DNMT3A and IDH mutations in acute myeloid leukemia and other myeloid malignancies: associations with prognosis and potential treatment strategies - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
DNMT3A and IDH mutations in acute myeloid leukemia and other myeloid malignancies: associations with prognosis and potential treatment strategies
A P Im et al. Leukemia. 2014 Sep.
Erratum in
- Leukemia. 2015 Feb;29(2):516
Abstract
The development of effective treatment strategies for most forms of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) has languished for the past several decades. There are a number of reasons for this, but key among them is the considerable heterogeneity of this disease and the paucity of molecular markers that can be used to predict clinical outcomes and responsiveness to different therapies. The recent large-scale sequencing of AML genomes is now providing opportunities for patient stratification and personalized approaches to treatment that are based on individual mutational profiles. It is particularly notable that studies by The Cancer Genome Atlas and others have determined that 44% of patients with AML exhibit mutations in genes that regulate methylation of genomic DNA. In particular, frequent mutation has been observed in the genes encoding DNA methyltransferase 3A (DNMT3A), isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) and isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2), as well as Tet oncogene family member 2. This review will summarize the incidence of these mutations, their impact on biochemical functions including epigenetic modification of genomic DNA and their potential usefulness as prognostic indicators. Importantly, the presence of DNMT3A, IDH1 or IDH2 mutations may confer sensitivity to novel therapeutic approaches, including the use of demethylating agents. Therefore, the clinical experience with decitabine and azacitidine in the treatment of patients harboring these mutations will be reviewed. Overall, we propose that understanding the role of these mutations in AML biology will lead to more rational therapeutic approaches targeting molecularly defined subtypes of the disease.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
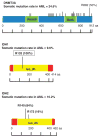
Figure 1
Location and frequency of DNMT3A, IDH1 and IDH2 mutations as determined by The Cancer Genome Atlas. Mutation data was obtained from the cBio portal.
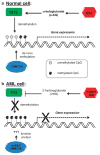
Figure 2
(a) Normal function of IDH1/2, TET2 and DNMT3A enzymes in DNA methylation and gene expression. (b) Pathogenic mechanism of mutated IDH1/2 and DNMT3A in gene silencing in AML.
Similar articles
- Perspectives for therapeutic targeting of gene mutations in acute myeloid leukaemia with normal cytogenetics.
Falini B, Sportoletti P, Brunetti L, Martelli MP. Falini B, et al. Br J Haematol. 2015 Aug;170(3):305-22. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13409. Epub 2015 Apr 19. Br J Haematol. 2015. PMID: 25891481 Review. - IDH1 and IDH2 mutations are frequent genetic alterations in acute myeloid leukemia and confer adverse prognosis in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia with NPM1 mutation without FLT3 internal tandem duplication.
Paschka P, Schlenk RF, Gaidzik VI, Habdank M, Krönke J, Bullinger L, Späth D, Kayser S, Zucknick M, Götze K, Horst HA, Germing U, Döhner H, Döhner K. Paschka P, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2010 Aug 1;28(22):3636-43. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.28.3762. Epub 2010 Jun 21. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20567020 - [Mutation of isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2) gene in Chinese AML patients and its clinical significance].
Shang Z, Wang D, Xiao M, Wang J, Li TJ, Zhao YC, Li CR, Zhou JF. Shang Z, et al. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Jun;21(3):607-12. doi: 10.7534/j.issn.1009-2137.2013.03.014. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23815907 Chinese. - [Research progress on genes associated with transformation of myelodysplastic syndromes to acute myeloid leukemia].
Zhu C, Ma Y, Xu XP. Zhu C, et al. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Jun;22(3):873-8. doi: 10.7534/j.issn.1009-2137.2014.03.057. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24989313 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
- Evaluation of DNMT3A genetic polymorphisms as outcome predictors in AML patients.
Yuan XQ, Zhang DY, Yan H, Yang YL, Zhu KW, Chen YH, Li X, Yin JY, Li XL, Zeng H, Chen XP. Yuan XQ, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 13;7(37):60555-60574. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11143. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27528035 Free PMC article. - Adverse Impact of DNA Methylation Regulatory Gene Mutations on the Prognosis of AML Patients in the 2017 ELN Favorable Risk Group, Particularly Those Defined by NPM1 Mutation.
Yu J, Sun J, Du Y, Patel R, Varela JC, Mori S, Chang CC. Yu J, et al. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 May 29;11(6):986. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11060986. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34072516 Free PMC article. - Association between increased mutation rates in DNMT3A and FLT3-ITD and poor prognosis of patients with acute myeloid leukemia.
Zhang Q, Wu X, Cao J, Gao F, Huang K. Zhang Q, et al. Exp Ther Med. 2019 Oct;18(4):3117-3124. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7891. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31572552 Free PMC article. - Rescue of TCA Cycle Dysfunction for Cancer Therapy.
Marquez J, Flores J, Kim AH, Nyamaa B, Nguyen ATT, Park N, Han J. Marquez J, et al. J Clin Med. 2019 Dec 6;8(12):2161. doi: 10.3390/jcm8122161. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31817761 Free PMC article. Review. - [Clinical analysis of the combination regimen with Bcl-2 inhibitor venetoclax in the treatment of 30 cases of acute myeloid leukemia with IDH1/2 mutation].
Wang X, Bao XB, Zhang J, Song BQ, Li MY, Xie JD, Shen HJ, Wu DP, Qiu HY. Wang X, et al. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Aug 14;43(8):691-694. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2022.08.014. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36709157 Free PMC article. Chinese. No abstract available.
References
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
- Dohner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Buchner T, Burnett AK, et al. Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2010;115:453–474. - PubMed
- Gupta V, Tallman MS, Weisdorf DJ. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adults with acute myeloid leukemia: myths, controversies, and unknowns. Blood. 2011;117:2307–2318. - PubMed
- Mayer RJ, Davis RB, Schiffer CA, Berg DT, Powell BL, Schulman P, et al. Intensive postremission chemotherapy in adults with acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer and Leukemia Group B. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:896–903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous