Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data - PubMed (original) (raw)
Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data
Anthony M Bolger et al. Bioinformatics. 2014.
Abstract
Motivation: Although many next-generation sequencing (NGS) read preprocessing tools already existed, we could not find any tool or combination of tools that met our requirements in terms of flexibility, correct handling of paired-end data and high performance. We have developed Trimmomatic as a more flexible and efficient preprocessing tool, which could correctly handle paired-end data.
Results: The value of NGS read preprocessing is demonstrated for both reference-based and reference-free tasks. Trimmomatic is shown to produce output that is at least competitive with, and in many cases superior to, that produced by other tools, in all scenarios tested.
Availability and implementation: Trimmomatic is licensed under GPL V3. It is cross-platform (Java 1.5+ required) and available at http://www.usadellab.org/cms/index.php?page=trimmomatic
Contact: usadel@bio1.rwth-aachen.de
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
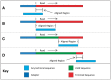
Fig. 1.
Putative sequence alignments as tested in simple mode. The alignment process begins with a partial overlap at the 5′ end of the read (A), increasing to a full-length 5′ overlap (B), followed by full overlaps at all positions (C) and finishes with a partial overlap at the 3′ end of the read (D).
Note that the upstream ‘adapter’ sequence is for illustration only and is not part of the read or the aligned region
Fig. 2.
Putative sequence alignments as tested in palindrome mode. The alignment process begins with the adapters completely overlapping the reads (A) testing for immediate ‘read-through’, then proceeds by checking for later overlap (B), including partial adapter read-through (C), finishing when the overlap indicates no read-through into the adapters (D)
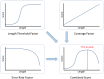
Fig. 3.
How Maximum Information mode combines uniqueness, coverage and error rate to determine the optimal trimming point
Similar articles
- Ktrim: an extra-fast and accurate adapter- and quality-trimmer for sequencing data.
Sun K. Sun K. Bioinformatics. 2020 Jun 1;36(11):3561-3562. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa171. Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32159761 - IMSEQ--a fast and error aware approach to immunogenetic sequence analysis.
Kuchenbecker L, Nienen M, Hecht J, Neumann AU, Babel N, Reinert K, Robinson PN. Kuchenbecker L, et al. Bioinformatics. 2015 Sep 15;31(18):2963-71. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv309. Epub 2015 May 18. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25987567 - ACE: accurate correction of errors using K-mer tries.
Sheikhizadeh S, de Ridder D. Sheikhizadeh S, et al. Bioinformatics. 2015 Oct 1;31(19):3216-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv332. Epub 2015 May 28. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26026137 - Trowel: a fast and accurate error correction module for Illumina sequencing reads.
Lim EC, Müller J, Hagmann J, Henz SR, Kim ST, Weigel D. Lim EC, et al. Bioinformatics. 2014 Nov 15;30(22):3264-5. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu513. Epub 2014 Jul 29. Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 25075116 - FastqPuri: high-performance preprocessing of RNA-seq data.
Pérez-Rubio P, Lottaz C, Engelmann JC. Pérez-Rubio P, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 May 3;20(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2799-0. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31053060 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Comparative genomics of Plasmodium yoelii nigeriensis N67 and N67C: genome-wide polymorphisms, differential gene expression, and drug resistance.
Wu J, Oguz C, Teklemichael AA, Xu F, Stadler RV, Lucky AB, Liu S, Kaneko O, Lack J, Su XZ. Wu J, et al. BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 5;25(1):1035. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10961-4. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39497038 Free PMC article. - Stabilizing selection and adaptation shape cis and trans gene expression variation in C. elegans.
Bell AD, Valencia F, Paaby AB. Bell AD, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 18:2024.10.15.618466. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.15.618466. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39464158 Free PMC article. Preprint. - Limited Variation in Codon Usage across Mitochondrial Genomes of Non-Biting Midges (Diptera: Chironomidae).
Lei T, Zheng X, Song C, Jin H, Chen L, Qi X. Lei T, et al. Insects. 2024 Sep 28;15(10):752. doi: 10.3390/insects15100752. Insects. 2024. PMID: 39452328 Free PMC article. - Effects of brain microRNAs in cognitive trajectory and Alzheimer's disease.
Vattathil SM, Tan SSM, Kim PJ, Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Wingo AP, Wingo TS. Vattathil SM, et al. Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Oct 30;148(1):59. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02818-7. Acta Neuropathol. 2024. PMID: 39477879 Free PMC article. - Radiation-induced morphea of the breast - characterization and treatment of fibroblast dysfunction with repurposed mesalazine.
Künzel SR, Klapproth E, Zimmermann N, Kämmerer S, Schubert M, Künzel K, Hoffmann M, Drukewitz S, Vehlow A, Eitler J, Arriens M, Thiel J, Kronstein-Wiedemann R, Tietze M, Beissert S, Renner B, El-Armouche A, Günther C. Künzel SR, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 30;14(1):26132. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74206-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39477958 Free PMC article.
References
- Aronesty E. Comparison of sequencing utility programs. Open Bioinform. J. 2013;7:1–8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous