The role of EGFR and ErbB family related proteins in the oligodendrocyte specification in germinal niches of the adult mammalian brain - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The role of EGFR and ErbB family related proteins in the oligodendrocyte specification in germinal niches of the adult mammalian brain
Alma Y Galvez-Contreras et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013.
Abstract
IN THE ADULT BRAIN, MULTIPOTENT PROGENITOR CELLS HAVE BEEN IDENTIFIED IN THREE AREAS: the ventricular-subventricular zone (VZ-SVZ), adjacent to the striatal wall of the lateral ventricles, the subgranular zone (SGZ), located at the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus and the subcallosal zone (SCZ), located between the corpus callosum and the CA1 and CA2 regions of the hippocampus. The neural progenitor cells of these regions express the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR, ErbB-1 or HER1). EGF, the most important ligand for the EGFR, is a potent mitogenic agent that stimulates proliferation, survival, migration and differentiation into the oligodendrocyte lineage. Other ErbB receptors also activate several intracellular pathways for oligodendrocyte specification, migration and survival. However, the specific downstream pathways related to oligodendrogenesis and the hierarchic interaction among intracellular signaling cascades is not well-known. We summarize the current data regarding the role of EGFR and ErbB family signaling on neural stem cells and the downstream cascades involved in oligodendrogenesis in the neurogenic niches of the adult brain. Understanding the mechanisms that regulate proliferation, differentiation, migration of oligodendrocytes and myelination is of critical importance for the field of neurobiology and constitutes a crucial step in the design of stem-cell-based therapies for demyelinating diseases.
Keywords: NG2 glia; epidermal growth factor; myelin; neural stem cell; oligodendrocyte; platelet-derived growth factor.
Figures
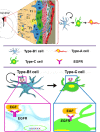
Figure 1
The adult ventricular-subventricular zone (VZ-SVZ). 3-D reconstruction of this niche of neural stem cells located within the lateral wall of the lateral ventricles. Multiciliated ependymal cells, also called E2 cells, form pinwheel-like structures (in peach color) around the apical processes of type B1 cells (in blue). Biciliated ependymal cells as referred to E1 cells (in yellow). Type-C cells (in green) and type-A cells (in red). Type-B1 progenitors are neural stem cells that generate secondary progenitors (type-C cells), which in turn give rise to migrating neuroblast (type-A cells). Additionally, type-B1 cells generate oligodendrocyte progenitors in vivo. Both type-B and type-C progenitors express the EGFR. Note that type-B neural stem cells are in close contact with the cerebrospinal fluid and the adjacent blood vessels (BV).
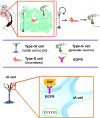
Figure 2
The subgranular zone (SGZ) in the dentate gyrus of the adult hippocampus. Type-B1 cells (in blue) also known as type-1 cells or type-rA cells (radial astrocytes) are the neuronal progenitor cells in this region. Type-rA cells divide and produce type-D cells as referred to type-2 cells. Hippocampal neuroblasts migrate locally and incorporate into the granular layer where they differentiate in mature granular neurons (type-G cells). Type-B1 cells express EGFR and behave as putative neural stem cells in vitro.
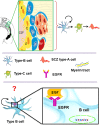
Figure 3
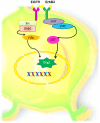
The subcallosal zone (SCZ) is located between the hippocampus and the corpus callosum. The SCZ is a caudal extension of the VZ-SVZ that is no longer associated to the ventricular system. Type-B cells (in blue) generate type-C cells that, in turn, give rise to oligodendrocyte precursors (also called SCZ type-A cells) that migrate into the neighboring corpus callosum. Type-B and type-C cells isolated from the SCZ and cultured as neurospheres behave as neural stem cells in vitro. However, the cell type that expresses in vivo the ErbB family receptors is unknown.
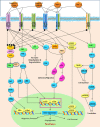
Figure 4
The ErbB family receptors and their main cell signaling pathways: the Ras/MAPK, the PI3K/AKT and the PLCy pathways.
Figure 5
Biological effects reported in ErbB family proteins. The homo or heterodimerization of the ErbB proteins may generate similar effects. Homodimerization between EGFR/EGFR can originates proliferation MAPK activation and the heterodimeriizations of EGFR/ErbB2 undifferentiated state and enhanced mitogenic activity; EGFR/ErbB3 oligodendroglial cell fate via AKT and EGFR/ErbB4 neuronal and survival cell fate.
Figure 6
Hypothetical model of oligodendrocyte cell signaling, via EGFR and ErbB3 in adult neural stem and progenitors cells. Homodimerization between these two ErbB members could activate the PI3K or the STAT pathways that in turn can activate AKT and induces the expression of Olig-2, which in turn may determine oligodendroglial lineage.
Similar articles
- The ventricular-subventricular, subgranular and subcallosal zones: three niches of neural stem cells in the postnatal brain.
Lopez-Virgen V, Gonzalez-Morales O, Gonzalez-Perez O. Lopez-Virgen V, et al. Exp Brain Res. 2023 Jun;241(6):1463-1470. doi: 10.1007/s00221-023-06621-w. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Exp Brain Res. 2023. PMID: 37083843 Review. - Diphenylhydantoin promotes proliferation in the subventricular zone and dentate gyrus.
Galvez-Contreras AY, Gonzalez-Castaneda RE, Luquin S, Guzman-Muniz J, Moy-Lopez NA, Ramos-Zuniga R, Gonzalez-Perez O. Galvez-Contreras AY, et al. Am J Neurosci. 2012 Mar 6;3(1):1-9. doi: 10.3844/amjnsp.2012.1.9. Am J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 24478822 Free PMC article. - Grafted Subventricular Zone Neural Stem Cells Display Robust Engraftment and Similar Differentiation Properties and Form New Neurogenic Niches in the Young and Aged Hippocampus.
Shetty AK, Hattiangady B. Shetty AK, et al. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016 Sep;5(9):1204-15. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0270. Epub 2016 May 18. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27194744 Free PMC article. - Endogenous Neural Stem Cell Mediated Oligodendrogenesis in the Adult Mammalian Brain.
Radecki DZ, Samanta J. Radecki DZ, et al. Cells. 2022 Jul 2;11(13):2101. doi: 10.3390/cells11132101. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805185 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of fibroblast growth factor receptors in astrocytic stem cells.
Galvez-Contreras AY, Gonzalez-Castaneda RE, Luquin S, Gonzalez-Perez O. Galvez-Contreras AY, et al. Curr Signal Transduct Ther. 2012 Jan;7(1):81-86. doi: 10.2174/157436212799278205. Curr Signal Transduct Ther. 2012. PMID: 22347841 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- EGF signaling promotes the lineage conversion of astrocytes into oligodendrocytes.
Liu X, Li C, Li J, Xie L, Hong Z, Zheng K, Zhao X, Yang A, Xu X, Tao H, Qiu M, Yang J. Liu X, et al. Mol Med. 2022 May 4;28(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00478-5. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35508991 Free PMC article. - Drug connectivity mapping and functional analysis reveal therapeutic small molecules that differentially modulate myelination.
Rivera AD, Pieropan F, Williams G, Calzolari F, Butt AM, Azim K. Rivera AD, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Jan;145:112436. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112436. Epub 2021 Nov 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 34813998 Free PMC article. - The EGFR-HER2 module: a stem cell approach to understanding a prime target and driver of solid tumors.
Schneider MR, Yarden Y. Schneider MR, et al. Oncogene. 2016 Jun 9;35(23):2949-60. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.372. Epub 2015 Oct 5. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26434585 Free PMC article. Review. - Alterations of Growth Factors in Autism and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder.
Galvez-Contreras AY, Campos-Ordonez T, Gonzalez-Castaneda RE, Gonzalez-Perez O. Galvez-Contreras AY, et al. Front Psychiatry. 2017 Jul 13;8:126. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00126. eCollection 2017. Front Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28751869 Free PMC article. - EGFR promoter exhibits dynamic histone modifications and binding of ASH2L and P300 in human germinal matrix and gliomas.
Erfani P, Tome-Garcia J, Canoll P, Doetsch F, Tsankova NM. Erfani P, et al. Epigenetics. 2015;10(6):496-507. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1042645. Epub 2015 May 21. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 25996283 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous