Changing the core of transcription - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comment
Changing the core of transcription
Katherine A Jones. Elife. 2014.
Abstract
Different members of the TAF family of proteins work in differentiated cells, such as motor neurons or brown fat cells, to control the expression of genes that are specific to each cell type.
Keywords: TBP-associated factor TAF; motor neurons; neuronal enhancers; neuronal gene expression; stem cells; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2014, Jones.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests:The author declares that no competing interests exist.
Figures
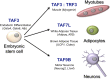
Figure 1.. TATA-binding protein associated factors (TAFs) regulate transcription in specific cell types.
TAF3, for example, works with another transcription factor to regulate the expression of genes that are critical for the differentiation of the endoderm in the early embryo (Liu et al., 2011). TAF3 also forms a complex with the TATA-related factor, TRF3, to regulate Myogenin and other muscle-specific genes to form myotubes (Deato et al., 2008). TAF7L interacts with another transcription factor to activate genes involved in the formation of adipocytes (‘fat cells’) and adipose tissue (Zhou et al., 2013; Zhou et al., 2014). Finally, TAF9B is a key regulator of transcription in motor neurons (Herrera et al., 2014). The names of some of the genes regulated by the TAFs are shown in brackets.
Comment on
- Core promoter factor TAF9B regulates neuronal gene expression.
Herrera FJ, Yamaguchi T, Roelink H, Tjian R. Herrera FJ, et al. Elife. 2014 Jul 8;3:e02559. doi: 10.7554/eLife.02559. Elife. 2014. PMID: 25006164 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- Core promoter factor TAF9B regulates neuronal gene expression.
Herrera FJ, Yamaguchi T, Roelink H, Tjian R. Herrera FJ, et al. Elife. 2014 Jul 8;3:e02559. doi: 10.7554/eLife.02559. Elife. 2014. PMID: 25006164 Free PMC article. - An extensive requirement for transcription factor IID-specific TAF-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans embryonic transcription.
Walker AK, Shi Y, Blackwell TK. Walker AK, et al. J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 9;279(15):15339-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310731200. Epub 2004 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14726532 - Developmental regulation of transcription initiation: more than just changing the actors.
Müller F, Zaucker A, Tora L. Müller F, et al. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010 Oct;20(5):533-40. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2010.06.004. Epub 2010 Jul 2. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010. PMID: 20598874 Review. - The TAFs of TFIID Bind and Rearrange the Topology of the TATA-Less RPS5 Promoter.
Le SN, Brown CR, Harvey S, Boeger H, Elmlund H, Elmlund D. Le SN, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 4;20(13):3290. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133290. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31277458 Free PMC article. - Roles for BTAF1 and Mot1p in dynamics of TATA-binding protein and regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription.
Pereira LA, Klejman MP, Timmers HT. Pereira LA, et al. Gene. 2003 Oct 2;315:1-13. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(03)00714-5. Gene. 2003. PMID: 14557059 Review.
Cited by
- The Core Promoter Is a Regulatory Hub for Developmental Gene Expression.
Sloutskin A, Shir-Shapira H, Freiman RN, Juven-Gershon T. Sloutskin A, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 10;9:666508. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.666508. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34568311 Free PMC article. Review. - Eukaryotic core promoters and the functional basis of transcription initiation.
Haberle V, Stark A. Haberle V, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Oct;19(10):621-637. doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0028-8. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29946135 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bhattacharya S, Lou X, Hwang P, Rajashankar KR, Wang X, Gustafsson J-A, Fletterick RJ, Jacobson RH, Webb P. 2014. Structural and functional insight into TAF1-TAF7, a subcomplex of transcription factor II D. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 111:9103–9108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1408293111 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources