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values, all with 95% confidence intervals (CI). A total of 23 cases with both FNA and surgical specimens were evaluated. We found that ZIP4 was significantly overexpressed in tumor cells from both sets of samples. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) of ZIP4 for the diagnosis of PDAC were 72.9%, 72.5%, 76.1%, and 69.0% in EUS-FNA samples, and were 97.9%, 65.4%, 83.9%, and 94.4% in surgical specimens, respectively. The association between the positive rate of ZIP4 expression in FNA and surgical samples is statistically significant (P=0.0216). Both the intensity and percentage of ZIP4 positive cells from the surgical samples correlated significantly with tumor stage (P=0.0025 and P=0.0002). ZIP4 intensity level in FNA samples was significantly associated with tumor differentiation and patient survival. These results indicate that EUS-FNA is capable of non-operative detection of ZIP4, thus offering the potential to direct pre-operative detection and targeted therapy of PDAC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Dr. Michael B. Wallace received research funding from Boston Scientific. Other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
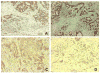
Fig. 1. ZIP4 is overexpressed in PDAC surgical samples
IHC staining of ZIP4 in surgically resected human PDAC tissues with AEC substrate. (A) ZIP4 positive staining with surrounding non-tumoral glands as an internal negative control. The upper half is pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with strongly positive (3+) ZIP4 staining. The lower half is benign pancreatic tissue including glands, ducts, and stroma which are negative for ZIP4. (B) ZIP4 positive staining with 3+ intensity. (C) ZIP4 positive staining with 2+ intensity. (D) ZIP4 positive staining with 1+ intensity.
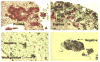
Fig. 2. ZIP4 is overexpressed in FNA samples
IHC staining of ZIP4 in EUS-FNA human PDAC samples with AEC substrate. (A) ZIP4 positive staining with 3+ intensity. (B) ZIP4 positive staining with 2+ intensity. (C) ZIP4 positive staining with 1+ intensity. (D) ZIP4 negative staining.
Similar articles
- [Value of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration in pretest prediction and diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma].
Wu L, Guo W, Li Y, Cheng T, Yao Y, Zhang Y, Liu B, Zhong M, Li S, Deng X, Zhu W. Wu L, et al. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2018 Sep 30;38(10):1171-1178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2018.10.04. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2018. PMID: 30377133 Free PMC article. Chinese. - Prognostic influence of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration in IPMN-derived invasive adenocarcinoma.
Suzuki R, Irie H, Takagi T, Sugimoto M, Konno N, Sato Y, Watanabe K, Nakamura J, Marubashi S, Hikichi T, Ohira H. Suzuki R, et al. BMC Cancer. 2018 Oct 12;18(1):974. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4896-2. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30314433 Free PMC article. - Immunocytochemistry for SOX-11 and TFE3 as diagnostic markers for solid pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas in FNA biopsies.
Foo WC, Harrison G, Zhang X. Foo WC, et al. Cancer Cytopathol. 2017 Nov;125(11):831-837. doi: 10.1002/cncy.21931. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Cancer Cytopathol. 2017. PMID: 29045075 - Pathological and Molecular Aspects to Improve Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration From Solid Pancreatic Lesions.
Matsubayashi H, Sasaki K, Ono S, Abe M, Ishiwatari H, Fukutomi A, Uesaka K, Ono H. Matsubayashi H, et al. Pancreas. 2018 Feb;47(2):163-172. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000986. Pancreas. 2018. PMID: 29346217 Review.
Cited by
- A Novel ZIP4-HDAC4-VEGFA Axis in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer.
Fan Q, Li L, Wang TL, Emerson RE, Xu Y. Fan Q, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 29;13(15):3821. doi: 10.3390/cancers13153821. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359722 Free PMC article. - Analysis the prognostic values of solute carrier (SLC) family 39 genes in gastric cancer.
Ding B, Lou W, Xu L, Li R, Fan W. Ding B, et al. Am J Transl Res. 2019 Jan 15;11(1):486-498. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 30788004 Free PMC article. - Current status of biomarker and targeted nanoparticle development: The precision oncology approach for pancreatic cancer therapy.
Zhu L, Staley C, Kooby D, El-Rays B, Mao H, Yang L. Zhu L, et al. Cancer Lett. 2017 Mar 1;388:139-148. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.11.030. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 27916607 Free PMC article. - Role of methylation-related genes CRYAB and SLC39A11 in the occurrence and development of lung adenocarcinoma.
Wang S, Gui P, Liu Y, Liang X, Fan B, Shang W, Wang D, Shao S, Sun L. Wang S, et al. Ann Transl Med. 2022 Oct;10(20):1126. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3576. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36388803 Free PMC article. - ZIP4 Promotes Muscle Wasting and Cachexia in Mice With Orthotopic Pancreatic Tumors by Stimulating RAB27B-Regulated Release of Extracellular Vesicles From Cancer Cells.
Yang J, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Ni X, Zhang G, Cui X, Liu M, Xu C, Zhang Q, Zhu H, Yan J, Zhu VF, Luo Y, Hagan JP, Li Z, Fang J, Jatoi A, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Zheng L, Edil BH, Bronze MS, Houchen CW, Li YP, Li M. Yang J, et al. Gastroenterology. 2019 Feb;156(3):722-734.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.10.026. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30342032 Free PMC article.
References
- Campen CJ, Dragovich T, Baker AF. Management strategies in pancreatic cancer. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2011;68(7):573–84. - PubMed
- Lewis JJ, Kowalski TE. Endoscopic ultrasound and fine needle aspiration in pancreatic cancer. Cancer J. 2012;18(6):523–9. - PubMed
- Chen G, Liu S, Zhao Y, Dai M, Zhang T. Diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. Pancreatology. 2013;13(3):298–304. - PubMed
- Meftah SP, Kuivaniemi H, Tromp G, et al. A new mutation in exon 3 of the SCL39A4 gene in a Tunisian family with severe acrodermatitis enteropathica. Nutrition. 2006;22(10):1067–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical