miR-27a regulates cisplatin resistance and metastasis by targeting RKIP in human lung adenocarcinoma cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
miR-27a regulates cisplatin resistance and metastasis by targeting RKIP in human lung adenocarcinoma cells
Jipeng Li et al. Mol Cancer. 2014.
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been identified as important posttranscriptional regulators involved in various biological and pathological processes of cells, but their association with tumor chemoresistance has not been fully understood.
Methods: We detected miR-27a expression in two lung adenocarcinoma cell lines, A549 and A549/CDDP, and then investigated the effects of miR-27a on the metastasis and the chemosensitivity of cancer cells, using both gain- and loss-of-function studies. The correlation between miR-27a level and chemoresistance was further investigated in clinical lung adenocarcinoma specimens.
Results: miR-27a was significantly up-regulated in cisplatin-resistant lung adenocarcinoma A549/CDDP cells compared with parental A549 cells. miR-27a regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cisplatin resistance in vitro and modulates response of lung adenocarcinoma cells to cisplatin in vivo. Further studies identified Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein (RKIP) as a direct and functional target of miR-27a. Small interfering RNA-mediated RKIP knockdown revealed similar effects as that of ectopic miR-27a expression, while overexpression of RKIP attenuated the function of miR-27a in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Increased miR-27a expression was also detected in tumor tissues sampled from lung adenocarcinoma patients treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy and was proved to be correlated with low expression of RKIP, decreased sensitivity to cisplatin, and poor prognosis.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that up-regulation of miR-27a could suppress RKIP expression and in turn contribute to chemoresistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells to cisplatin.
Figures
Figure 1
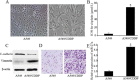
Differences between A549/CDDP cells and parental A549 cells are shown. (A) A549/CDDP cells exhibiting fibroblastic morphology and the A549 cells showing epithelial-like appearance (original magnification, ×100). (B) MTT assay shows that A549/CDDP cells are much more resistant to cisplatin than A549 cells. (C) Western blotting illustrates reduced expression of E-cadherin and increased expression of vimentin in A549/CDDP cells. β-actin was used as an internal control. (D) Invasion assay reveals significant enhancement of invasion ability of A549/CDDP cells in vitro. (E) qRT-PCR indicates a significant up-regulation of miR-27a in A549/CDDP cells compared with A549 cells. miRNA abundance was normalized to U6 RNA. Data are means of three separated experiments ± SD; *P < 0.01.
Figure 2
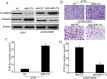
miR-27a promotes EMT and cisplatin resistance in vitro . A549 cells were transfected with NC or miR-27a mimics, A549/CDDP cells were transfected with anti-NC or miR-27a inhibitors respectively. Western blotting was used to detect E-cadherin and vimentin expression, β-actin was used as an internal control (A). transwell invasion assay (B) and MTT assay (C and D) were used to measure invasion ability and cisplatin sensitivity. Data are means of three separated experiments ± SD; *P < 0.01.
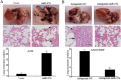
Figure 3
miR-27a regulates response of lung adenocarcinoma cells to cisplatin in vivo. (A) A549 cells were performed after transduction by miR-27a-expressing or vector lentivirus. Representative images of nude mouse lungs (scale bars: 5 mm) and H&E stain of lungs (scale bars: 100 μm) are shown. (B) A549/CDDP cells were performed after transduction by miR-27a-inhibiting or antagomir-NC. Representative images of nude mouse lungs (scale bars: 5 mm) and H&E stain of lungs (scale bars: 100 μm) are shown. *P < 0.01.
Figure 4
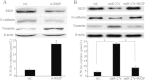
RKIP is a direct target of miR-27a. (A) The predicted miR-27a binding site within RKIP 3′UTR and its mutated version by site mutagenesis are as shown. (B) Variable RKIP expression in A549 and A549/CDDP was obtained by western blot. (C) A549 cells were transfected with NC or miR-27a mimics, A549/CDDP cells were transfected with anti-NC or miR-27a inhibitors respectively. Western blotting was used to detect RKIP expression; β-actin was used as an internal control. (D) Luciferase assay was performed in A549 cells that were co-transfected with miRNA mimics and reporter vectors carrying RKIP 3′ UTR with wild type versus mutated miR-27a response element. Data are means of three separated experiments ± SD; *P < 0.01.
Figure 5
RKIP is involved in miR-27a-induced EMT and cisplatin resistance. (A) A549 cells were transfected with RKIP siRNAs, then RKIP, E-cadherin and vimentin protein levels were detected by western blot analysis. β-actin was used as an internal control. MTT assays were used to measure cisplatin sensitivity. (B) A549 cells were transfected with NC, miR-27a mimics or plasmid lacking 3′UTR along with miR-27a, RKIP, E-cadherin and vimentin protein levels were detected by western blot analysis. β-actin was used as an internal control. MTT assays were used to measure cisplatin sensitivity. Data are means of three separated experiments ± SD; *P < 0.01.
Figure 6
The inverse correlation between miR-27a and RKIP expression in lung adenocarcinoma tissue samples and the clinical significance of miR-27a are shown. Relative expression levels of (A) miR-27a and (B) RKIP mRNA were detected in cisplatin-sensitive (n =13) and insensitive (n = 17) lung adenocarcinoma tissues via qRT-PCR. Abundance of miRNA and RKIP mRNA was normalized to U6 RNA and GAPDH, respectively. (C) Expression levels of miR-27a and RKIP mRNA are inversely correlated among all the tissue samples (n = 30) as indicated by two-tailed Pearson’s correlation analysis, r = −0.691; p < 0.01. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curve indicates that patients with high miR-27a expression have shorter overall survival than those with low miR-27a expression (log-rank test, P < 0.01).
Similar articles
- miR-15b regulates cisplatin resistance and metastasis by targeting PEBP4 in human lung adenocarcinoma cells.
Zhao Z, Zhang L, Yao Q, Tao Z. Zhao Z, et al. Cancer Gene Ther. 2015 Apr;22(3):108-14. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2014.73. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Cancer Gene Ther. 2015. PMID: 25721211 - Bmi-1-induced miR-27a and miR-155 promote tumor metastasis and chemoresistance by targeting RKIP in gastric cancer.
Li Y, Tian Z, Tan Y, Lian G, Chen S, Chen S, Li J, Li X, Huang K, Chen Y. Li Y, et al. Mol Cancer. 2020 Jun 24;19(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01229-y. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32580736 Free PMC article. - miR-206 regulates cisplatin resistance and EMT in human lung adenocarcinoma cells partly by targeting MET.
Chen QY, Jiao DM, Wang J, Hu H, Tang X, Chen J, Mou H, Lu W. Chen QY, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 26;7(17):24510-26. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8229. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27014910 Free PMC article. - The increase of miR-27a affects the role of cisplatin on proliferation and migration capacities of liver cancer cells.
Li W, Yu ZX, Ma BF. Li W, et al. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Sep;22(17):5490-5498. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201809_15809. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30229820 - Lung cancer cells and their sensitivity/resistance to cisplatin chemotherapy: Role of microRNAs and upstream mediators.
Ashrafizadeh M, Zarrabi A, Hushmandi K, Hashemi F, Moghadam ER, Owrang M, Hashemi F, Makvandi P, Goharrizi MASB, Najafi M, Khan H. Ashrafizadeh M, et al. Cell Signal. 2021 Feb;78:109871. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109871. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 33279671 Review.
Cited by
- Relationship of Signaling Pathways between RKIP Expression and the Inhibition of EMT-Inducing Transcription Factors SNAIL1/2, TWIST1/2 and ZEB1/2.
Bustamante A, Baritaki S, Zaravinos A, Bonavida B. Bustamante A, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 17;16(18):3180. doi: 10.3390/cancers16183180. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335152 Free PMC article. Review. - Emerging role of non-coding RNAs in resistance to platinum-based anti-cancer agents in lung cancer.
Mondal P, Meeran SM. Mondal P, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 26;14:1105484. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1105484. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36778005 Free PMC article. Review. - MicroRNA-27a-3p Reverses Adriamycin Resistance by Targeting BTG2 and Activating PI3K/Akt Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells.
Zhu B, Chen W, Fu Y, Cui X, Jin L, Chao J, Yun X, Gao P, Shan S, Li J, Yin X, Zhu C, Qin X. Zhu B, et al. Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jul 14;13:6873-6884. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S256153. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32764979 Free PMC article. - Association between pre-miR-27a functional polymorphism and risk of colorectal cancer in north Chinese Han population.
Bian Q, Chen JJ, Gu JP, Xu J. Bian Q, et al. Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Oct 19;8:3003-7. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S89754. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 26527885 Free PMC article. - MiR-424 and miR-27a increase TRAIL sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia by targeting PLAG1.
Sun YP, Lu F, Han XY, Ji M, Zhou Y, Zhang AM, Wang HC, Ma DX, Ji CY. Sun YP, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 May 3;7(18):25276-90. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8252. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27013583 Free PMC article.
References
- Jemal A, Thun MJ, Ries LA, Howe HL, Weir HK, Center MM, Ward E, Wu XC, Eheman C, Anderson R, Ajani UA, Kohler B, Edwards BK. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2005, featuring trends in lung cancer, tobacco use, and tobacco control. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:1672–1694. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djn389. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous