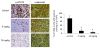Berberine suppresses tumorigenicity and growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by inhibiting STAT3 activation induced by tumor associated fibroblasts - PubMed (original) (raw)
Berberine suppresses tumorigenicity and growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by inhibiting STAT3 activation induced by tumor associated fibroblasts
Chi Man Tsang et al. BMC Cancer. 2013.
Abstract
Background: Cortidis rhizoma (Huanglian) and its major therapeutic component, berberine, have drawn extensive attention in recent years for their anti-cancer properties. Growth inhibitory effects of berberine on multiple types of human cancer cells have been reported. Berberine inhibits invasion, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human cancer cells. The anti-inflammatory property of berberine, involving inhibition of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) activation, has also been documented.
Methods: In this study, we have examined the effects of berberine on tumorigenicity and growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cells and their relationship to STAT3 signaling using both in vivo and in vitro models.
Results: Berberine effectively inhibited the tumorigenicity and growth of an EBV-positive NPC cell line (C666-1) in athymic nude mice. Inhibition of tumorigenic growth of NPC cells in vivo was correlated with effective inhibition of STAT3 activation in NPC cells inside the tumor xenografts grown in nude mice. In vitro, berberine inhibited both constitutive and IL-6-induced STAT3 activation in NPC cells. Inhibition of STAT3 activation by berberine induced growth inhibition and apoptotic response in NPC cells. Tumor-associated fibroblasts were found to secret IL-6 and the conditioned medium harvested from the fibroblasts also induced STAT3 activation in NPC cells. Furthermore, STAT3 activation by conditioned medium of tumor-associated fibroblasts could be blocked by berberine or antibodies against IL-6 and IL-6R.
Conclusions: Our observation that berberine effectively inhibited activation of STAT3 induced by tumor-associated fibroblasts suggests a role of berberine in modulating the effects of tumor stroma on the growth of NPC cells. The effective inhibition of STAT3 activation in NPC cells by berberine supports its potential use in the treatment of NPC.
Figures
Figure 1
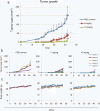
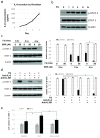
Suppression of tumorigenicity and growth of NPC cells by berberine in vivo . (a) Berberine could suppress the tumor initiation and growth of C666-1 xenografts in mice models. 1 X 106 Tumor cells were injected subcutaneously into nude mice. Mice were either treated with berberine (low dose: 5 mg/kg or high dose: 10 mg/kg; i.p.) or treated with saline (as control) for every other two days. Both low and high dose of berberine could significantly suppress the tumor growth (p < 0.05) when compared to that of the control mice. (b) Individual growth curves of tumors in control and berberine-treated mice. The tumor sizes of individual mouse under control treatment (PBS-treated; n = 4), under low dose of berberine treatment (5 mg/kg berberine-treated; n = 5) and under high dose of berberine treatment (10 mg/kg berberine-treated; n = 5) were followed from 14 to 43 days post-injection of tumor cells. (c) The body weights of the mice within the treatment and control groups were comparable. The weights of the mice were recorded from the day of injection until 43 days post-infection of tumor cells. Both the control mice and berberine-treated mice showed a steady increase of body weight. Both 5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg treatment of berberine did not cause drastic variation of body weight to the mice.
Figure 2
Activation of STAT3 was inhibited by berberine in vivo . Mice were continuously treated with saline (control group), low dose of berberine (5 mg/kg) and high dose of berberine (10 mg/kg) for every other two days up to a period of 43 days. The mice were then sacrificed and the tumors were sectioned and detected for p-STAT3. The sections were also stained with cytokeratin antibodies to identify the C666-1 cells from the fibroblasts. 5 random microscopic fields which consist of more than 95% of C666-1 cells were chosen for examination. Both low and high dose of berberine could significantly suppress the activation of STAT3 (p < 0.05) in C666-1 cells when compared to the controls.
Figure 3
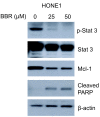
Constitutive activation of STAT3 was downregulated by berberine in HONE1 cells. HONE1 cells were treated with 25 and 50 μM berberine for 24 h. The activation of STAT3 was strongly suppressed by the treatment of berberine with a downregulation of survival protein (Mcl-1) and upregulation of apoptotic protein (cleaved-PARP-1). β-actin was probed for loading controls.
Figure 4
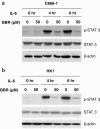
Berberine inhibited the IL-6-activated STAT3 in C666-1 and HK1 cells. Western blots analysis of (a) C666-1 and (b) HK1 cells with or without addition of berberine (50 μM) after IL-6 treatment (20 ng/ml) for 0, 4 and 6 hr. The cell lysate was probed with anti-STAT3 and anti-p-STAT3. Equal protein loading was established with anti-β-actin antibody.
Figure 5
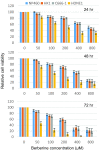
Berberine exhibited higher toxicity towards HONE1 cells. MTT assays were performed on one non-neoplastic nasopharyngeal epithelial cell line (NP460), and three NPC cell lines (HK1, C666-1 and HONE1) for 24, 48 and 72 hr under the indicated doses of berberine (0, 50, 100, 200, 400 and 800 μM). For each time point, the growth rates of each untreated cell line were arbitrarily assigned as 100. Mean ± SD were calculated from triplicate of two independent experiments.
Figure 6
Berberine could suppress the STAT3 activation in NPC cells induced by IL-6 secreted from fibroblasts. (a) IL-6 was secreted by tumor-associated fibroblasts. 1 x 106 fibroblasts were seeded in each well of a 6-well plate. Fibroblast supernatant was collected after 1, 2, 3 and 4 days of incubation in culture hood. The concentration of IL-6 was assessed by ELISA. (b) Fibroblast supernatant (FS) could activate the STAT3 signaling in C666-1 cells. FS collected after 4 days of incubation was used to treat C666-1 for 1, 2, 4 and 6 hr. Increasing levels of p-STAT3 could be detected in a time-dependent manner. (c) Berberine could inhibit the activation of STAT3 induced by FS. 50 μM of berberine could effectively suppress the FS-induced STAT3 activation at 4 hr time points. Three independent experiments were carried out, relative ratio to β-actin was calculated, and data are represented as mean ± S.D. from three experiments. *, p < 0.05. (d) The activation of STAT3 in FS-treated NPC cells was dependent on the IL-6\IL-6R signaling pathway. C666-1 cells were pretreated with anti-IL-6 or anti-IL-6R antibodies for 30 mins before the addition of FS. Protein was collected after 4 hr treatment of FS. Anti-IL-6 or anti-IL-6R antibodies could significantly suppressed the FS-induced activation of STAT-3. Three independent experiments were carried out, relative ratio to β-actin was calculated, and data are represented as mean ± S.D. from three experiments. *, p < 0.05. (e) IL-6 could enhance the growth rate of C666-1 cells. The cells were treated with IL-6 (20 ng/ml) or pretreated with anti-IL-6 antibody for 30 mins before the addition of IL-6. After 24 hr, the growth rate was determined by MTT assay. Mean ± SD were calculated from triplicate of two independent experiments. *, p < 0.05.
Similar articles
- Enhanced IL-6/IL-6R signaling promotes growth and malignant properties in EBV-infected premalignant and cancerous nasopharyngeal epithelial cells.
Zhang G, Tsang CM, Deng W, Yip YL, Lui VW, Wong SC, Cheung AL, Hau PM, Zeng M, Lung ML, Chen H, Lo KW, Takada K, Tsao SW. Zhang G, et al. PLoS One. 2013 May 1;8(5):e62284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062284. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23658720 Free PMC article. - Activation of miR-21 by STAT3 induces proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting PTEN gene.
Ou H, Li Y, Kang M. Ou H, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Nov 3;9(11):e109929. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109929. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25365510 Free PMC article. - LPLUNC1 suppresses IL-6-induced nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation via inhibiting the Stat3 activation.
Liao Q, Zeng Z, Guo X, Li X, Wei F, Zhang W, Li X, Chen P, Liang F, Xiang B, Ma J, Wu M, Tang H, Deng M, Zeng X, Tang K, Xiong W, Li G. Liao Q, et al. Oncogene. 2014 Apr 17;33(16):2098-109. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.161. Epub 2013 May 27. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23708661 - Role of STAT3 in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its significance in anticancer therapy.
Si Y, Xu J, Meng L, Wu Y, Qi J. Si Y, et al. Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 13;12:1021179. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1021179. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36313702 Free PMC article. Review. - Metabolic Reprogramming and Immune Evasion in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.
Huang H, Li S, Tang Q, Zhu G. Huang H, et al. Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 9;12:680955. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.680955. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34566954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Update of Natural Products and Their Derivatives Targeting Epstein-Barr Infection.
Pennisi R, Trischitta P, Costa M, Venuti A, Tamburello MP, Sciortino MT. Pennisi R, et al. Viruses. 2024 Jan 15;16(1):124. doi: 10.3390/v16010124. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38257824 Free PMC article. Review. - Berberine Inhibits Invasion and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer Cells via COX-2/PGE2 Mediated JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway.
Liu X, Ji Q, Ye N, Sui H, Zhou L, Zhu H, Fan Z, Cai J, Li Q. Liu X, et al. PLoS One. 2015 May 8;10(5):e0123478. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123478. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25954974 Free PMC article. - Natural Products and Their Derivatives against Human Herpesvirus Infection.
Ruchawapol C, Yuan M, Wang SM, Fu WW, Xu HX. Ruchawapol C, et al. Molecules. 2021 Oct 18;26(20):6290. doi: 10.3390/molecules26206290. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34684870 Free PMC article. Review. - Addition of Berberine to 5-Aminosalicylic Acid for Treatment of Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Chronic Colitis in C57BL/6 Mice.
Li YH, Zhang M, Xiao HT, Fu HB, Ho A, Lin CY, Huang Y, Lin G, Bian ZX. Li YH, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Dec 7;10(12):e0144101. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144101. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26642326 Free PMC article. - The role of Epstein-Barr virus infection in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Tsang CM, Tsao SW. Tsang CM, et al. Virol Sin. 2015 Apr;30(2):107-21. doi: 10.1007/s12250-015-3592-5. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Virol Sin. 2015. PMID: 25910483 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous