Type 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGlu1) trigger the gating of GluD2 delta glutamate receptors - PubMed (original) (raw)
Type 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGlu1) trigger the gating of GluD2 delta glutamate receptors
Visou Ady et al. EMBO Rep. 2014 Jan.
Abstract
The orphan GluD2 receptor belongs to the ionotropic glutamate receptor family but does not bind glutamate. Ligand-gated GluD2 currents have never been evidenced, and whether GluD2 operates as an ion channel has been a long-standing question. Here, we show that GluD2 gating is triggered by type 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors, both in a heterologous expression system and in Purkinje cells. Thus, GluD2 is not only an adhesion molecule at synapses but also works as a channel. This gating mechanism reveals new properties of glutamate receptors that emerge from their interaction and opens unexpected perspectives regarding synaptic transmission and plasticity.
Figures
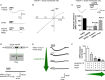
Figure 1. mGlu1 triggers GluD2 currents in HEK293 cells
- DHPG induced current at −60 mV in cells expressing mGlu1, GluD2 or NR1-NR2B subunits, alone or in combination.
- The I–V relationship of the DHPG current in a cell expressing mGlu1 and GluD2.
- NASPM, D-serine but not Pyr3 inhibit the DHPG current in cells transfected with GluD2 and mGlu1.
- The GluD2V617R dominant-negative construct (top, S1, S2: LBD). Lack of DHPG current in cells expressing mGlu1 and GluD2V617R (bottom).
- GluD2V617R reduces the DHPG current. Representative traces from cells transfected with mGlu1 and GluD2 together with increasing amounts of GluD2V617R plasmid (green arrow).
- Averaged amplitude of DHPG currents (± s.e.m.) as a function of the quantity of plasmids co-transfected as indicated below.
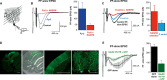
Figure 2. GluD2 channels contribute to mGlu1 slow EPSC in cerebellar Purkinje cells
- A Experimental arrangement for the mGlu1 synaptic activation.
- B,C mGlu1-slow ESPCs are inhibited by Pyr3, NASPM (B) and D-serine (C). Representative sweeps. Histograms show the PF-slow EPSC averaged peak amplitudes.
- D A slice from WT cerebellum infected with Sinbis carrying GFP and GluD2V617R. Scale bars: 500 μm (three left images), 100 μm (right).
- E Averaged PF-slow EPSC from V617RGluD2 (green) or GFP (black) expressing cells. Histograms: Corresponding PF-slow EPSCs averaged peak amplitudes.
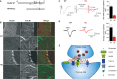
Figure 3. The mGlu1 current is strongly reduced in HO-Nancy Purkinje cells
- A WT and HO-Nancy schematic proteins. Amino-acid numbers flanking the deletion are indicated. Arrows: transmembrane domains. P: channel pore.
- B Confocal images of calbindin and GluD2 immunolabelings in WT (top) and HO-Nancy (bottom) cerebella. Scale bar in top left image represents 45 μm.
- C,D Representative PF-slow ESPCs (C) and DHPG currents (D) from WT (left) and HO-Nancy (right) Purkinje cells. Histograms: averaged peak amplitude of PF-slow ESPCs (C) or DHPG currents (D) from all the cells (± s.e.m.).
- E Schematic representation of PF synapses. GluD2s are not directly activated by glutamate (red spots) but require mGlu1 activation and thus presynaptic PF bursts.
Similar articles
- mGlu1 receptor canonical signaling pathway contributes to the opening of the orphan GluD2 receptor.
Dadak S, Bouquier N, Goyet E, Fagni L, Levenes C, Perroy J. Dadak S, et al. Neuropharmacology. 2017 Mar 15;115:92-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27276689 - Lack of evidence for direct ligand-gated ion channel activity of GluD receptors.
Itoh M, Piot L, Mony L, Paoletti P, Yuzaki M. Itoh M, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 30;121(31):e2406655121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2406655121. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39052831 Free PMC article. - Probing the ionotropic activity of glutamate GluD2 receptor in HEK cells with genetically-engineered photopharmacology.
Lemoine D, Mondoloni S, Tange J, Lambolez B, Faure P, Taly A, Tricoire L, Mourot A. Lemoine D, et al. Elife. 2020 Oct 28;9:e59026. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59026. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33112237 Free PMC article. - Structural biology of ionotropic glutamate delta receptors and their crosstalk with metabotropic glutamate receptors.
Burada AP, Vinnakota R, Lambolez B, Tricoire L, Kumar J. Burada AP, et al. Neuropharmacology. 2021 Sep 15;196:108683. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108683. Epub 2021 Jun 26. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34181979 Review. - Cbln1 and the δ2 glutamate receptor--an orphan ligand and an orphan receptor find their partners.
Matsuda K, Yuzaki M. Matsuda K, et al. Cerebellum. 2012 Mar;11(1):78-84. doi: 10.1007/s12311-010-0186-5. Cerebellum. 2012. PMID: 20535596 Review.
Cited by
- Delta glutamate receptor conductance drives excitation of mouse dorsal raphe neurons.
Gantz SC, Moussawi K, Hake HS. Gantz SC, et al. Elife. 2020 Apr 1;9:e56054. doi: 10.7554/eLife.56054. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32234214 Free PMC article. - Protein Networks Associated with Native Metabotropic Glutamate 1 Receptors (mGlu1) in the Mouse Cerebellum.
Mansouri M, Kremser L, Nguyen TP, Kasugai Y, Caberlotto L, Gassmann M, Sarg B, Lindner H, Bettler B, Carboni L, Ferraguti F. Mansouri M, et al. Cells. 2023 May 5;12(9):1325. doi: 10.3390/cells12091325. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37174725 Free PMC article. - Are Type 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors a viable therapeutic target for the treatment of cerebellar ataxia?
Power EM, English NA, Empson RM. Power EM, et al. J Physiol. 2016 Aug 15;594(16):4643-52. doi: 10.1113/JP271153. Epub 2016 Feb 24. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26748626 Free PMC article. Review. - Loss of activation by GABA in vertebrate delta ionotropic glutamate receptors.
Rosano G, Barzasi A, Lynagh T. Rosano G, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Feb 6;121(6):e2313853121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2313853121. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38285949 Free PMC article. - The low binding affinity of D-serine at the ionotropic glutamate receptor GluD2 can be attributed to the hinge region.
Tapken D, Steffensen TB, Leth R, Kristensen LB, Gerbola A, Gajhede M, Jørgensen FS, Olsen L, Kastrup JS. Tapken D, et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 7;7:46145. doi: 10.1038/srep46145. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28387240 Free PMC article.
References
- Kohda K, Wang Y, Yuzaki M. Mutation of a glutamate receptor motif reveals its role in gating and delta2 receptor channel properties. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:315–322. - PubMed
- Lomeli H, Sprengel R, Laurie DJ, Kohr G, Herb A, Seeburg PH, Wisden W. The rat delta-1 and delta-2 subunits extend the excitatory amino acid receptor family. FEBS Lett. 1993;315:318–322. - PubMed
- Kashiwabuchi N, Ikeda K, Araki K, Hirano T, Shibuki K, Takayama C, Inoue Y, Kutsuwada T, Takeshi Yagi T, Kang Y, Aizawa S, Mishina M. Impairement of motor coordination, Purkinje cell synapses formation, and cerebellar long-term depression in GluR-delta-2 mutant mice. Cell. 1995;81:245–252. - PubMed
- Filali M, Lalonde R, Bensoula AN, Guastavino JM, Lestienne F. Spontaneous alternation, motor activity, and spatial learning in hot-foot mutant mice. J Comp Physiol A. 1996;178:101–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases