Structural permutation of potent cytotoxin, polytheonamide B: discovery of cytotoxic Peptide with altered activity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Structural permutation of potent cytotoxin, polytheonamide B: discovery of cytotoxic Peptide with altered activity
Hiroaki Itoh et al. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012.
Abstract
Polytheonamide B (1) is an ion-channel forming natural peptide with a d,l-alternating 48 amino acid sequence, which is an exceedingly potent cytotoxin. We recently designed and synthesized a simplified dansylated polytheonamide mimic 2, in which six amino acid residues were modified from 1, and demonstrated that 2 emulated the functions of 1. Here we report a comprehensive structure-activity relationship study of substructures of 2. A unified synthetic strategy was developed for highly automated syntheses of 13 peptide sequences of 27 to 39 amino acid residues, and the artificial 37-mer peptide 6 was discovered to be significantly more toxic than the other 12 compounds toward P388 mouse leukemia cells (IC50 = 3.7 nM). Ion exchange activity experiments of 6 using the liposome and P388 cells both demonstrated that 6 did not possess ion-channel activity, strongly suggesting that 6 exerted its potent cytoxicity through a distinct mode of action from 1 and 2.
Keywords: Cytotoxic agents; natural products; solid-phase synthesis; structure−activity relationships; synthetic ion channels.
Figures
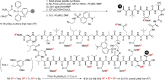
Figure 1
Structures of polytheonamide B, dansylated polytheonamide mimic, and gramicidin D.
Scheme 1. Representative Synthetic Scheme of the Substructures of 2
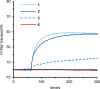
Figure 2
Time-course of H+/Na+ exchange across lipid bilayers of pH-gradient liposomes (EYPC/cholesterol = 2:1) caused by 1, 2, 3, and 6. The ion transport was evaluated as the pH-dependent fluorescence from pyranine standardized against the maximum exchange by Triton X-100. In all the experiments, the peptides were added at 60 s.
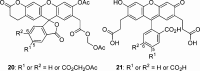
Figure 3
Structures of BCECF-AM (20) and BCECF (21).
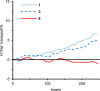
Figure 4
Time-course of H+/Na+ exchange across cell membranes of the P388 leukemia cells caused by 1, 3, and 6. Intracellular pH values were evaluated by the pH-dependent fluorescence of 21. In all the experiments, peptides were added at 0 s.
Similar articles
- Chemical construction and structural permutation of potent cytotoxin polytheonamide B: discovery of artificial peptides with distinct functions.
Itoh H, Inoue M. Itoh H, et al. Acc Chem Res. 2013 Jul 16;46(7):1567-78. doi: 10.1021/ar300315p. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Acc Chem Res. 2013. PMID: 23488446 Review. - Design, synthesis and functional analysis of dansylated polytheonamide mimic: an artificial peptide ion channel.
Itoh H, Matsuoka S, Kreir M, Inoue M. Itoh H, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Aug 29;134(34):14011-8. doi: 10.1021/ja303831a. Epub 2012 Aug 20. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22861006 - Dual Chemical Modification of a Polytheonamide Mimic: Rational Design and Synthesis of Ion-Channel-Forming 48-mer Peptides with Potent Cytotoxicity.
Hayata A, Itoh H, Matsutaka S, Inoue M. Hayata A, et al. Chemistry. 2016 Mar 1;22(10):3370-3377. doi: 10.1002/chem.201504632. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Chemistry. 2016. PMID: 26833801 - Solid-Phase Total Synthesis and Dual Mechanism of Action of the Channel-Forming 48-mer Peptide Polytheonamide B.
Hayata A, Itoh H, Inoue M. Hayata A, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2018 Aug 22;140(33):10602-10611. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b06755. Epub 2018 Aug 7. J Am Chem Soc. 2018. PMID: 30040396 - Total synthesis and functional analysis of non-ribosomal peptides.
Inoue M. Inoue M. Chem Rec. 2011 Sep;11(5):284-94. doi: 10.1002/tcr.201100014. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Chem Rec. 2011. PMID: 21905205 Review.
Cited by
- Mechanism of Action of Ribosomally Synthesized and Post-Translationally Modified Peptides.
Ongpipattanakul C, Desormeaux EK, DiCaprio A, van der Donk WA, Mitchell DA, Nair SK. Ongpipattanakul C, et al. Chem Rev. 2022 Sep 28;122(18):14722-14814. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00210. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 36049139 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Hamada T.; Matsunaga S.; Yano G.; Fusetani N. Polytheonamides A and B, Highly Cytotoxic, Linear Polypeptides with Unprecedented Structural Features, from the Marine Sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 110–118. - PubMed
- Hamada T.; Sugawara T.; Matsunaga S.; Fusetani N. Polytheonamides, Unprecedented Highly Cytotoxic Polypeptides, from the Marine Sponge Theonella swinhoei: 1. Isolation and Component Amino Acids. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 719–720.
- Hamada T.; Matsunaga S.; Fujiwara M.; Fujita K.; Hirota H.; Schmucki R.; Güntert P.; Fusetani N. Solution Structure of Polytheonamide B, a Highly Cytotoxic Nonribosomal Polypeptide from Marine Sponge. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12941–12945. - PubMed
- Iwamoto M.; Shimizu H.; Muramatsu I.; Oiki S. A Cytotoxic Peptide from a Marine Sponge Exhibits Ion Channel Activity through Vectorial-Insertion into the Membrane. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3995–3999. - PubMed
- Oiki S.; Muramatsu I.; Matsunaga S.; Fusetani N.. A Channel-Forming Peptide Toxin: Polytheonamide from Marine Sponge (Theonella swinhoei). Folia Pharmacol. Jpn. 1997, 110(Suppl.1), 195–198. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous