Stem cell-based cell therapy for glomerulonephritis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Stem cell-based cell therapy for glomerulonephritis
Meiling Jin et al. Biomed Res Int. 2014.
Abstract
Glomerulonephritis (GN), characterized by immune-mediated inflammatory changes in the glomerular, is a common cause of end stage renal disease. Therapeutic options for glomerulonephritis applicable to all cases mainly include symptomatic treatment and strategies to delay progression. In the attempt to yield innovative interventions fostering the limited capability of regeneration of renal tissue after injury and the uncontrolled pathological process by current treatments, stem cell-based therapy has emerged as novel therapy for its ability to inhibit inflammation and promote regeneration. Many basic and clinical studies have been performed that support the ability of various stem cell populations to ameliorate glomerular injury and improve renal function. However, there is a long way before putting stem cell-based therapy into clinical practice. In the present article, we aim to review works performed with respect to the use of stem cell of different origins in GN, and to discuss the potential mechanism of therapeutic effect and the challenges for clinical application of stem cells.
Figures
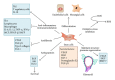
Figure 1
Potential mechanisms of therapeutical effect of stem cells on glomerulonephritis (GN). Stem cell-based cell therapy is likely to improve the kidney injury in GN mainly via (trans)differentiation of transplant cells into renal cells and paracrine mechanisms. Paracrine mechanisms include anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory, antifibrosis, antiapoptosis, oxidative stress inhibition, and maintaining normal structure and regeneration. (IL: interleukin, TNF: tumor necrosis factor, IFN-γ: interferon γ, MCP: monocyte chemotactic protein, PDGF-β: platelet-derived growth factor β, BAFF: B-cell activating factor, CTGF: connective tissue growth factor, TGF-β: transforming growth factor-β, PAI-1: plasminogen activator inhibitor 1, EGF: epithelial growth factor, VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor, HGF: hepatocyte growth factor, IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor, BMP-7: bone morphogenic protein-7, ROS: reactive oxygen species, RNS: reactive nitrogen species.).
Similar articles
- Stem cell therapy: An emerging modality in glomerular diseases.
Thakkar UG, Vanikar AV, Trivedi HL. Thakkar UG, et al. Cytotherapy. 2017 Mar;19(3):333-348. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2016.11.003. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Cytotherapy. 2017. PMID: 28089754 Review. - Metanephric mesenchyme-derived Foxd1+ mesangial precursor cells alleviate mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis.
Jin M, Yin Z, Wei K, Xie Y, Bai X, Fu B, Feng Z, Li Q, Chen X. Jin M, et al. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019 Apr;97(4):553-561. doi: 10.1007/s00109-019-01749-1. Epub 2019 Feb 27. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30810761 - Systematic implantation of dedifferentiated fat cells ameliorated monoclonal antibody 1-22-3-induced glomerulonephritis by immunosuppression with increases in TNF-stimulated gene 6.
Maruyama T, Fukuda N, Matsumoto T, Kano K, Endo M, Kazama M, Kazama T, Ikeda J, Matsuda H, Ueno T, Abe M, Okada K, Soma M, Matsumoto K, Kawachi H. Maruyama T, et al. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 Apr 16;6(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0069-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25889917 Free PMC article. - Therapeutic effects of human mesenchymal stem cells in Wistar-Kyoto rats with anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis.
Suzuki T, Iyoda M, Shibata T, Ohtaki H, Matsumoto K, Shindo-Hirai Y, Kuno Y, Wada Y, Yamamoto Y, Kawaguchi M, Shioda S, Akizawa T. Suzuki T, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Jun 24;8(6):e67475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067475. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23826305 Free PMC article. - Nephrotoxic nephritis and glomerulonephritis: animal model versus human disease.
Muhammad S. Muhammad S. Br J Biomed Sci. 2014;71(4):168-71. doi: 10.1080/09674845.2014.11669982. Br J Biomed Sci. 2014. PMID: 25562994 Review.
Cited by
- Safety and Biodistribution of an Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived Mononuclear Cell Infusion into Renal Arteries in Patients with Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis: A Phase 1 Study.
Botelho BF, Barreira AL, Filippo MG, Asensi KD, Faccioli LAP, Dos Santos Salgado AB, de Salles EF, Marques CEC, Silva PL, Dos Santos Goldenberg RC, Maiolino A, Gutfilen B, de Souza SAL, Junior ML, Morales MM. Botelho BF, et al. Stem Cells Int. 2024 Jul 9;2024:2385568. doi: 10.1155/2024/2385568. eCollection 2024. Stem Cells Int. 2024. PMID: 39015674 Free PMC article. - Selected microRNA Expression and Protein Regulator Secretion by Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Metabolic Syndrome.
Wystrychowski G, Simka-Lampa K, Witkowska A, Sobecko E, Skubis-Sikora A, Sikora B, Wojtyna E, Golda A, Gwizdek K, Wróbel M, Sędek Ł, Górczyńska-Kosiorz S, Szweda-Gandor N, Trautsolt W, Francuz T, Kruszniewska-Rajs C, Gola J. Wystrychowski G, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 17;25(12):6644. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126644. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928349 Free PMC article. - Extracellular Vesicles Released from Stem Cells as a New Therapeutic Strategy for Primary and Secondary Glomerulonephritis.
Quaglia M, Merlotti G, Fornara L, Colombatto A, Cantaluppi V. Quaglia M, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 20;23(10):5760. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105760. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628570 Free PMC article. Review. - Crescentic Glomerulonephritis: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Potential of Human Amniotic Stem Cells.
Al Mushafi A, Ooi JD, Odobasic D. Al Mushafi A, et al. Front Physiol. 2021 Oct 15;12:724186. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.724186. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34721059 Free PMC article. Review. - Therapeutic Insights in Chronic Kidney Disease Progression.
Shabaka A, Cases-Corona C, Fernandez-Juarez G. Shabaka A, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 23;8:645187. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.645187. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33708784 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Couser WG. Glomerulonephritis. The Lancet. 1999;353(9163):1509–1515. - PubMed
- Tanna A, Tam FW, Pusey CD. B-cell-targeted therapy in adult glomerulonephritis. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 2013;13(12):1691–1706. - PubMed
- Couchoud C, Stengel B, Landais P, et al. The renal epidemiology and information network (REIN): a new registry for end-stage renal disease in France. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 2006;21(2):411–418. - PubMed
- Trivedi HS, Pang MM, Campbell A, Saab P. Slowing the progression of chronic renal failure: economic benefits and patients’ perspectives. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 2002;39(4):721–729. - PubMed
- Chadban SJ, Atkins RC. Glomerulonephritis. The Lancet. 2005;365(9473):1797–1806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical