Renal sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors as a novel therapeutic approach to treatment of type 2 diabetes: Clinical data and mechanism of action - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2014 May 4;5(3):265-75.
doi: 10.1111/jdi.12214. Epub 2014 Apr 2.
Affiliations
- PMID: 24843771
- PMCID: PMC4020327
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12214
Review
Renal sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors as a novel therapeutic approach to treatment of type 2 diabetes: Clinical data and mechanism of action
Yoshihito Fujita et al. J Diabetes Investig. 2014.
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by impaired insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells and/or reduced response of target tissues to insulin. Good glycemic control delays the development and slows the progression of micro- and macrovascular complications. Although there are numerous glucose-lowering agents in clinical use, only approximately half of type 2 diabetic patients achieve glycemic control, and undesirable side-effects often hamper treatment in those treated with the medications. There is a need for novel treatment options that can help overcome these difficulties. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have recently been developed as a novel potential therapeutic option for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. These drugs lower the plasma glucose concentration through inhibition of glucose reuptake in the kidney, independent of insulin secretion and insulin action, with a consequent lower risk of hypoglycemia. The data of clinical trials with monotherapy as well as combination therapy show that SGLT2 inhibitors have a blood glucose-lowering effect and also reduce bodyweight. A follow-up study shows long-term efficacy and the durability of these effects. SGLT2 inhibitors have the potential to reverse glucose toxicity, and to improve insulin resistance, blood pressure and lipid profile. The available data suggest a good tolerability profile. However, clinicians should carefully prescribe these drugs in light of already reported and/or unexpected side-effects. Further studies in larger numbers and longer-term clinical use data are required to place these agents in standard treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Novel antidiabetic agents; Renal glucose reabsorption; Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
Figures
Figure 1
Renal glucose handling in a non‐diabetic individual. (a) Glucose reabsorption in the kidney. (b) Glucose reabsorption through sodium glucose cotransporter (
SGLT
)1 and
SGLT
2 in the proximal renal tubular cell.
ADP
, adenosine diphosphate;
ATP
, adenosine triphosphate;
GLUT
, glucose transporter; S1, segment1; S2, segment 2; S3, segment 3.
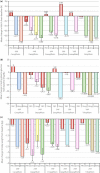
Figure 2
Results of trials with sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. Changes in (a) glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), (b) fasting plasma glucose and (c) bodyweight39.
PBO
, placebo.
Similar articles
- Oral antidiabetic agents: current role in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Krentz AJ, Bailey CJ. Krentz AJ, et al. Drugs. 2005;65(3):385-411. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200565030-00005. Drugs. 2005. PMID: 15669880 Review. - Clinical potential of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in the management of type 2 diabetes.
Kim Y, Babu AR. Kim Y, et al. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2012;5:313-27. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S22545. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2012. PMID: 22977310 Free PMC article. - The Role of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes.
Whalen K, Miller S, Onge ES. Whalen K, et al. Clin Ther. 2015 Jun 1;37(6):1150-66. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 25891804 Review. - Ipragliflozin and other sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: preclinical and clinical data.
Kurosaki E, Ogasawara H. Kurosaki E, et al. Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jul;139(1):51-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.04.003. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23563279 Review.
Cited by
- Comparison of protective effects of teneligliptin and luseogliflozin on pancreatic β-cell function: randomized, parallel-group, multicenter, open-label study (SECRETE-I study).
Shimoda M, Katakura Y, Mashiko A, Iwamoto M, Nakanishi S, Anno T, Kawasaki F, Obata A, Fushimi Y, Sanada J, Kohara K, Isobe H, Iwamoto Y, Hirukawa H, Tatsumi F, Kimura Y, Kimura T, Mune T, Kaku K, Kaneto H. Shimoda M, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 21;15:1412553. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1412553. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39497800 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Efficacy and Safety of Adding Empagliflozin to Liraglutide on Renal Function in Patients with Advanced-Stage Type 2 Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial.
Sunagawa K, Hirai K, Sunagawa S, Kamiya N, Komesu I, Sunagawa Y, Sunagawa H, Nakachi K, Hirai A, Ookawara S, Morishita Y. Sunagawa K, et al. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Oct 14;17:3767-3781. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S471535. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39430135 Free PMC article. - Relationship between SGLT2 inhibitor use and specific cancer types: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Obaid MI, Shahzad MS, Latif F, Khan MH, Akram M, Mehdi Rizvi SA, Umer Nasrullah RM, Asad D, Obaid MA. Obaid MI, et al. Future Sci OA. 2024 Dec 31;10(1):2400797. doi: 10.1080/20565623.2024.2400797. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Future Sci OA. 2024. PMID: 39344829 Free PMC article. Review. - Sex-dependent effects of Canagliflozin on kidney protection in mice with combined hypertension-type 1 diabetes.
Trentin-Sonoda M, Cheff V, Gutsol A, Hébert RL. Trentin-Sonoda M, et al. PLoS One. 2023 Dec 6;18(12):e0295284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295284. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38055691 Free PMC article. - Prescribing SGLT2 Inhibitors in Patients With CKD: Expanding Indications and Practical Considerations.
Yau K, Dharia A, Alrowiyti I, Cherney DZI. Yau K, et al. Kidney Int Rep. 2022 May 5;7(7):1463-1476. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.04.094. eCollection 2022 Jul. Kidney Int Rep. 2022. PMID: 35812300 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas, 6th edn International Brussels, Brussels, Belgium, Belgium, International Diabetes Federation, 2013
- Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lu Y, et al National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country‐years and 2.7 million participants. Lancet 2011; 378: 31–40 - PubMed
- O'Rahilly S. Human obesity and insulin resistance: lessons from experiments of nature. Biochem Soc Trans 2007; 35: 33–36 - PubMed
- Pirola L, Balcerczyk A, Okabe J, et al Epigenetic phenomena linked to diabetic complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2010; 6: 665–675 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources