Frequencies of circulating MDSC correlate with clinical outcome of melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab - PubMed (original) (raw)
Frequencies of circulating MDSC correlate with clinical outcome of melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab
Christiane Meyer et al. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014 Mar.
Abstract
Metastatic melanoma has a poor prognosis with high resistance to chemotherapy and radiation. Recently, the anti-CTLA-4 antibody ipilimumab has demonstrated clinical efficacy, being the first agent to significantly prolong the overall survival of inoperable stage III/IV melanoma patients. A major aim of patient immune monitoring is the identification of biomarkers that predict clinical outcome. We studied circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) in ipilimumab-treated patients to detect alterations in the myeloid cell compartment and possible correlations with clinical outcome. Lin(-) CD14(+) HLA-DR(-) monocytic MDSC were enriched in peripheral blood of melanoma patients compared to healthy donors (HD). Tumor resection did not significantly alter MDSC frequencies. During ipilimumab treatment, MDSC frequencies did not change significantly compared to baseline levels. We observed high inter-patient differences. MDSC frequencies in ipilimumab-treated patients were independent of baseline serum lactate dehydrogenase levels but tended to increase in patients with severe metastatic disease (M1c) compared to patients with metastases in skin or lymph nodes only (M1a), who had frequencies comparable to HD. Interestingly, clinical responders to ipilimumab therapy showed significantly less lin(-) CD14(+) HLA-DR(-) cells as compared to non-responders. The data suggest that the frequency of monocytic MDSC may be used as predictive marker of response, as low frequencies identify patients more likely benefitting from ipilimumab treatment. Prospective clinical trials assessing MDSC frequencies as potential biomarkers are warranted to validate these observations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
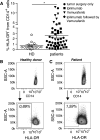
Fig. 1
MDSC frequencies are increased in patients with melanoma. PBMC from healthy donors and melanoma patients were assessed by flow cytometry. a % lin− CD14+ HLA-DR− cells (monocytic MDSC) in healthy donors (HD; 0.69 ± 0.67 %, N = 15) and melanoma patients (2.57 ± 2.97 %, N = 49). Symbols in the figure correspond to either 1 blood sample per patient or the average frequency from several blood samples obtained per patient. Melanoma treatments received: tumor surgery only (circles), ipilimumab (squares), vemurafenib (triangles), ipilimumab followed by vemurafenib (diamonds). b Representative dot plots for one healthy donor and c one melanoma patient. *p < 0.05
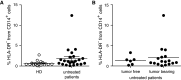
Fig. 2
MDSC in untreated patients with and without active diseases. PBMC from healthy donors and untreated melanoma patients were assessed by flow cytometry. a % lin− CD14+ HLA-DR− cells in HD (0.69 ± 0.67 %, N = 15) and non-treated melanoma patients (1.86 ± 2.56 %, N = 23). b % lin− CD14+ HLA-DR− cells in untreated patients after tumor resection (1.36 ± 1.10 %, N = 6) and untreated patients with tumor burden (2.03 ± 2.92 %, N = 17). Symbols in the figure correspond to 1 blood sample per patient
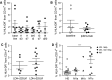
Fig. 3
MDSC in ipilimumab-treated patients and in patients with different disease stages. PBMC from melanoma patients receiving ipilimumab treatment were assessed by flow cytometry. a % lin− CD14+ HLA-DR− cells in melanoma patients receiving ipilimumab treatment. MDSC frequencies are displayed for each day of blood withdrawal: baseline 3.02 ± 3.53 % (N = 8), t1d3 1.07 ± 0.75 % (N = 7), t1d7 1.69 ± 1.90 % (N = 8), before t3 1.00 ± 0.75 % (N = 5), t3d7 2.10 ± 1.77 % (N = 6) and t4d20 2.09 ± 2.50 % (N = 3). b MDSC frequencies are displayed at baseline (3.02 ± 3.53 %, N = 8) and during/after treatment (1.46 ± 1.17 %, N = 8). c % lin− CD14+ HLA-DR− cells in ipilimumab-treated patients with normal baseline serum LDH level (1.73 ± 1.42 %, N = 5) and elevated baseline serum LDH level (2.31 ± 1.55 %, N = 9). d % lin− CD14+ HLA-DR− cells in HD (0.69 ± 0.67 %, N = 15) and ipilimumab-treated patients with metastatic staging M1a (0.78 ± 0.45 %, N = 4), M1b (N = 2) and M1c (2.58 ± 1.69 %, N = 8). Symbols in the figure correspond to either 1 blood sample per patient or the average frequency from several blood samples obtained per patient. Clinical responder (triangle upward) and clinical non-responder (triangle downward). ***p < 0.001. LDH serum lactate dehydrogenase
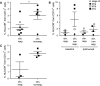
Fig. 4
MDSC in patients responding or non-responding to ipilimumab treatments. PBMC from melanoma patients receiving ipilimumab treatment were assessed by flow cytometry. a % lin− CD14+ HLA-DR− cells in ipilimumab-treated patients responding (1.24 ± 1.11 %, N = 8) or non-responding (3.06 ± 1.51 %, N = 6) to the treatment. b Baseline levels of % lin− CD14+ HLA-DR− cells for clinical responders (0.93 ± 0.75 %, N = 3) and clinical non-responders (4.85 ± 4.42 %, N = 4) and frequencies during treatment for clinical responders (1.00 ± 0.97 %, N = 3) and non-responders (1.87 ± 1.45 %, N = 4). c % lin− CD14+ HLA-DR− cells in ipilimumab-treated patients with distant metastasis (M1c) responding (1.39 ± 1.94 %, N = 3) or non-responding (3.77 ± 0.59 %, N = 4) to the treatment. Symbols in the figure correspond to either 1 blood sample per patient or the average frequency from several blood samples obtained per patient. *p < 0.05
Similar articles
- Clinical Significance of Circulating CD33+CD11b+HLA-DR- Myeloid Cells in Patients with Stage IV Melanoma Treated with Ipilimumab.
Sade-Feldman M, Kanterman J, Klieger Y, Ish-Shalom E, Olga M, Saragovi A, Shtainberg H, Lotem M, Baniyash M. Sade-Feldman M, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Dec 1;22(23):5661-5672. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-3104. Epub 2016 May 13. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27178742 - Baseline Peripheral Blood Biomarkers Associated with Clinical Outcome of Advanced Melanoma Patients Treated with Ipilimumab.
Martens A, Wistuba-Hamprecht K, Geukes Foppen M, Yuan J, Postow MA, Wong P, Romano E, Khammari A, Dreno B, Capone M, Ascierto PA, Di Giacomo AM, Maio M, Schilling B, Sucker A, Schadendorf D, Hassel JC, Eigentler TK, Martus P, Wolchok JD, Blank C, Pawelec G, Garbe C, Weide B. Martens A, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jun 15;22(12):2908-18. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2412. Epub 2016 Jan 19. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26787752 Free PMC article. - Ipilimumab-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity of regulatory T cells ex vivo by nonclassical monocytes in melanoma patients.
Romano E, Kusio-Kobialka M, Foukas PG, Baumgaertner P, Meyer C, Ballabeni P, Michielin O, Weide B, Romero P, Speiser DE. Romano E, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 12;112(19):6140-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417320112. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25918390 Free PMC article. - Adjuvant therapy for resected stage III melanoma patients: high-dose interferon-alpha versus ipilimumab combined with kinases inhibitors.
Minutilli E, Feliciani C. Minutilli E, et al. Tumori. 2012 Mar-Apr;98(2):185-90. doi: 10.1177/030089161209800202. Tumori. 2012. PMID: 22677983 Review. - Ipilimumab in melanoma.
Specenier P. Specenier P. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2016 Aug;16(8):811-26. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2016.1211936. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27403706 Review.
Cited by
- Unlocking the potential of immunotherapy in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer: rationale, challenges, and novel strategies.
Kefas J, Flynn M. Kefas J, et al. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024 Oct 15;7:39. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.67. eCollection 2024. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39534871 Free PMC article. Review. - Inhibition of Notch enhances efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade in triple-negative breast cancer.
Shen Q, Murakami K, Sotov V, Butler M, Ohashi PS, Reedijk M. Shen Q, et al. Sci Adv. 2024 Nov;10(44):eado8275. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ado8275. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39475614 Free PMC article. - NAC1 promotes stemness and regulates myeloid-derived cell status in triple-negative breast cancer.
Ngule C, Shi R, Ren X, Jia H, Oyelami F, Li D, Park Y, Kim J, Hemati H, Zhang Y, Xiong X, Shinkle A, Vanderford NL, Bachert S, Zhou BP, Wang J, Song J, Liu X, Yang JM. Ngule C, et al. Mol Cancer. 2024 Sep 6;23(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02102-y. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39243032 Free PMC article. - Neutrophil-like Monocytes Increase in Patients with Colon Cancer and Induce Dysfunctional TIGIT+ NK Cells.
Calabrò A, Drommi F, Sidoti Migliore G, Pezzino G, Vento G, Freni J, Costa G, Cavaliere R, Bonaccorsi I, Sionne M, Nigro S, Navarra G, Ferlazzo G, De Pasquale C, Campana S. Calabrò A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 2;25(15):8470. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158470. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39126041 Free PMC article. - Dual blockade immunotherapy targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in lung cancer.
Cheng W, Kang K, Zhao A, Wu Y. Cheng W, et al. J Hematol Oncol. 2024 Jul 27;17(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01581-2. J Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39068460 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Atkins MB, Lotze MT, Dutcher JP, Fisher RI, Weiss G, Margolin K, Abrams J, Sznol M, Parkinson D, Hawkins M, Paradise C, Kunkel L, Rosenberg SA. High-dose recombinant interleukin 2 therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma: analysis of 270 patients treated between 1985 and 1993. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(7):2105–2116. - PubMed
- Sosman JA, Kim KB, Schuchter L, Gonzalez R, Pavlick AC, Weber JS, McArthur GA, Hutson TE, Moschos SJ, Flaherty KT, Hersey P, Kefford R, Lawrence D, Puzanov I, Lewis KD, Amaravadi RK, Chmielowski B, Lawrence HJ, Shyr Y, Ye F, Li J, Nolop KB, Lee RJ, Joe AK, Ribas A. Survival in BRAF V600-mutant advanced melanoma treated with vemurafenib. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(8):707–714. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1112302. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Flaherty KT, Robert C, Hersey P, Nathan P, Garbe C, Milhem M, Demidov LV, Hassel JC, Rutkowski P, Mohr P, Dummer R, Trefzer U, Larkin JM, Utikal J, Dreno B, Nyakas M, Middleton MR, Becker JC, Casey M, Sherman LJ, Wu FS, Ouellet D, Martin AM, Patel K, Schadendorf D. Improved survival with MEK inhibition in BRAF-mutated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(2):107–114. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1203421. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials