Extracellular Vesicles in Multiple Sclerosis: What are They Telling Us? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Extracellular Vesicles in Multiple Sclerosis: What are They Telling Us?
Matías Sáenz-Cuesta et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014.
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane-bound particles secreted by almost all cell types. They are classified depending on their biogenesis and size into exosomes and microvesicles or according to their cell origin. EVs play a role in cell-to-cell communication, including contact-free cell synapsis, carrying active membrane proteins, lipids, and genetic material both inside the particle and on their surface. They have been related to several physiological and pathological conditions. In particular, increasing concentrations of EVs have been found in many autoimmune diseases including multiple sclerosis (MS). MS is a central nervous system (CNS) demyelinating disease characterized by relapsing of symptoms followed by periods of remission. Close interaction between endothelial cells, leukocytes, monocytes, and cells from CNS is crucial for the development of MS. This review summarizes the pathological role of EVs in MS and the relationship of EVs with clinical characteristics, therapy, and biomarkers of the disease.
Keywords: biomarker; exosomes; extracellular vesicle; microvesicle; multiple sclerosis; therapy.
Figures
Figure 1
Electron microscopy image of EVs. An electron microscopy image of an EV cluster obtained from peripheral blood. Note the rounded shape and cell membrane-like appearance of EV surfaces.
Figure 2
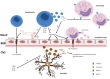
Pathogenic roles of EV in MS. EVs are involved in the transendothelial cell migration of lymphocytes and monocytes and the spread of neuroinflammation. Metalloproteases carried by EEVs promote BBB disruption. The release of proinflammatory cytokines from lymphocytes augments adhesion molecules on endothelial cells facilitating cell adhesion. In the CNS compartment, microglia play a key role in propagation of neuroinflammation shedding MEVs containing IL1-b and MHC-II. BBB, blood–brain barrier; CNS, central nervous system; AA, arachidonic acid; EEV, endothelial-derived extracellular vesicle; LEV, leukocyte-derived extracellular vesicle; MEV, microglia-derived extracellular vesicle.
Similar articles
- Extracellular Vesicles as Pro- and Anti-inflammatory Mediators, Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutic Agents in Multiple Sclerosis.
Manu MS, Hohjoh H, Yamamura T. Manu MS, et al. Aging Dis. 2021 Sep 1;12(6):1451-1461. doi: 10.14336/AD.2021.0513. eCollection 2021 Sep. Aging Dis. 2021. PMID: 34527421 Free PMC article. Review. - Appearance of claudin-5+ leukocytes in the central nervous system during neuroinflammation: a novel role for endothelial-derived extracellular vesicles.
Paul D, Baena V, Ge S, Jiang X, Jellison ER, Kiprono T, Agalliu D, Pachter JS. Paul D, et al. J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Nov 16;13(1):292. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0755-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27852330 Free PMC article. - Extracellular Vesicles in Neuroinflammation.
Marostica G, Gelibter S, Gironi M, Nigro A, Furlan R. Marostica G, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 21;8:623039. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.623039. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33553161 Free PMC article. Review. - Brain and immune system-derived extracellular vesicles mediate regulation of complement system, extracellular matrix remodeling, brain repair and antigen tolerance in Multiple sclerosis.
Torres Iglesias G, Fernández-Fournier M, Botella L, Piniella D, Laso-García F, Carmen Gómez-de Frutos M, Chamorro B, Puertas I, Tallón Barranco A, Fuentes B, Alonso de Leciñana M, Alonso-López E, Bravo SB, Eugenia Miranda-Carús M, Montero-Calle A, Barderas R, Díez-Tejedor E, Gutiérrez-Fernández M, Otero-Ortega L. Torres Iglesias G, et al. Brain Behav Immun. 2023 Oct;113:44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.06.025. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Brain Behav Immun. 2023. PMID: 37406976 - Sulfatides in extracellular vesicles isolated from plasma of multiple sclerosis patients.
Moyano AL, Li G, Boullerne AI, Feinstein DL, Hartman E, Skias D, Balavanov R, van Breemen RB, Bongarzone ER, Månsson JE, Givogri MI. Moyano AL, et al. J Neurosci Res. 2016 Dec;94(12):1579-1587. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23899. Epub 2016 Aug 25. J Neurosci Res. 2016. PMID: 27557608
Cited by
- The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Demyelination of the Central Nervous System.
López-Guerrero JA, Ripa I, Andreu S, Bello-Morales R. López-Guerrero JA, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 30;21(23):9111. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239111. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33266211 Free PMC article. Review. - Modulation of cellular function through immune-activated exosomes.
Pulliam L, Gupta A. Pulliam L, et al. DNA Cell Biol. 2015 Jul;34(7):459-63. doi: 10.1089/dna.2015.2884. Epub 2015 May 6. DNA Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25945690 Free PMC article. - Extracellular Vesicles as Pro- and Anti-inflammatory Mediators, Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutic Agents in Multiple Sclerosis.
Manu MS, Hohjoh H, Yamamura T. Manu MS, et al. Aging Dis. 2021 Sep 1;12(6):1451-1461. doi: 10.14336/AD.2021.0513. eCollection 2021 Sep. Aging Dis. 2021. PMID: 34527421 Free PMC article. Review. - Unravelling the mechanisms driving multimorbidity in COPD to develop holistic approaches to patient-centred care.
Burke H, Wilkinson TMA. Burke H, et al. Eur Respir Rev. 2021 Jun 1;30(160):210041. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0041-2021. Print 2021 Jun 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2021. PMID: 34415848 Free PMC article. Review. - Extracellular Vesicles in Immune System Regulation and Type 1 Diabetes: Cell-to-Cell Communication Mediators, Disease Biomarkers, and Promising Therapeutic Tools.
Grieco GE, Fignani D, Formichi C, Nigi L, Licata G, Maccora C, Brusco N, Sebastiani G, Dotta F. Grieco GE, et al. Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 9;12:682948. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.682948. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34177928 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bianco F., Pravettoni E., Colombo A., Schenk U., Möller T., Matteoli M., et al. (2005). Astrocyte-derived ATP induces vesicle shedding and IL-1 beta release from microglia. J. Immunol. 174, 7268–7277 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources