Emotion dysregulation in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Emotion dysregulation in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Philip Shaw et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2014 Mar.
Abstract
Although it has long been recognized that many individuals with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) also have difficulties with emotion regulation, no consensus has been reached on how to conceptualize this clinically challenging domain. The authors examine the current literature using both quantitative and qualitative methods. Three key findings emerge. First, emotion dysregulation is prevalent in ADHD throughout the lifespan and is a major contributor to impairment. Second, emotion dysregulation in ADHD may arise from deficits in orienting toward, recognizing, and/or allocating attention to emotional stimuli; these deficits implicate dysfunction within a striato-amygdalo-medial prefrontal cortical network. Third, while current treatments for ADHD often also ameliorate emotion dysregulation, a focus on this combination of symptoms reframes clinical questions and could stimulate novel therapeutic approaches. The authors then consider three models to explain the overlap between emotion dysregulation and ADHD: emotion dysregulation and ADHD are correlated but distinct dimensions; emotion dysregulation is a core diagnostic feature of ADHD; and the combination constitutes a nosological entity distinct from both ADHD and emotion dysregulation alone. The differing predictions from each model can guide research on the much-neglected population of patients with ADHD and emotion dysregulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures. All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Figure 1
Forest Plots With Standardized Mean Difference between the ADHD and control groups, effect size and homogeneity statistics are given. (A) Aggression: more aggressive behavior is seen in the ADHD groups (the effect size for the Abikoff study (ref 11) of boys was 14). (B) Emotion recognition deficits are seen in ADHD; (C) Reward processing here is measured by the tendency to immediate small rewards over larger, delayed ones. The ADHD participants show a tendency to prefer immediate, small rewards. Further details are given in Supplemental Material.
Figure 2
Correlations between infantile temperament and later externalizing and ADHD symptoms. Significance levels: *= p<0.05; **=p<0.01; NS= not significant.
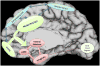
Figure 3
Neural circuits implicated in emotion dysregulation in ADHD. The circuitry which underpins deficits in early orienting to emotional stimuli and their perception is shown in red. Regions which interface between emotional and cognitive circuits, allocating attention to emotional stimuli are show in green. Circuitry implicated in cognitive control, motor planning and attention is shown in blue. (OFC=orbitofrontal cortex; VLPFC=ventrolateral prefrontal cortex; ACC= anterior cingulate cortex; PFC=prefrontal cortex).
Similar articles
- [Is emotional dysregulation a component of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)?].
Villemonteix T, Purper-Ouakil D, Romo L. Villemonteix T, et al. Encephale. 2015 Apr;41(2):108-14. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2013.12.004. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Encephale. 2015. PMID: 24703785 French. - Clinical features and subjective/physiological responses to emotional stimuli in the presence of emotion dysregulation in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder.
Taskiran C, Karaismailoglu S, Cak Esen HT, Tuzun Z, Erdem A, Balkanci ZD, Dolgun AB, Cengel Kultur SE. Taskiran C, et al. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2018 May;40(4):389-404. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2017.1353952. Epub 2017 Jul 19. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2018. PMID: 28721740 - Emotional dysregulation is a primary symptom in adult Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
Hirsch O, Chavanon M, Riechmann E, Christiansen H. Hirsch O, et al. J Affect Disord. 2018 May;232:41-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.02.007. Epub 2018 Feb 13. J Affect Disord. 2018. PMID: 29477097 - Emotional dysregulation in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
van Stralen J. van Stralen J. Atten Defic Hyperact Disord. 2016 Dec;8(4):175-187. doi: 10.1007/s12402-016-0199-0. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Atten Defic Hyperact Disord. 2016. PMID: 27299358 Free PMC article. Review. - Neurobiological and psychophysiological correlates of emotional dysregulation in ADHD patients.
Herrmann MJ, Biehl SC, Jacob C, Deckert J. Herrmann MJ, et al. Atten Defic Hyperact Disord. 2010 Dec;2(4):233-9. doi: 10.1007/s12402-010-0047-6. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Atten Defic Hyperact Disord. 2010. PMID: 21432610 Review.
Cited by
- Psychiatric disorders in term-born children with marginally low birth weight: a population-based study.
Wu SI, Huang YH, Kao KL, Lin YW, Tsai PL, Chiu NC, Chung CH, Chen CP. Wu SI, et al. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2024 Feb 8;18(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13034-024-00714-2. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2024. PMID: 38331844 Free PMC article. - Association between irritability and bias in attention orienting to threat in children and adolescents.
Salum GA, Mogg K, Bradley BP, Stringaris A, Gadelha A, Pan PM, Rohde LA, Polanczyk GV, Manfro GG, Pine DS, Leibenluft E. Salum GA, et al. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2017 May;58(5):595-602. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12659. Epub 2016 Oct 26. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27782299 Free PMC article. - ADHD symptoms in non-treatment seeking young adults: relationship with other forms of impulsivity.
Chamberlain SR, Ioannidis K, Leppink EW, Niaz F, Redden SA, Grant JE. Chamberlain SR, et al. CNS Spectr. 2017 Feb;22(1):22-30. doi: 10.1017/S1092852915000875. Epub 2016 Sep 29. CNS Spectr. 2017. PMID: 27680974 Free PMC article. - Influence of emotional stimulus valence on inhibitory control in adults with and without ADHD.
Cavallet M, Chaim-Avancini TM, Biazoli CE Jr, Bazán PR, da Silva MA, Cunha PJ, Miguel CS, Busatto GF, Louzã MR, Gawryszewski LG. Cavallet M, et al. Exp Brain Res. 2016 Nov;234(11):3213-3223. doi: 10.1007/s00221-016-4719-0. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Exp Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27388167
References
- Clements S. In: Minimal Brain Dysfunction in Children: terminology and identification: phase one of a three-phase project. US Dept of Health EaW, editor. Washington, DC: 1966.
- Thompson RA. Emotion regulation: A theme in search of definition. Monographs of the society for research in child development. 1994;59(2Äê3):25–52. - PubMed
- Stringaris A. Irritability in children and adolescents: a challenge for DSM-5. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2011;20(2):61–6. - PubMed
- Dodge KA, Pepler D, Rubin K. The structure and function of reactive and proactive aggression. The development and treatment of childhood aggression. 1991;16(5):201–18.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical