Irisin Levels are Not Affected by Physical Activity in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa - PubMed (original) (raw)
Irisin Levels are Not Affected by Physical Activity in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa
Tobias Hofmann et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014.
Abstract
Irisin was recently identified as muscle-derived hormone that increases energy expenditure. Studies in normal weight and obese subjects reported an increased irisin expression following physical activity, although inconsistent results were observed. Increased physical activity in a subgroup of patients with anorexia nervosa (AN) complicates the course of the disease. Since irisin could account for differences in clinical outcomes, we investigated irisin levels in anorexic patients with high and moderate physical activity to evaluate whether irisin differs with increasing physical activity. Hospitalized female anorexic patients (n = 39) were included. Plasma irisin measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and locomotor activity were assessed at the same time. Patients were separated into two groups (n = 19/group; median excluded): moderate and high activity (6331 ± 423 vs. 13743 ± 1047 steps/day, p < 0.001). The groups did not differ in body mass index (14.2 ± 0.4 vs. 15.0 ± 0.4 kg/m(2)), irisin levels (558.2 ± 26.1 vs. 524.9 ± 25.2 ng/ml), and body weight-adjusted resting energy expenditure (17.6 ± 0.3 vs. 18.0 ± 0.3 kcal/kg/day, p > 0.05), whereas body weight-adjusted total energy expenditure (46.0 ± 1.4 vs. 41.1 ± 1.1 kcal/kg/day), metabolic equivalents (METs, 1.9 ± 0.1 vs. 1.7 ± 0.1 METs/day), body weight-adjusted exercise activity thermogenesis (1.8 ± 0.5 vs. 0.6 ± 0.3 kcal/kg/day), duration of exercise (18.6 ± 4.7 vs. 6.2 ± 3.1 min/day), and body weight-adjusted non-exercise activity thermogenesis (21.6 ± 1.0 vs. 18.8 ± 0.8 kcal/kg/day) were higher in the high activity compared to the moderate activity group (p < 0.05). No correlations were observed between irisin and activity parameters in the whole sample (p > 0.05). In conclusion, the current data do not support the concept of irisin being induced by exercise, at least not under conditions of severely reduced body weight like AN.
Keywords: FNDC5; SenseWear™ armband; brown adipose tissue; energy expenditure; exercise; myokine.
Figures
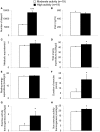
Figure 1
Parameters of energy expenditure in anorexic patients with moderate and high physical activity. Per definition, the high activity group showed a higher number of steps compared to the moderate activity group (A). Irisin levels did not differ between the two groups (B). The metabolic equivalents per day (C) as well as body weight-adjusted total energy expenditure (D) were higher in the high compared to the moderate activity group, while no differences were observed for body weight-adjusted resting energy expenditure (E). Duration of exercise (F), body weight-adjusted exercise activity thermogenesis (G), and body weight-adjusted non-exercise activity thermogenesis (H) were higher in the high compared to the moderate activity group. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 in the high vs. moderate activity group (n = 19/group).
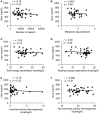
Figure 2
Correlations between circulating irisin concentrations and number of steps per day (A), metabolic equivalents per day (B), body weight-adjusted total energy expenditure (C), body weight-adjusted resting energy expenditure (D), body weight-adjusted exercise activity thermogenesis (E), and body weight-adjusted non-exercise activity thermogenesis (F). Values for r and p are indicated in each graph, n = 39 patients.
Similar articles
- Circulating levels of irisin in patients with anorexia nervosa and different stages of obesity--correlation with body mass index.
Stengel A, Hofmann T, Goebel-Stengel M, Elbelt U, Kobelt P, Klapp BF. Stengel A, et al. Peptides. 2013 Jan;39:125-30. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2012.11.014. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Peptides. 2013. PMID: 23219488 - Association of irisin with fat mass, resting energy expenditure, and daily activity in conditions of extreme body mass index.
Pardo M, Crujeiras AB, Amil M, Aguera Z, Jiménez-Murcia S, Baños R, Botella C, de la Torre R, Estivill X, Fagundo AB, Fernández-Real JM, Fernández-García JC, Fruhbeck G, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Rodríguez R, Tinahones FJ, Fernández-Aranda F, Casanueva FF. Pardo M, et al. Int J Endocrinol. 2014;2014:857270. doi: 10.1155/2014/857270. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Int J Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24864142 Free PMC article. - Abdominal fat sub-depots and energy expenditure: Magnetic resonance imaging study.
Serfaty D, Rein M, Schwarzfuchs D, Shelef I, Gepner Y, Bril N, Cohen N, Shemesh E, Sarusi B, Kovsan J, Kenigsbuch S, Chassidim Y, Golan R, Witkow S, Henkin Y, Stampfer MJ, Rudich A, Shai I. Serfaty D, et al. Clin Nutr. 2017 Jun;36(3):804-811. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.05.009. Epub 2016 May 27. Clin Nutr. 2017. PMID: 27288327 - Irisin as a muscle-derived hormone stimulating thermogenesis--a critical update.
Hofmann T, Elbelt U, Stengel A. Hofmann T, et al. Peptides. 2014 Apr;54:89-100. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2014.01.016. Epub 2014 Jan 26. Peptides. 2014. PMID: 24472856 Review. - Irisin: what promise does it hold?
Elbelt U, Hofmann T, Stengel A. Elbelt U, et al. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2013 Sep;16(5):541-7. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e328363bc65. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2013. PMID: 23799326 Review.
Cited by
- Increased 24-hour ad libitum food intake is associated with lower plasma irisin concentrations the following morning in adult humans.
Schlögl M, Piaggi P, Votruba SB, Walter M, Krakoff J, Thearle MS. Schlögl M, et al. Appetite. 2015 Jul;90:154-9. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Appetite. 2015. PMID: 25765248 Free PMC article. - Exercise Induces White Adipose Tissue Browning Across the Weight Spectrum in Humans.
Otero-Díaz B, Rodríguez-Flores M, Sánchez-Muñoz V, Monraz-Preciado F, Ordoñez-Ortega S, Becerril-Elias V, Baay-Guzmán G, Obando-Monge R, García-García E, Palacios-González B, Villarreal-Molina MT, Sierra-Salazar M, Antuna-Puente B. Otero-Díaz B, et al. Front Physiol. 2018 Dec 11;9:1781. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01781. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30618796 Free PMC article. - The Role of Objectively Measured, Altered Physical Activity Patterns for Body Mass Index Change during Inpatient Treatment in Female Patients with Anorexia Nervosa.
Lehmann CS, Hofmann T, Elbelt U, Rose M, Correll CU, Stengel A, Haas V. Lehmann CS, et al. J Clin Med. 2018 Sep 18;7(9):289. doi: 10.3390/jcm7090289. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 30231527 Free PMC article. - Association of Irisin Plasma Levels with Anthropometric Parameters in Children with Underweight, Normal Weight, Overweight, and Obesity.
Elizondo-Montemayor L, Silva-Platas C, Torres-Quintanilla A, Rodríguez-López C, Ruiz-Esparza GU, Reyes-Mendoza E, Garcia-Rivas G. Elizondo-Montemayor L, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:2628968. doi: 10.1155/2017/2628968. Epub 2017 May 3. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28553647 Free PMC article. - Irisin - a myth rather than an exercise-inducible myokine.
Albrecht E, Norheim F, Thiede B, Holen T, Ohashi T, Schering L, Lee S, Brenmoehl J, Thomas S, Drevon CA, Erickson HP, Maak S. Albrecht E, et al. Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 9;5:8889. doi: 10.1038/srep08889. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25749243 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources