Protein nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers for cancer therapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Protein nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers for cancer therapy
Warangkana Lohcharoenkal et al. Biomed Res Int. 2014.
Abstract
Nanoparticles have increasingly been used for a variety of applications, most notably for the delivery of therapeutic and diagnostic agents. A large number of nanoparticle drug delivery systems have been developed for cancer treatment and various materials have been explored as drug delivery agents to improve the therapeutic efficacy and safety of anticancer drugs. Natural biomolecules such as proteins are an attractive alternative to synthetic polymers which are commonly used in drug formulations because of their safety. In general, protein nanoparticles offer a number of advantages including biocompatibility and biodegradability. They can be prepared under mild conditions without the use of toxic chemicals or organic solvents. Moreover, due to their defined primary structure, protein-based nanoparticles offer various possibilities for surface modifications including covalent attachment of drugs and targeting ligands. In this paper, we review the most significant advancements in protein nanoparticle technology and their use in drug delivery arena. We then examine the various sources of protein materials that have been used successfully for the construction of protein nanoparticles as well as their methods of preparation. Finally, we discuss the applications of protein nanoparticles in cancer therapy.
Figures
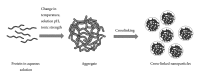
Figure 1
Preparation of protein nanoparticles by coacervation or phase separation method.
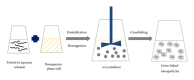
Figure 2
Preparation of protein nanoparticles by emulsion/solvent extraction method.
Figure 3
Preparation of protein nanoparticles by complex coacervation method.
Similar articles
- Natural Ingredient-Based Polymeric Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment.
Wong KH, Lu A, Chen X, Yang Z. Wong KH, et al. Molecules. 2020 Aug 9;25(16):3620. doi: 10.3390/molecules25163620. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32784890 Free PMC article. Review. - Dendronized Systems for the Delivery of Chemotherapeutics.
Dockery L, Daniel MC. Dockery L, et al. Adv Cancer Res. 2018;139:85-120. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 May 18. Adv Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29941108 Review. - Recent Advances in Nanoparticle-Based Cancer Drug and Gene Delivery.
Amreddy N, Babu A, Muralidharan R, Panneerselvam J, Srivastava A, Ahmed R, Mehta M, Munshi A, Ramesh R. Amreddy N, et al. Adv Cancer Res. 2018;137:115-170. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Adv Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29405974 Free PMC article. Review. - A sight on protein-based nanoparticles as drug/gene delivery systems.
Salatin S, Jelvehgari M, Maleki-Dizaj S, Adibkia K. Salatin S, et al. Ther Deliv. 2015;6(8):1017-29. doi: 10.4155/tde.15.28. Epub 2015 Aug 25. Ther Deliv. 2015. PMID: 26305428 Review. - Nanocarriers for cancer-targeted drug delivery.
Kumari P, Ghosh B, Biswas S. Kumari P, et al. J Drug Target. 2016;24(3):179-91. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2015.1051049. Epub 2015 Jun 10. J Drug Target. 2016. PMID: 26061298 Review.
Cited by
- A new nanobiotic: synthesis and characterization of an albumin nanoparticle with intrinsic antibiotic activity.
Sheikh Hosseini M, Moosavi-Nejad Z, Mohammadi P. Sheikh Hosseini M, et al. Iran J Microbiol. 2023 Oct;15(5):697-704. doi: 10.18502/ijm.v15i5.13875. Iran J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37941877 Free PMC article. - Silver nanoparticles induce degradation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor activating transcription factor-6 leading to activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome.
Simard JC, Vallieres F, de Liz R, Lavastre V, Girard D. Simard JC, et al. J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 27;290(9):5926-39. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.610899. Epub 2015 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25593314 Free PMC article. - Gelatin Coating for the Improvement of Stability and Cell Uptake of Hydrophobic Drug-Containing Liposomes.
Battogtokh G, Joo Y, Abuzar SM, Park H, Hwang SJ. Battogtokh G, et al. Molecules. 2022 Feb 3;27(3):1041. doi: 10.3390/molecules27031041. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164305 Free PMC article. - Nanomedicine Strategies to Target Tumor-Associated Macrophages.
Binnemars-Postma K, Storm G, Prakash J. Binnemars-Postma K, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 May 4;18(5):979. doi: 10.3390/ijms18050979. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28471401 Free PMC article. Review. - Milk derived colloid as a novel drug delivery carrier for breast cancer.
Hayashi M, Silanikove N, Chang X, Ravi R, Pham V, Baia G, Paz K, Brait M, Koch WM, Sidransky D. Hayashi M, et al. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(8):1184-93. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1056416. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26046946 Free PMC article.
References
- Pathak Y. Drug Delivery Nanoparticles Formulation and Characterization. New York, NY, USA: Informa Healthcare USA; 2009. Recent developments in nanoparticulate drug delivery systems; pp. 1–7.
- Jahanshahi M, Zhang Z, Lyddiatt A. Subtractive chromatography for purification and recovery of nano-bioproducts. IEE Proceedings Nanobiotechnology. 2005;152(3):121–126. - PubMed
- Soppimath KS, Aminabhavi TM, Kulkarni AR, Rudzinski WE. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. Journal of Controlled Release. 2001;70(1-2):1–20. - PubMed
- Coester C, Nayyar P, Samuel J. In vitro uptake of gelatin nanoparticles by murine dendritic cells and their intracellular localisation. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics. 2006;62(3):306–314. - PubMed
- Verma RK, Garg S. Current status of drug delivery technologies and future directions. Pharmaceutical Technology. 2001;25:1–14.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources