Exosomal miR-1290 and miR-375 as prognostic markers in castration-resistant prostate cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.07.035. Epub 2014 Aug 14.
Tiezheng Yuan 2, Meihua Liang 3, Meijun Du 2, Shu Xia 4, Rachel Dittmar 2, Dian Wang 5, William See 6, Brian A Costello 7, Fernando Quevedo 7, Winston Tan 8, Debashis Nandy 7, Graham H Bevan 9, Sherri Longenbach 7, Zhifu Sun 10, Yan Lu 11, Tao Wang 12, Stephen N Thibodeau 13, Lisa Boardman 7, Manish Kohli 14, Liang Wang 15
Affiliations
- PMID: 25129854
- PMCID: PMC4252606
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.07.035
Exosomal miR-1290 and miR-375 as prognostic markers in castration-resistant prostate cancer
Xiaoyi Huang et al. Eur Urol. 2015 Jan.
Abstract
Background: Extracellular microRNAs (miRNAs) embedded in circulating exosomes may serves as prognostic biomarkers in cancer.
Objective: To identify and evaluate plasma exosomal miRNAs for prognosis in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).
Design, setting, and participants: RNA sequencing was performed to identify candidate exosomal miRNAs associated with overall survival in a screening cohort of 23 CRPC patients. Candidate miRNAs were further evaluated for prognosis using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in a follow-up cohort of 100 CRPC patients.
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: Cox regression and Kaplan-Meier survival analyses were used to evaluate survival association using candidate miRNAs along with clinical prognostic factors.
Results and limitations: RNA sequencing in screening cohort generated approximately 6.80 million mappable reads per patient. Of those with normalized read counts ≥ 5, 43% were mapped to miRNAs for a total of 375 known and 57 novel miRNAs. Cox regression analysis identified an association of miR-1290, -1246, and -375 with overall survival (false discover rate < 0.05). Of those, higher levels of miR-1290 and -375 were significantly associated with poor overall survival (p < 0.004) in the follow-up cohort. Incorporation of miR-1290/-375 into putative clinical prognostic factors-based models in CRPC stage significantly improved predictive performance with a time-dependent area under the curve increase from 0.66 to 0.73 (p = 6.57 × 10(-6)).
Conclusions: Plasma exosomal miR-1290 and miR-375 are promising prognostic biomarkers for CRPC patients. Prospective validation is needed for further evaluation of these candidate miRNAs.
Patient summary: In this study, we evaluated whether small RNAs circulating in blood could be used to predict clinical outcomes in late-stage prostate cancer patients. We identified two blood-based small RNAs whose levels showed significant association with survival. Our results warrant further investigation because the noninvasive blood-based test has great potential in the management of late-stage prostate cancer.
Keywords: Biomarker; Exosome; Extracellular RNA; Prognosis; Prostate cancer; RNA sequencing; Survival; microRNA.
Copyright © 2014 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Fig. 1
RNA species and their distributions in plasma exosomes. Raw reads are the sequences detected by RNA sequencing. Query reads are those after trimming. Mappable reads are those mapped to known human RNA or genome. lncRNA = long noncoding RNA; miRNA = micro RNA; piRNA = piwi-interacting RNA; rRNA = ribosomal RNA; snRNA = small nuclear RNA; snoRNA = small nucleolar RNA; tRNA = transfer RNA.
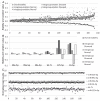
Fig. 2
Evaluations of microRNA (miRNA) candidates for endogenous normalization. (a) NormFinder-determined intergroup and intragroup stabilities of 173 miRNA candidates; (b) intergroup and intragroup variations of six selected candidates; (c) normalized read counts of six selected candidates in 192 individuals.
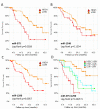
Fig. 3
MicroRNAs (miRNAs)-based survival analysis in follow-up cohort (time in months). (a, c) Kaplan-Meier curves show that relative expression levels of miR-375 and miR-1290 are associated with overall survival; (b) miR-1246 shows a trend association but not statistically significance; (d) combination of miR-1290 and miR-375 expressions demonstrated a strong synergistic effect.
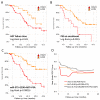
Fig. 4
Multivariate-based survival analysis in follow-up cohort. Kaplan-Meier curves show significant survival association in androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT) failure time defined as from (a) initiation of ADT for hormone-sensitive stage to development of castration-resistant prostate cancer; (b) prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level; (c) multivariate model. (d) Time-dependent area under the curve (AUC) analysis shows significant improvement of multivariate model over clinical factors-only model.
Comment in
- Exosomal microRNAs as potential biomarkers in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Haflidadóttir BS, Ceder Y. Haflidadóttir BS, et al. Eur Urol. 2015 Jan;67(1):42-43. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.08.067. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25199715 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Circulating exosomal microRNAs as prognostic biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer.
Liu Q, Yu Z, Yuan S, Xie W, Li C, Hu Z, Xiang Y, Wu N, Wu L, Bai L, Li Y. Liu Q, et al. Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 21;8(8):13048-13058. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14369. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28055956 Free PMC article. - Investigating miR-6880-5p in extracellular vesicle from plasma as a prognostic biomarker in endocrine therapy-treated castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Lee J, Hong J, Kim JW, Lim S, Choi SC, Gim JA, Kang SG, Noh TI, Park KH. Lee J, et al. BMC Cancer. 2024 Jul 29;24(1):909. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12460-x. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39075471 Free PMC article. - Exosomal miR-1246 and miR-155 as predictive and prognostic biomarkers for trastuzumab-based therapy resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer.
Zhang Z, Zhang L, Yu G, Sun Z, Wang T, Tian X, Duan X, Zhang C. Zhang Z, et al. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;86(6):761-772. doi: 10.1007/s00280-020-04168-z. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33068176 - The role of microRNA in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Thieu W, Tilki D, de Vere White R, Evans CP. Thieu W, et al. Urol Oncol. 2014 Jul;32(5):517-523. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2013.11.004. Urol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24935732 Free PMC article. Review. - The Crosstalk of Long Non-Coding RNA and MicroRNA in Castration-Resistant and Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer: Their Interaction and Clinical Importance.
Hu CY, Wu KY, Lin TY, Chen CC. Hu CY, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 30;23(1):392. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010392. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008817 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Role of extracellular vesicles in tumour microenvironment.
Tao SC, Guo SC. Tao SC, et al. Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Oct 20;18(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00643-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 33081785 Free PMC article. Review. - Exosomes in cancer: small particle, big player.
Zhang X, Yuan X, Shi H, Wu L, Qian H, Xu W. Zhang X, et al. J Hematol Oncol. 2015 Jul 10;8:83. doi: 10.1186/s13045-015-0181-x. J Hematol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26156517 Free PMC article. Review. - The Potential of MicroRNAs as Non-Invasive Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: A Systematic Literature Review Based on a Machine Learning Approach.
Bevacqua E, Ammirato S, Cione E, Curcio R, Dolce V, Tucci P. Bevacqua E, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 3;14(21):5418. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215418. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358836 Free PMC article. - Extracellular Vesicle (EVs) Associated Non-Coding RNAs in Lung Cancer and Therapeutics.
Paramanantham A, Asfiya R, Das S, McCully G, Srivastava A. Paramanantham A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 7;23(21):13637. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113637. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362424 Free PMC article. Review. - Predictive values of miR-129 and miR-139 for efficacy on patients with prostate cancer after chemotherapy and prognostic correlation.
Hu Z, Guo J, Zhao M, Jiang T, Yang X. Hu Z, et al. Oncol Lett. 2019 Dec;18(6):6187-6195. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10950. Epub 2019 Oct 2. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31788094 Free PMC article.
References
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
- Palmberg C, Koivisto P, Visakorpi T, Tammela TL. PSA decline is an independent prognostic marker in hormonally treated prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 1999;36:191–6. - PubMed
- Crawford ED, Eisenberger MA, McLeod DG, et al. A controlled trial of leuprolide with and without flutamide in prostatic carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:419–24. - PubMed
- Danila DC, Heller G, Gignac GA, et al. Circulating tumor cell number and prognosis in progressive castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:7053–8. - PubMed
- de Bono JS, Scher HI, Montgomery RB, et al. Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:6302–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases