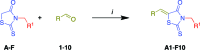The Rhodadyns, a New Class of Small Molecule Inhibitors of Dynamin GTPase Activity - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2012 Mar 26;3(5):352-6.
doi: 10.1021/ml200284s. eCollection 2012 May 10.
Gordana Hadzic 1, Joseph Ambrus 1, D Yuri Pomè 1, Emily Hyde 1, Ainslie Whiting 2, Anna Mariana 2, Lisa von Kleist 3, Ngoc Chau 2, Volker Haucke 3, Phillip J Robinson 2, Adam McCluskey 1
Affiliations
- PMID: 24900478
- PMCID: PMC4025782
- DOI: 10.1021/ml200284s
The Rhodadyns, a New Class of Small Molecule Inhibitors of Dynamin GTPase Activity
Mark J Robertson et al. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012.
Abstract
Six focused rhodanine-based libraries, 60 compounds in total, were synthesized and evaluated as potential dynamin I GTPase inhibitors. Twenty-six were more potent than the lead compound with 13 returning IC50 values ≤10 μM, making the Rhodadyn series among the most active dynamin inhibitors reported. Two analogues were highly effective at blocking receptor-mediated endocytosis: C10 and D10 with IC50(RME) = 7.0 ± 2.2 and 5.9 ± 1.0 μM, respectively. These compounds are equipotent with the best reported in-cell dynamin inhibitors.
Keywords: Knoevengal condensation; dynamin inhibition; rhodanine.
Figures
Figure 1
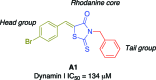
Chemical structure of the lead Rhodadyn A1.
Figure 2
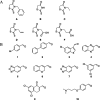
(a) Rhodanines (A–F) and (b) aldehydes (1–10) used in the synthesis of libraries A–F.
Scheme 1
Similar articles
- Development of quinone analogues as dynamin GTPase inhibitors.
MacGregor KA, Abdel-Hamid MK, Odell LR, Chau N, Whiting A, Robinson PJ, McCluskey A. MacGregor KA, et al. Eur J Med Chem. 2014 Oct 6;85:191-206. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.06.070. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Eur J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25084145 - Inhibition of dynamin mediated endocytosis by the dynoles--synthesis and functional activity of a family of indoles.
Hill TA, Gordon CP, McGeachie AB, Venn-Brown B, Odell LR, Chau N, Quan A, Mariana A, Sakoff JA, Chircop M, Robinson PJ, McCluskey A. Hill TA, et al. J Med Chem. 2009 Jun 25;52(12):3762-73. doi: 10.1021/jm900036m. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19459681 - Small molecule inhibitors of dynamin I GTPase activity: development of dimeric tyrphostins.
Hill T, Odell LR, Edwards JK, Graham ME, McGeachie AB, Rusak J, Quan A, Abagyan R, Scott JL, Robinson PJ, McCluskey A. Hill T, et al. J Med Chem. 2005 Dec 1;48(24):7781-8. doi: 10.1021/jm040208l. J Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 16302817 - Modulation of dynamin function by small molecules.
Eschenburg S, Reubold TF. Eschenburg S, et al. Biol Chem. 2018 Nov 27;399(12):1421-1432. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2018-0257. Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30067507 Review. - Regulating dynamin dynamics during endocytosis.
Sundborger AC, Hinshaw JE. Sundborger AC, et al. F1000Prime Rep. 2014 Oct 1;6:85. doi: 10.12703/P6-85. eCollection 2014. F1000Prime Rep. 2014. PMID: 25374663 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Insight into the role of clathrin-mediated endocytosis inhibitors in SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Alkafaas SS, Abdallah AM, Ghosh S, Loutfy SA, Elkafas SS, Abdel Fattah NF, Hessien M. Alkafaas SS, et al. Rev Med Virol. 2023 Jan;33(1):e2403. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2403. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Rev Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36345157 Free PMC article. Review. - Measuring Endocytosis During Proliferative Cell Quiescence.
Hinze C, McGourty K, Boucrot E. Hinze C, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2233:19-42. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1044-2_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33222125 - Building a better dynasore: the dyngo compounds potently inhibit dynamin and endocytosis.
McCluskey A, Daniel JA, Hadzic G, Chau N, Clayton EL, Mariana A, Whiting A, Gorgani NN, Lloyd J, Quan A, Moshkanbaryans L, Krishnan S, Perera S, Chircop M, von Kleist L, McGeachie AB, Howes MT, Parton RG, Campbell M, Sakoff JA, Wang X, Sun JY, Robertson MJ, Deane FM, Nguyen TH, Meunier FA, Cousin MA, Robinson PJ. McCluskey A, et al. Traffic. 2013 Dec;14(12):1272-89. doi: 10.1111/tra.12119. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Traffic. 2013. PMID: 24025110 Free PMC article. - Role of Clathrin and Dynamin in Clathrin Mediated Endocytosis/Synaptic Vesicle Recycling and Implications in Neurological Diseases.
Prichard KL, O'Brien NS, Murcia SR, Baker JR, McCluskey A. Prichard KL, et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jan 18;15:754110. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.754110. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35115907 Free PMC article. Review. - Prodrugs of the Archetypal Dynamin Inhibitor Bis-T-22.
Odell LR, Robertson MJ, Young KA, McGeachie AB, Quan A, Robinson PJ, McCluskey A. Odell LR, et al. ChemMedChem. 2022 Dec 16;17(24):e202200400. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202200400. Epub 2022 Nov 9. ChemMedChem. 2022. PMID: 36351775 Free PMC article.
References
- Krueger B. K.; Forn J.; Greengard P. Depolarization-induced phosphorylation of specific proteins, mediated by calcium ion influx, in rat brain synaptosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 2764–2773. - PubMed
- Van der Bliek A. M.; Meyerowitz E. M. Dynamin-like protein encoded by the Drosophila shibire gene associated with vesicular traffic. Nature 1991, 351, 411–414. - PubMed
- Chen M. S.; Obar R. A.; Schroeder C. C.; Austin T. W.; Poodry C. A.; Wadsworth S. C.; Vallee R. B. Multiple forms of dynamin are encoded by shibire, a Drosophila gene involved in endocytosis. Nature 1991, 351, 583–586. - PubMed
- Robinson P. J.; Sontag J. M.; Liu J. P.; Fykse E. M.; Slaughter C.; McMahon H.; Sudhof T. C. Dynamin GTPase regulated by protein kinase C phosphorylation in nerve terminals. Nature 1993, 365, 163–166. - PubMed
- Noda Y.; Nakata T.; Hirokawa N. Localization of dynamin: Widespread distribution in mature neurons and association with membranous organelles. Neuroscience 1993, 55, 113–127. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information