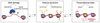Blurring the line between the DNA damage response and transcription: the importance of chromatin dynamics - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Blurring the line between the DNA damage response and transcription: the importance of chromatin dynamics
Salomé Adam et al. Exp Cell Res. 2014.
Abstract
DNA damage interferes with the progression of transcription machineries. A tight coordination of transcription with signaling and repair of DNA damage is thus critical for safeguarding genome function. This coordination involves modulations of chromatin organization. Here, we focus on the central role of chromatin dynamics, in conjunction with DNA Damage Response (DDR) factors, in controlling transcription inhibition and restart at sites of DNA damage in mammalian cells. Recent work has identified chromatin modifiers and histone chaperones as key regulators of transcriptional activity in damaged chromatin regions. Conversely, the transcriptional state of chromatin before DNA damage influences both DNA damage signaling and repair. We discuss the importance of chromatin plasticity in coordinating the interplay between the DDR and transcription, with major implications for cell fate maintenance.
Keywords: Chromatin modifications; DNA damage; Genome integrity; Histone dynamics; Transcription coupled repair; Transcription regulation.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
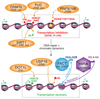
Figure 1. Importance of chromatin dynamics in the transcriptional regulation of damaged genes
Chromatin modifiers (orange) and histone chaperones (blue, purple) involved in regulating transcription inhibition (top) and recovery (bottom) in damaged chromatin regions in response to DSBs, UV lesions, oxidative damage (DNA damage is represented by a star). DNA-damage-responsive chromatin modifications associated with active transcription (green) and silencing (red) are represented. ac : acetylation ; me : methylation ; ub : ubiquitylation. Given that RNF8/168 ubiquitin ligases are not known to target K118/119 residues on H2A, an intermediate factor is likely involved as indicated by a question mark.
Figure 2. Histone dynamics at the core of the interplay between the DDR and transcription
DNA damage-induced histone dynamics, including histone exchange and post-translational modifications, govern local changes in chromatin transcriptional activity. Conversely, chromatin transcriptional state, via histone modifications, modulates DNA damage signaling and repair.
Similar articles
- Reshaping chromatin after DNA damage: the choreography of histone proteins.
Polo SE. Polo SE. J Mol Biol. 2015 Feb 13;427(3):626-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.05.025. Epub 2014 Jun 2. J Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 24887097 Free PMC article. Review. - Histone modifications: crucial elements for damage response and chromatin restoration.
Zhu Q, Wani AA. Zhu Q, et al. J Cell Physiol. 2010 May;223(2):283-8. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22060. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20112283 Free PMC article. Review. - Gearing up chromatin: A role for chromatin remodeling during the transcriptional restart upon DNA damage.
Mandemaker IK, Vermeulen W, Marteijn JA. Mandemaker IK, et al. Nucleus. 2014 May-Jun;5(3):203-10. doi: 10.4161/nucl.29085. Epub 2014 May 8. Nucleus. 2014. PMID: 24809693 Free PMC article. Review. - DNA damage leaves its mark on chromatin.
Polo SE, Almouzni G. Polo SE, et al. Cell Cycle. 2007 Oct 1;6(19):2355-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.19.4756. Epub 2007 Jul 18. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17703111 - Reprogramming transcription after DNA damage: recognition, response, repair, and restart.
Lu H, Yang M, Zhou Q. Lu H, et al. Trends Cell Biol. 2023 Aug;33(8):682-694. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2022.11.010. Epub 2022 Dec 10. Trends Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36513571 Review.
Cited by
- The emerging role of lysine demethylases in DNA damage response: dissecting the recruitment mode of KDM4D/JMJD2D to DNA damage sites.
Khoury-Haddad H, Nadar-Ponniah PT, Awwad S, Ayoub N. Khoury-Haddad H, et al. Cell Cycle. 2015;14(7):950-8. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1014147. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25714495 Free PMC article. - ATM-mediated ELL phosphorylation enhances its self-association through increased EAF1 interaction and inhibits global transcription during genotoxic stress.
Pal S, Yadav D, Biswas D. Pal S, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Oct 28;50(19):10995-11012. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac943. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36305813 Free PMC article. - HDAC2 and 7 down-regulation induces senescence in dermal fibroblasts.
Warnon C, Bouhjar K, Ninane N, Verhoyen M, Fattaccioli A, Fransolet M, Lambert de Rouvroit C, Poumay Y, Piel G, Mottet D, Debacq-Chainiaux F. Warnon C, et al. Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jul 12;13(14):17978-18005. doi: 10.18632/aging.203304. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34253688 Free PMC article. - Epigenome Maintenance in Response to DNA Damage.
Dabin J, Fortuny A, Polo SE. Dabin J, et al. Mol Cell. 2016 Jun 2;62(5):712-27. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.04.006. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27259203 Free PMC article. Review. - AFF1 acetylation by p300 temporally inhibits transcription during genotoxic stress response.
Kumari N, Hassan MA, Lu X, Roeder RG, Biswas D. Kumari N, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Oct 29;116(44):22140-22151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1907097116. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31611376 Free PMC article.
References
- Soria G, Polo SE, Almouzni G. Prime, repair, restore: the active role of chromatin in the DNA damage response. Mol Cell. 2012;46:722–734. - PubMed
- Svejstrup JQ. The interface between transcription and mechanisms maintaining genome integrity. Trends Biochem Sci. 2010;35:333–338. - PubMed
- Mayne LV, Lehmann AR. Failure of RNA synthesis to recover after UV irradiation: an early defect in cells from individuals with Cockayne's syndrome and xeroderma pigmentosum. Cancer Res. 1982;42:1473–1478. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources