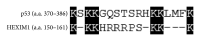Brd4 and HEXIM1: multiple roles in P-TEFb regulation and cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Brd4 and HEXIM1: multiple roles in P-TEFb regulation and cancer
Ruichuan Chen et al. Biomed Res Int. 2014.
Abstract
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (Brd4) and hexamethylene bisacetamide (HMBA) inducible protein 1 (HEXIM1) are two opposing regulators of the positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb), which is the master modulator of RNA polymerase II during transcriptional elongation. While Brd4 recruits P-TEFb to promoter-proximal chromatins to activate transcription, HEXIM1 sequesters P-TEFb into an inactive complex containing the 7SK small nuclear RNA. Besides regulating P-TEFb's transcriptional activity, recent evidence demonstrates that both Brd4 and HEXIM1 also play novel roles in cell cycle progression and tumorigenesis. Here we will discuss the current knowledge on Brd4 and HEXIM1 and their implication as novel therapeutic options against cancer.
Figures
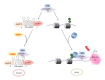
Figure 1
Regulation of P-TEFb activity by its positive regulator HEXIM1 and negative regulator Brd4.
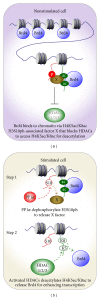
Figure 2
Regulation of the association between Brd4 and chromatins in the nonstimulated (a) and stimulated (b) cells.
Figure 3
Alignment of the HDM2 ubiquitination sites between p53 (amino acids 370–386) and HEXIM1 (amino acids 150–161). The HDM2-ubiquitinated lysine residues are indicated in black boxes.
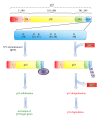
Figure 4
HEXIM1 stabilizes p53 by blocking the HDM2-mediated ubiquitination of p53. Human p53 protein can be divided into five domains: transactivation (TA), proline rich (PR), DNA binding (DB), oligomerization (OLI), and negative (NEG) domains. The HDM2 ubiquitination sites are located with the NEG domain. HEXIM1 interacts with the NEG domain of p53 and prevents the binding between p53 and HDM2.
Similar articles
- Bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) bromodomain inhibition activate transcription via transient release of positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) from 7SK small nuclear ribonucleoprotein.
Bartholomeeusen K, Xiang Y, Fujinaga K, Peterlin BM. Bartholomeeusen K, et al. J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 19;287(43):36609-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.410746. Epub 2012 Sep 5. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22952229 Free PMC article. - Two-pronged binding with bromodomain-containing protein 4 liberates positive transcription elongation factor b from inactive ribonucleoprotein complexes.
Schröder S, Cho S, Zeng L, Zhang Q, Kaehlcke K, Mak L, Lau J, Bisgrove D, Schnölzer M, Verdin E, Zhou MM, Ott M. Schröder S, et al. J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 6;287(2):1090-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.282855. Epub 2011 Nov 14. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22084242 Free PMC article. - Release of positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) from 7SK small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) activates hexamethylene bisacetamide-inducible protein (HEXIM1) transcription.
Liu P, Xiang Y, Fujinaga K, Bartholomeeusen K, Nilson KA, Price DH, Peterlin BM. Liu P, et al. J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 4;289(14):9918-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.539015. Epub 2014 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24515107 Free PMC article. - HEXIM1 and the control of transcription elongation: from cancer and inflammation to AIDS and cardiac hypertrophy.
Dey A, Chao SH, Lane DP. Dey A, et al. Cell Cycle. 2007 Aug 1;6(15):1856-63. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.15.4556. Epub 2007 Jun 6. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17671421 Review. - The Yin and Yang of P-TEFb regulation: implications for human immunodeficiency virus gene expression and global control of cell growth and differentiation.
Zhou Q, Yik JH. Zhou Q, et al. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006 Sep;70(3):646-59. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00011-06. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16959964 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A Novel Phenanthridionone Based Scaffold As a Potential Inhibitor of the BRD2 Bromodomain: Crystal Structure of the Complex.
Tripathi S, Mathur S, Deshmukh P, Manjula R, Padmanabhan B. Tripathi S, et al. PLoS One. 2016 May 31;11(5):e0156344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156344. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27243809 Free PMC article. - Transcriptome-Wide Association Analysis Identifies Novel Candidate Susceptibility Genes for Prostate-Specific Antigen Levels in Men Without Prostate Cancer.
Chen DM, Dong R, Kachuri L, Hoffmann T, Jiang Y, Berndt SI, Shelley JP, Schaffer KR, Machiela MJ, Freedman ND, Huang WY, Li SA, Lilja H, Van Den Eeden SK, Chanock S, Haiman CA, Conti DV, Klein RJ, Mosley JD, Witte JS, Graff RE. Chen DM, et al. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 5:2023.05.04.23289526. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.04.23289526. medRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37205487 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint. - Reconstitution of a functional 7SK snRNP.
Brogie JE, Price DH. Brogie JE, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jun 20;45(11):6864-6880. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx262. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28431135 Free PMC article. - Transcriptome-wide association analysis identifies candidate susceptibility genes for prostate-specific antigen levels in men without prostate cancer.
Chen DM, Dong R, Kachuri L, Hoffmann TJ, Jiang Y, Berndt SI, Shelley JP, Schaffer KR, Machiela MJ, Freedman ND, Huang WY, Li SA, Lilja H, Justice AC, Madduri RK, Rodriguez AA, Van Den Eeden SK, Chanock SJ, Haiman CA, Conti DV, Klein RJ, Mosley JD, Witte JS, Graff RE. Chen DM, et al. HGG Adv. 2024 Jul 18;5(3):100315. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2024.100315. Epub 2024 Jun 6. HGG Adv. 2024. PMID: 38845201 Free PMC article. - RNA polymerase II pausing as a context-dependent reader of the genome.
Scheidegger A, Nechaev S. Scheidegger A, et al. Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Feb;94(1):82-92. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2015-0045. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Biochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26555214 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Marshall NF, Price DH. Purification of P-TEFb, a transcription factor required for the transition into productive elongation. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1995;270(21):12335–12338. - PubMed
- Yamaguchi Y, Takagi T, Wada T, et al. NELF, a multisubunit complex containing RD, cooperates with DSIF to repress RNA polymerase II elongation. Cell. 1999;97(1):41–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials