Predictive value of imaging markers at multiple sclerosis disease onset based on gadolinium- and USPIO-enhanced MRI and machine learning - PubMed (original) (raw)
Predictive value of imaging markers at multiple sclerosis disease onset based on gadolinium- and USPIO-enhanced MRI and machine learning
Alessandro Crimi et al. PLoS One. 2014.
Abstract
Objectives: A novel characterization of Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) patients according to lesion patterns is proposed. More specifically, patients are classified according to the nature of inflammatory lesions patterns. It is expected that this characterization can infer new prospective figures from the earliest imaging signs of Multiple Sclerosis (MS), since it can provide a classification of different types of lesions across patients.
Methods: The method is based on a two-tiered classification. Initially, the spatio-temporal lesion patterns are classified. The discovered lesion patterns are then used to characterize groups of patients. The patient groups are validated using statistical measures and by correlations at 24-month follow-up with hypointense lesion loads.
Results: The methodology identified 3 statistically significantly different clusters of lesion patterns showing p-values smaller than 0.01. Moreover, these patterns defined at baseline correlated with chronic hypointense lesion volumes by follow-up with an R(2) score of 0.90.
Conclusions: The proposed methodology is capable of identifying three major different lesion patterns that are heterogeneously present in patients, allowing a patient classification using only two MRI scans. This finding may lead to more accurate prognosis and thus to more suitable treatments at early stage of MS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: Gilles Edan received research support and compensation as a speaker from Biogen Idec, Serono and Sanofi-Aventis, Bayer Schering Pharma AG, and LFB; and has acted as a consultant for Teva Pharmaceuticals, Merck-Serono, Bayer-Schering, Biogenidec, and LFB. This does not alter the authors' adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
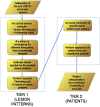
Figure 1. Classification work-flow showing all the steps of the proposed framework.
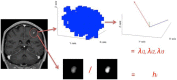
Figure 2. The feature extraction process for a single time point.
First all the lesions are delineated, then all the identified voxels are considered to compute the hollow index  and to build the covariance matrix. Finally, the eigenvalues are obtained from this covariance matrix. The process is repeated for all time points and the lesions which match at the different time point are ordered in the same feature vector.
and to build the covariance matrix. Finally, the eigenvalues are obtained from this covariance matrix. The process is repeated for all time points and the lesions which match at the different time point are ordered in the same feature vector.
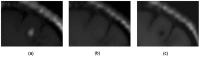
Figure 3. The same lesion at the same time point: (a) Gd-enhanced, (b) USPIO-enhanced and (c) pre-contrast.
It can be noticed that the USPIO enhancements are generally very mild compared to the Gd enhancements.
Figure 4. Illustration of a spatio-temporal evolution of the same lesion for both contrast agents and pre-contrast belonging to C 1.
In general,  is the less specific which comprises lesions of different dimensions (small, medium, large) appearing at the first time point
is the less specific which comprises lesions of different dimensions (small, medium, large) appearing at the first time point  and then disappearing, and generally Gd-enhanced only.
and then disappearing, and generally Gd-enhanced only.
Figure 5. Illustration of a spatio-temporal evolution of the same lesion for both contrast agents and pre-contrast belonging to C 2.
In general,  includes relatively medium and large lesions present at both the first two time points, and with co-presence of ringing USPIO and focal Gd enhancement.
includes relatively medium and large lesions present at both the first two time points, and with co-presence of ringing USPIO and focal Gd enhancement.
Figure 6. Illustration of a spatio-temporal evolution of the same lesion for both contrast agents and pre-contrast belonging to C 3.
In general,  comprises relatively medium lesions present mainly at the first time point with non focal USPIO and Gd enhancement.
comprises relatively medium lesions present mainly at the first time point with non focal USPIO and Gd enhancement.
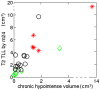
Figure 7. Patients according to their chronic hypointense lesions and TLLs by .
The red stars are patients of Group A reported in Table 2 which presented at least one lesion pattern  or
or  , the green diamonds are the patients of Group C with no active lesions at the two time points, and the black circles are the reminding patients of Group B.
, the green diamonds are the patients of Group C with no active lesions at the two time points, and the black circles are the reminding patients of Group B.
Similar articles
- Assessment of disease activity in multiple sclerosis phenotypes with combined gadolinium- and superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced MR imaging.
Tourdias T, Roggerone S, Filippi M, Kanagaki M, Rovaris M, Miller DH, Petry KG, Brochet B, Pruvo JP, Radüe EW, Dousset V. Tourdias T, et al. Radiology. 2012 Jul;264(1):225-33. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12111416. Radiology. 2012. PMID: 22723563 Clinical Trial. - Ultra-small superparamagnetic iron oxide enhancement is associated with higher loss of brain tissue structure in clinically isolated syndrome.
Maarouf A, Ferré JC, Zaaraoui W, Le Troter A, Bannier E, Berry I, Guye M, Pierot L, Barillot C, Pelletier J, Tourbah A, Edan G, Audoin B, Ranjeva JP. Maarouf A, et al. Mult Scler. 2016 Jul;22(8):1032-9. doi: 10.1177/1352458515607649. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Mult Scler. 2016. PMID: 26453679 - Pluriformity of inflammation in multiple sclerosis shown by ultra-small iron oxide particle enhancement.
Vellinga MM, Oude Engberink RD, Seewann A, Pouwels PJ, Wattjes MP, van der Pol SM, Pering C, Polman CH, de Vries HE, Geurts JJ, Barkhof F. Vellinga MM, et al. Brain. 2008 Mar;131(Pt 3):800-7. doi: 10.1093/brain/awn009. Epub 2008 Feb 1. Brain. 2008. PMID: 18245785 Clinical Trial. - The role of magnetic resonance techniques in understanding and managing multiple sclerosis.
Miller DH, Grossman RI, Reingold SC, McFarland HF. Miller DH, et al. Brain. 1998 Jan;121 ( Pt 1):3-24. doi: 10.1093/brain/121.1.3. Brain. 1998. PMID: 9549485 Review. - Correlations between monthly enhanced MRI lesion rate and changes in T2 lesion volume in multiple sclerosis.
Molyneux PD, Filippi M, Barkhof F, Gasperini C, Yousry TA, Truyen L, Lai HM, Rocca MA, Moseley IF, Miller DH. Molyneux PD, et al. Ann Neurol. 1998 Mar;43(3):332-9. doi: 10.1002/ana.410430311. Ann Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9506550 Review.
Cited by
- Machine learning assisted-nanomedicine using magnetic nanoparticles for central nervous system diseases.
Tomitaka A, Vashist A, Kolishetti N, Nair M. Tomitaka A, et al. Nanoscale Adv. 2023 Jul 28;5(17):4354-4367. doi: 10.1039/d3na00180f. eCollection 2023 Aug 24. Nanoscale Adv. 2023. PMID: 37638161 Free PMC article. Review. - Dimensional Neuroimaging Endophenotypes: Neurobiological Representations of Disease Heterogeneity Through Machine Learning.
Wen J, Antoniades M, Yang Z, Hwang G, Skampardoni I, Wang R, Davatzikos C. Wen J, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 1;96(7):564-584. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2024.04.017. Epub 2024 May 6. Biol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38718880 Review. - Myelin-specific T cells carry and release magnetite PGLA-PEG COOH nanoparticles in the mouse central nervous system.
D'Elios MM, Aldinucci A, Amoriello R, Benagiano M, Bonechi E, Maggi P, Flori A, Ravagli C, Saer D, Cappiello L, Conti L, Valtancoli B, Bencini A, Menichetti L, Baldi G, Ballerini C. D'Elios MM, et al. RSC Adv. 2018 Jan 3;8(2):904-913. doi: 10.1039/c7ra11290d. eCollection 2018 Jan 2. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35538965 Free PMC article. - A comprehensive literatures update of clinical researches of superparamagnetic resonance iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging.
Wáng YX, Idée JM. Wáng YX, et al. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2017 Feb;7(1):88-122. doi: 10.21037/qims.2017.02.09. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2017. PMID: 28275562 Free PMC article. Review. - Iron Oxide as an MRI Contrast Agent for Cell Tracking.
Korchinski DJ, Taha M, Yang R, Nathoo N, Dunn JF. Korchinski DJ, et al. Magn Reson Insights. 2015 Oct 6;8(Suppl 1):15-29. doi: 10.4137/MRI.S23557. eCollection 2015. Magn Reson Insights. 2015. PMID: 26483609 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Steinman L (2001) Multiple sclerosis: A two-stage disease. Nature Immunology 2: 762–764. - PubMed
- Confavreux C, Vukusic S, Adeleine P (2003) Early clinical predictors and progression of irreversible disability in multiple sclerosis: An amnesic process. Brain 126: 770–82. - PubMed
- Miller D, Barkhof F, Montalban X, Thompson A, Filippi M (2005) Clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis, part 2: Non-conventional MRI, recovery processes, and management. The Lancet Neurology 4: 341–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
The study was supported by ARSEP (Foundation pour l′Aide a la Recherche sur la Scelerose en Plaques). The scholarship of Dr. Crimi has been financed by ERCIM (European Research Consortium for Informatics and Mathematics). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical